If your website is not showing up on Google, a variety of factors could be responsible.
In this post, I will explain why your website is not appearing on Google and how to fix it.
10 Fixes For When Your Page Is Missing From Google Search
- Your Website Is Brand New
- Google Crawler Is Blocked
- You Added The NOINDEX Tag On Your Pages
- Your Website Is Under a Google Penalty
- Your Website Lacks Original Content
- Your Website Does Not Have Any Backlinks
- Your Targeting Highly Competitive Keywords
- Your Website Is Too Slow
- Your Website Has Technical Issues
- Your Website Is Hacked And Removed From Google
1. Your Website Is Brand New
The first reason your website may not appear in Google is simply that your site is new. Google only shows sites that are stored in its index.
When you create a website, Google does not know it exists. It takes time for search engines to discover new sites and add to their index.
To check if your website is in Google, perform a site search on Google.com. In the search box, type in site:yoursitename and press enter.
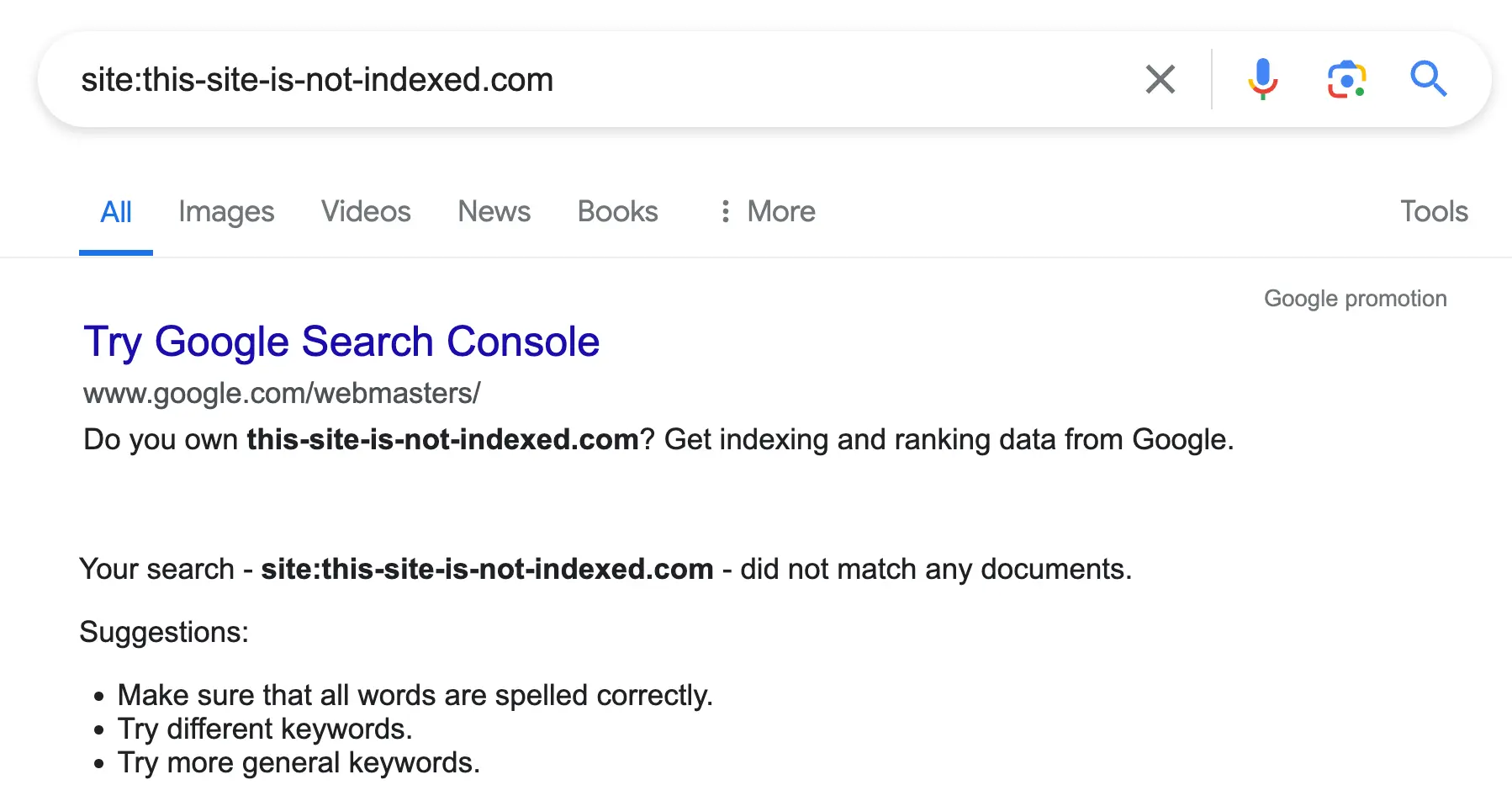
In the results, you will see all the pages from your website that are in Google’s index.
If no results appear, none of your pages are currently on Google.
Solution:
There are a couple of solutions to getting your new website to appear on Google.
You could wait for Google to find it, but this isn’t the best idea, especially if no other websites link to you.
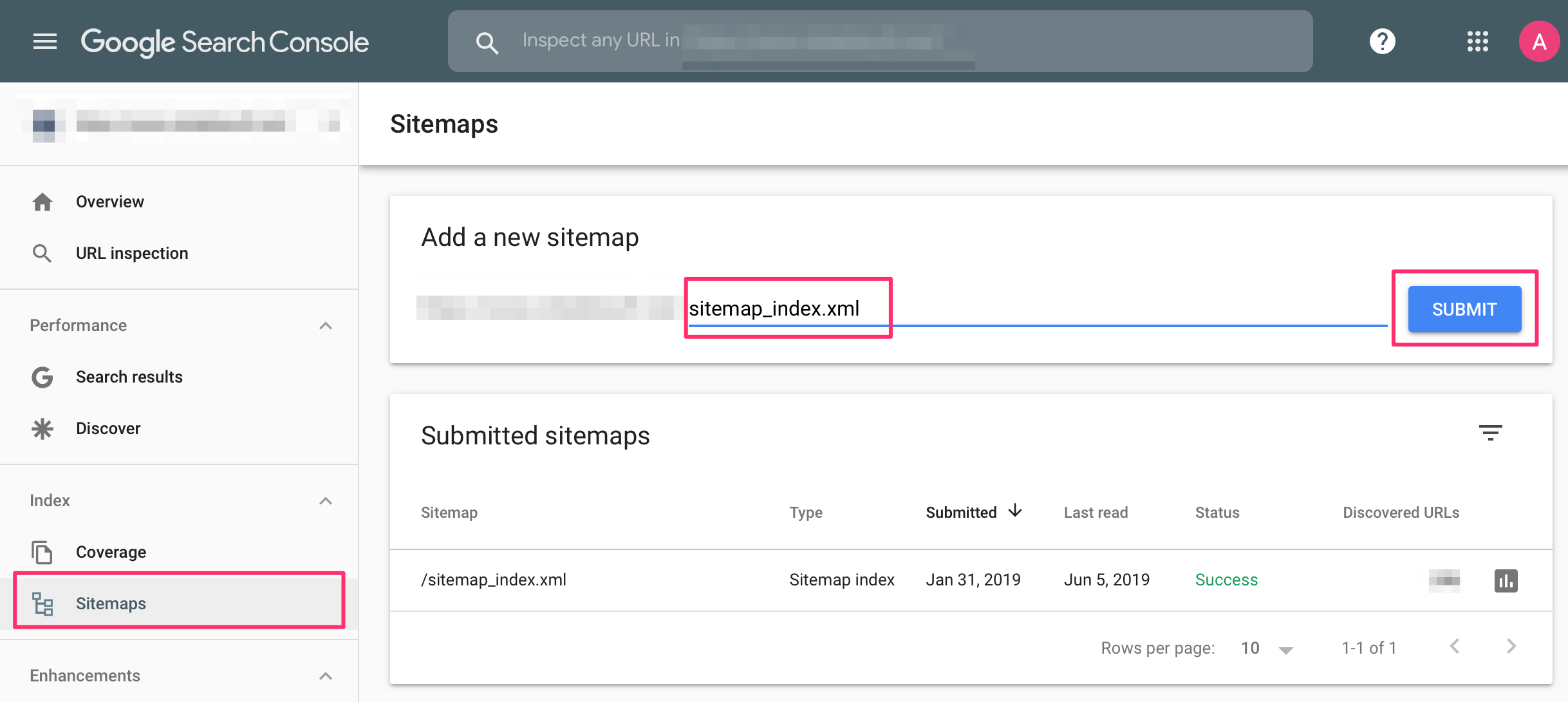
Your other option is to create a sitemap and submit it through Google Search Console. This will tell Google that your site exists and that you want it included in the index.
2. Google Crawler Is Blocked
Google finds websites through a process called crawling. In this process, they use special programs known as crawlers to find new websites to add to their index.
If you are blocking Google from crawling your website, then their crawlers will skip over your pages, and they will not be available to appear on Google.
The most common way Google crawlers are blocked is through the robots.txt file. This file gives Google instructions on how to treat a website. Most websites have one, which is usually stored in the root directory of a site.
Solution:
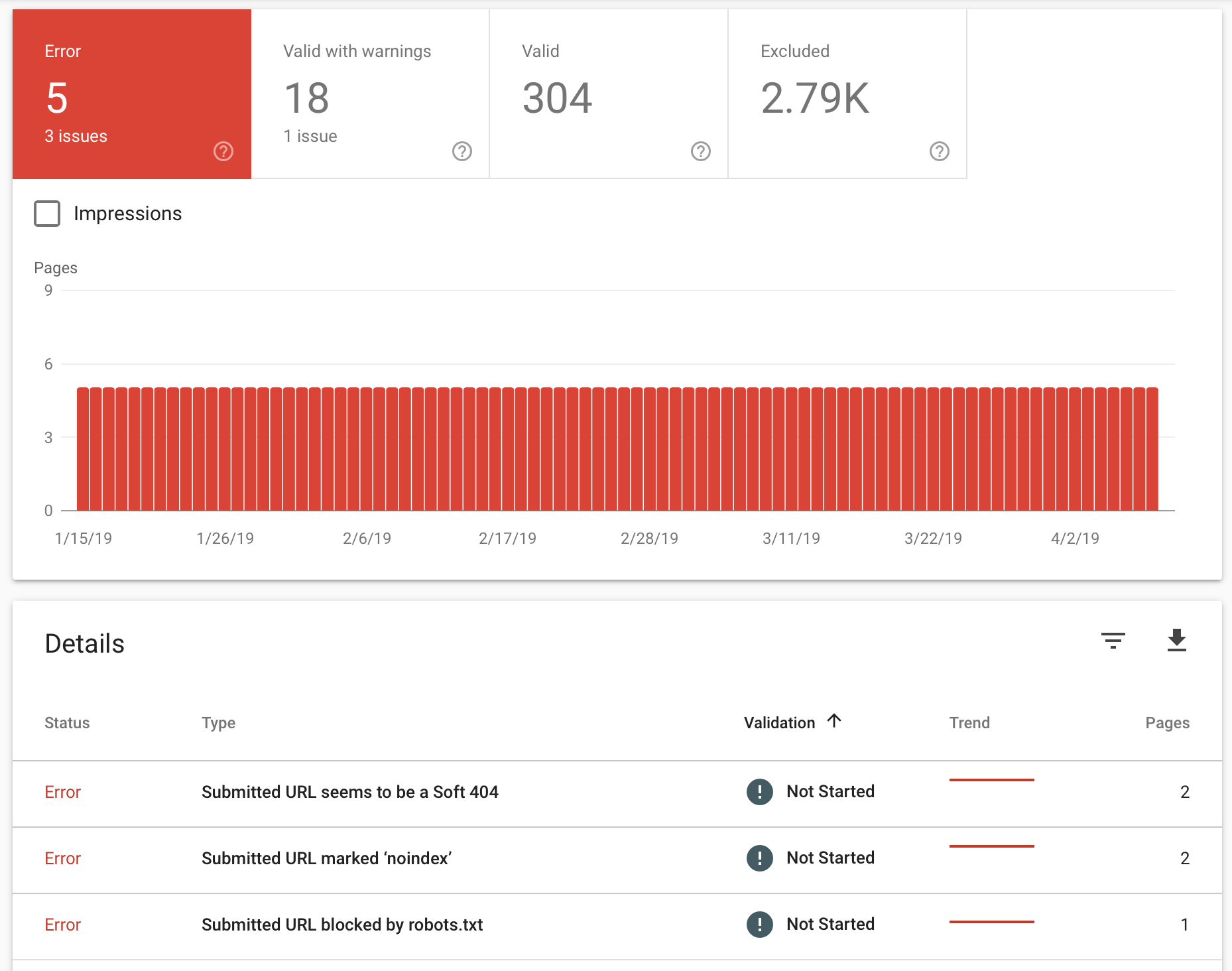
You can check if your robots.txt file is blocking Google from crawling your site within Google Search Console.
Log in to Google Search Console and go to the Index Coverage Report. Look for a message that says, "Submitted URL blocked by robots.txt.”
Another way is to check the robots.txt file directly.
The robots.txt file should be located in the root folder.
When you open the file, look for the following user agents:
User-agent: *
User-agent: Googlebot
If you find code with "Disallow: /" beneath either of these, you block Google from crawling your site.
To permit Google to crawl your site, simply delete the "Disallow: /" snippet and save the robots.txt file.
The next time Google attempts to crawl your website, there should not be any issues.
3. You Added The NOINDEX Tag On Your Pages
Letting Google crawl your pages is just part of having your site appear in the Google search results. You also need to ensure that you allow Google to index your pages.
Now, the process for indexing your pages is similar to crawling. If you specify to Google that you don’t want certain pages included in the index, then it won’t include them.
This is typically done by using a noindex meta tag. The tag is a small piece of HTML code added to a page. It simply tells Google not to include that page in its index.

Usually, these tags won’t be added to your site unless you do so. However, there are situations when you could unexpectedly apply the “noindex” tag to your pages.
For example, if your site uses WordPress, there is a “Search Engine Visibility” setting. If you check the box that says “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” then the “noindex” tag will be added to all your pages.
Solution:
You can check in Google Search Console to see if your pages have the “noindex” tag applied. Go to the Index Coverage report and look for errors that say “Submitted URL marked ‘noindex’.
If you find the tag on any unwanted pages, there are several ways to get rid of it. You can dive into that page's HTML code and remove it yourself or, using software like the Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress. This will allow you to specify which pages have the tag and will ensure it isn’t added to pages you don’t want.
4. Your Website Is Under a Google Penalty
Google has guidelines that website owners must follow for their websites to be eligible to rank in search results. If you violate these guidelines (or Google suspects you are), your site will receive a penalty.
This will either cause your pages to rank lower or be excluded entirely from the index. Google can impose two types of penalties: algorithmic and manual.
Algorithmic penalties occur when Google’s algorithm deems quality issues with your site and penalizes you accordingly.
Manual penalties occur when a human reviews your website and determines that it does not comply with Google's webmaster quality guidelines.
Some of the reasons you could receive a manual penalty include the following:
- User-generated spam
- Structured data problems
- Bad links pointing to your site
- Unnatural links from your site
- Hidden text and keyword stuffing
- Deceptive redirects
Solution:
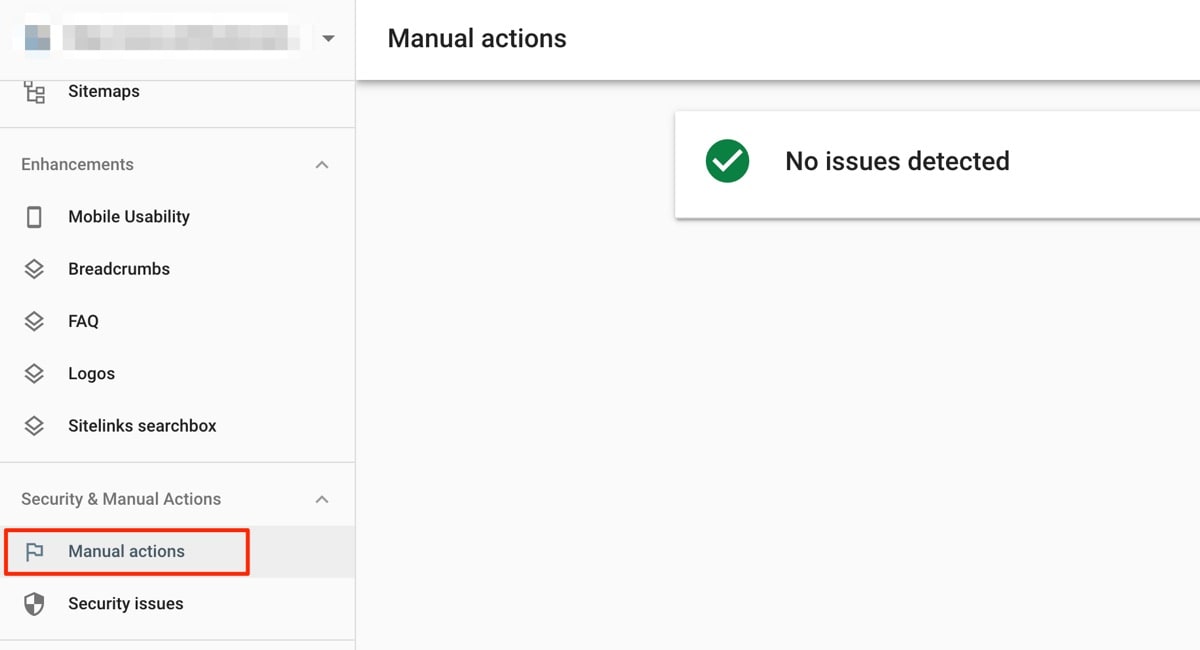
The quickest way to check for Google penalties is to search within Google Search Console. Go to the "Security & Manual Actions” section and click "Manual Actions".
This will show if Google has applied manual penalties to your site.
If you have not been penalized, you will see a message that says, "No issues detected". If any manual actions have been taken against your site, they will be listed on the page.
Google will give you the opportunity to fix the issues and submit a request to have the penalty removed. Once you have addressed the issues, select “Request Review” from the manual actions page. Google states that it looks for the following in review requests:
- An explanation of the exact quality issue on your site.
- Description of the steps you’ve taken to fix the problem.
- The outcome of your efforts.
Now, algorithmic penalties are more challenging to track, as Google will not notify you if you have received one. If your site fails to appear in Google, it is likely not an algorithmic penalty.
However, if your site has previously ranked well and experienced a sudden drop in your ranking, it may be because of an algorithmic penalty.
The best course of action is to perform a content audit. Look for duplicate content issues or serious performance problems.
5. Your Website Lacks Original Content
Another possible reason your website does not appear on Google is a lack of quality, original content.
Google aims to provide users with the most relevant results to their search queries. To do this, it will rank the content it deems the best at the top of its results.
Google values original, in-depth content. If your pages reiterate the same ideas found on other websites, they are unlikely to rank very high.
Solution:
Create fresh, original, evergreen content around your target keywords. Look to approach a topic from a different angle and provide valuable insights not present in similar pieces around the web.
6. Your Website Does Not Have Any Backlinks
Backlinks are a signal of quality and are one of the most important factors in search engine rankings.
If your website doesn’t have many backlinks, it indicates a lack of authority. With a lower page and domain authority, it is harder to show up in Google results.
Solution:
Getting high-quality backlinks can take time, especially if your site is new. The first step in earning links is to create high-quality content.
If you don’t have pages worth linking to, earning links will be even more challenging.
Once you have created several high-value pages, contact authoritative sites in your industry and ask them to link back to your site.
However you choose to conduct your outreach, I recommend focusing on reciprocity when gaining links. People will be likelier to link to you if you provide some value in return.
This could involve linking back to them or offering to write a guest post on their site for free.
7. Your Targeting Highly Competitive Keywords
Depending on your industry, the SEO keywords you are trying to rank for may be highly competitive. Naturally, this will make it harder for your site to appear for these terms.
Failing to rank for these keywords could be attributed to the industry you are in rather than any issue with your site.
You’ll need to verify that this is the case and that your lack of visibility does not result from a deeper issue.
Solution:
Check the Coverage section within Google Search Console or perform a site search in Google using your website’s name to see if your website is included in the index at all.
Once you confirm that your site is, in fact, in Google, you will know that the issue is you not ranking for particular keywords rather than a complete lack of visibility.
In this situation, you will have to work to boost your ranking so that you appear at the top for the keywords you are targeting. This will mean creating useful content, increasing your domain authority through high-quality backlinks, and ensuring your site's technical factors are in order.
If you do this, you should see your rankings improve over time. While you wait for your site to rank for more competitive keywords, you should consider targeting some other keywords with a lower difficulty to help your site build momentum.
Use your preferred keyword research tool to find less competitive long-tail keywords and create content and pages to target those. You will be able to rank these pages faster.
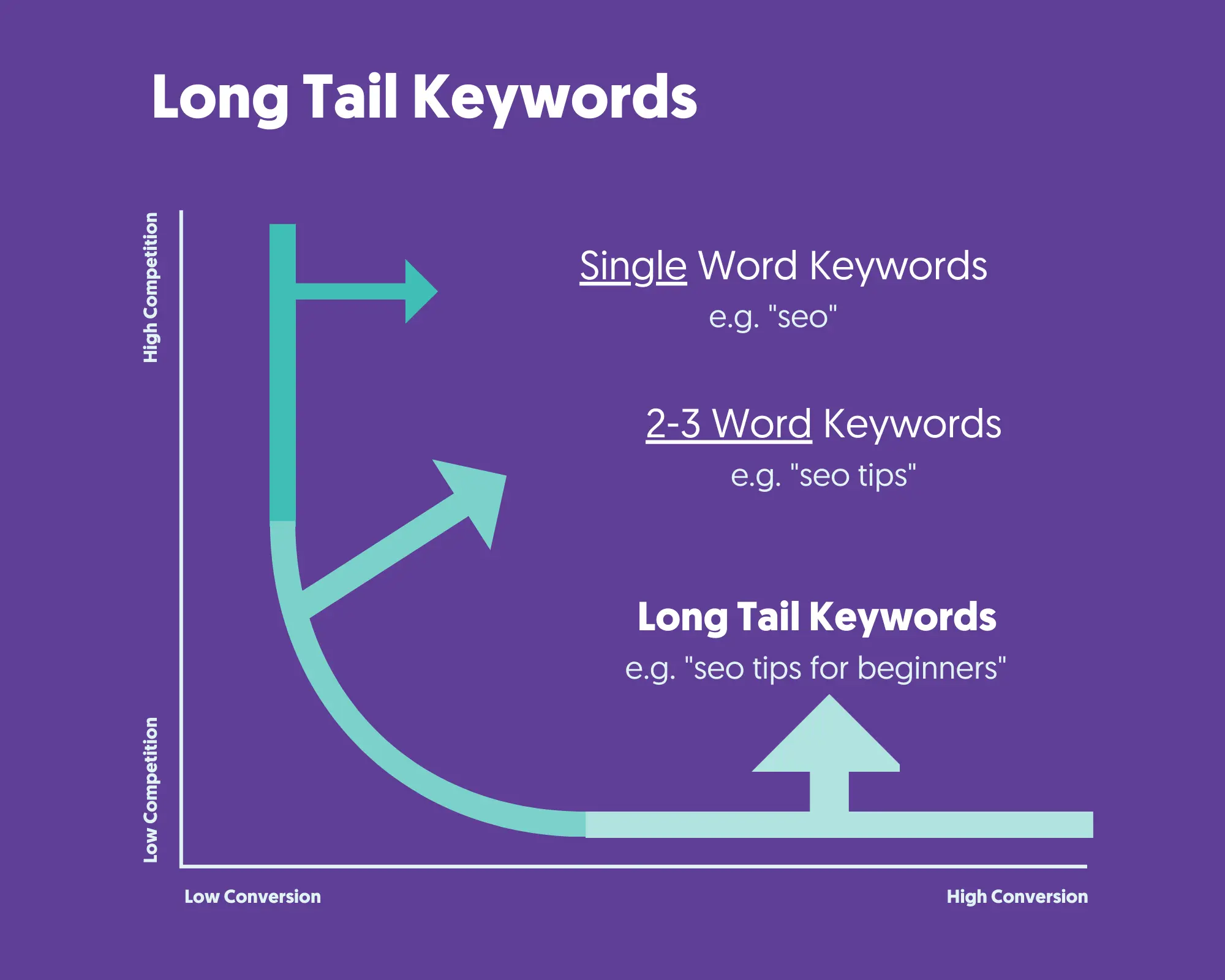
While the traffic you may receive may be lower than that afforded by your primary keyword targets, bringing visitors to your pages will help boost your site's authority, helping you rank for your primary keywords faster.
8. Your Website Is Too Slow
In Google’s effort to provide users with the best possible experience, it considers many technical factors when indexing and ranking websites. One of the technical factors they will evaluate is your website’s speed.
Slow-loading pages lead to a poor user experience and, as a result, will affect your site's visibility on Google.
Your mobile website's performance is given precedence over the desktop version, as Google follows a “mobile-first indexing” strategy when crawling, indexing, and ranking pages.
This means that your mobile site serves as the baseline when evaluating the quality of your site.
Generally, a slow-loading site won’t cause your entire site to be absent from Google, but it can affect individual pages from ranking high for competitive keywords.
The common causes of slow-loading pages are JavaScript issues, large images, and a lack of server resources.
Solution:
You can use plenty of tools to test your website’s loading speed.
If your website has enough data, you can use Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals Report to measure the performance of your web pages.
Beyond Search Console, several free website speed testing tools exist, including Google’s Pagespeed Insights and Pingdom’s Website Speed Test.
Make sure that you are caching your pages and using a CDN. This will allow you to serve saved versions of your website's static elements.
9. Your Website Has Technical Issues
If your website experiences frequent technical issues, it can be difficult to appear on Google.
Problems like server crashes, DNS problems, and HTTP errors affect the user experience and inhibit Google’s ability to crawl and index your site.
Another common technical issue is the heavy use of JavaScript on a site.
JavaScript can be difficult for search engines to crawl, which can lead to trouble with Google finding and indexing your pages.
This is a typical issue if your navigational elements are in JavaScript. For example, if your site uses a mega menu in JavaScript, Google will have trouble crawling the links to the deeper pages in the menu. This can lead to reduced visibility for many of your web pages.
Solution:
Perform a comprehensive technical SEO audit for your website. This will provide you with details of all the different technical problems your website may be experiencing.
You can minimize the number of technical problems you experience by using a high-quality web host. Doing so will help ensure that you don’t run into server issues.
Look to minimize the amount of JavaScript on your site when possible. You use the URL inspection tool on Google Search Console to see which particular JavaScript elements are causing problems.
10. Your Website Is Hacked And Removed From Google
If your website is hacked, it may affect your ability to appear in Google's search results.
The site could be blacklisted and removed from the index entirely, or Google could add a message to any results your site ranks for saying, "This site may be hacked".
With the latter, your site may still be on Google, but the chances of having visitors click through to the page are low.
Solution:
You can check to see if a hack affects your website's position in Google through your Search Console account.
Go to the "Security Issues" section to see if any URLs are listed.
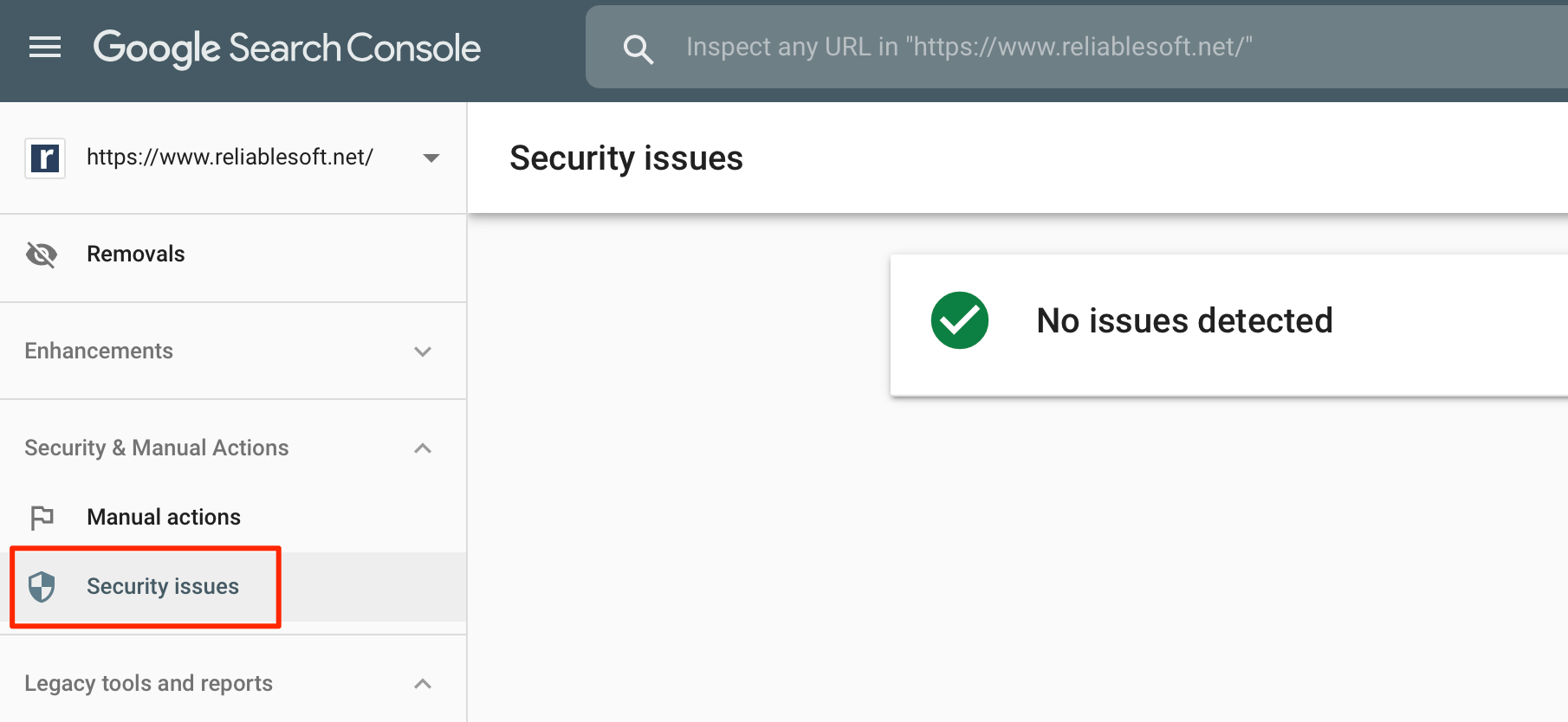
If any of your pages are having issues, Google will provide more details about the problem. You can then work on fixing the issues to get your site back in order.
Once you have cleaned up your site, you can request a review from Google in the Security Issues section. Once verified that your site is fixed, they will remove the warning from your site's listing.
Look to keep your site secure going forward. Users are only allowed one review request every 30 days, so if your site is frequently hacked or injected with malware, you will severely limit your chances of gaining any traffic from Google.
How to Get Your Website To Show Up on Google
If you’re struggling to get your site to appear on Google at all or are having trouble achieving the rankings you desire, here are some actionable steps you can take to improve your search engine visibility:
1. Set up Google Search Console - The first step to getting your site to appear on Google is to set up your Google Search Console account. The platform will serve as a hub for monitoring your performance in the search engine and provide useful tools to take action when needed.
2. Submit your sitemap - After setting up your Search Console account, you should submit your website's sitemap. This file will let Google know that your site exists and give a list of all the URLs that you want crawled and indexed.
Once you submit your sitemap, Google will add your site to a queue of sites to crawl. With the sitemap on file, it will also know where to go for future crawls and will do so regularly based on how often you post and update your content.
3. Use the URL inspection tool - The URL inspection tool inside the Search Console allows you to evaluate the status of any individual URL. When you type a URL into the field, you are taken to a page with all of Google's index data for that URL. You will see if it is currently on Google if the page is mobile-friendly, and when the last crawl was.
If the page is not on Google, or if you have made updates, you can click the "Request Indexing" button to have Google recrawl your site.
It will quickly scan the page to see if it is eligible. If it is, Google will add it to a queue to crawl and index.
4. Perform a technical SEO audit - A thorough website review is the most effective way to diagnose any technical issues that may negatively impact your website’s search engine rankings.
Some of the main areas to examine during a technical SEO audit include the following:
- HTTPS status codes
- Site load times
- Sitemap status
- Duplicate content
- Issues with metadata
- Broken links
- Crawling errors
5. Create unique content - Without high-quality and unique content, Google has little reason to rank your site well. Good content is also essential to providing value to your audience and establishing your brand's authority.
Create original pieces focusing on your target keywords. Look to pages that rank high for those phrases and look at your unique angle on the topic.
You should also check to ensure that your website has no errors with duplicate content, which can lead to a penalty from Google. This is usually part of a comprehensive SEO audit.
6. Generate high-quality links—Backlinks are critical to high rankings, especially for competitive keywords. As you begin to fill your site with quality content, look to start a link-building campaign by asking other site owners to link back to your site.
Stick with websites with high domain authority, as links from these sites will most effectively improve your rankings.
Key Learnings
There are several reasons your website may not be showing up on Google.
It could be because your site is new, and Google hasn’t found it yet.
It could be because you are obstructing Google in some way, either by blocking the crawlers or tagging your pages as “noindex”.
If none of these are responsible, you likely have an aspect of your site you need to improve. It could be a technical error like slow load times or server crashes. Or, it could be a lack of original content and high-quality backlinks.
In rare cases, you may have even been penalized by Google.
The best way to make your site show up on Google is to complete the following steps:
- Create your Google Search Console account
- Submit your Sitemap
- Create unique content
- Gain high-quality backlinks
- Perform regular technical SEO audits
By following these steps, you can proactively manage and monitor your site's performance on Google and make any necessary changes quickly.



