What Is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that helps website owners monitor, maintain, and improve their site’s presence in Google Search results. While you don’t need to sign up for GSC to appear in search results, using it gives you valuable insights into how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your site.
It also helps you identify and fix issues that could impact your search performance.
What Is Google Search Console Used For?
You can use Google's search console to optimize your website for technical SEO, understand what Google knows about your website, and view historical data about your website’s performance on Google.
Below is a breakdown of the most popular Search Console functions.
- Use Search Analytics to optimize your content
- Troubleshoot crawling and indexing issues
- Get alerts for critical website errors
- Analyze your pages using the URL Inspection tool
- Analyze your backlink and internal link profile
- Notify Google of changes made to your website
- Measure performance in Google Discover
- View your Core Web Vitals report
How To Use Google Search Console
- Setup Search Console Account
- Submit an XML Sitemap
- Find and Fix Crawling And Indexing Errors
- Check For Manual Actions
- Analyze Impact of Google Updates On Your Traffic
- Find Pages With A Low CTR (Click Through Rate)
- Use Search Analytics To Evaluate Search Performance
- Rank For More Keywords (For The Same Page)
- Analyze Your Pages Using The URL Inspection Tool
- Analyze Your Backlink and Internal Link Profile
- Communicate Important Site Changes to Google
- Measure Performance in Google Discover
- View Core Web Vitals Reports
- View Enhancements Reports
- Check Crawl Stats
1. Setup Search Console Account
The first step to start with Google Search Console is registering for a free account and adding and verifying your website.
This will give you access to all Google search console tools and reports.
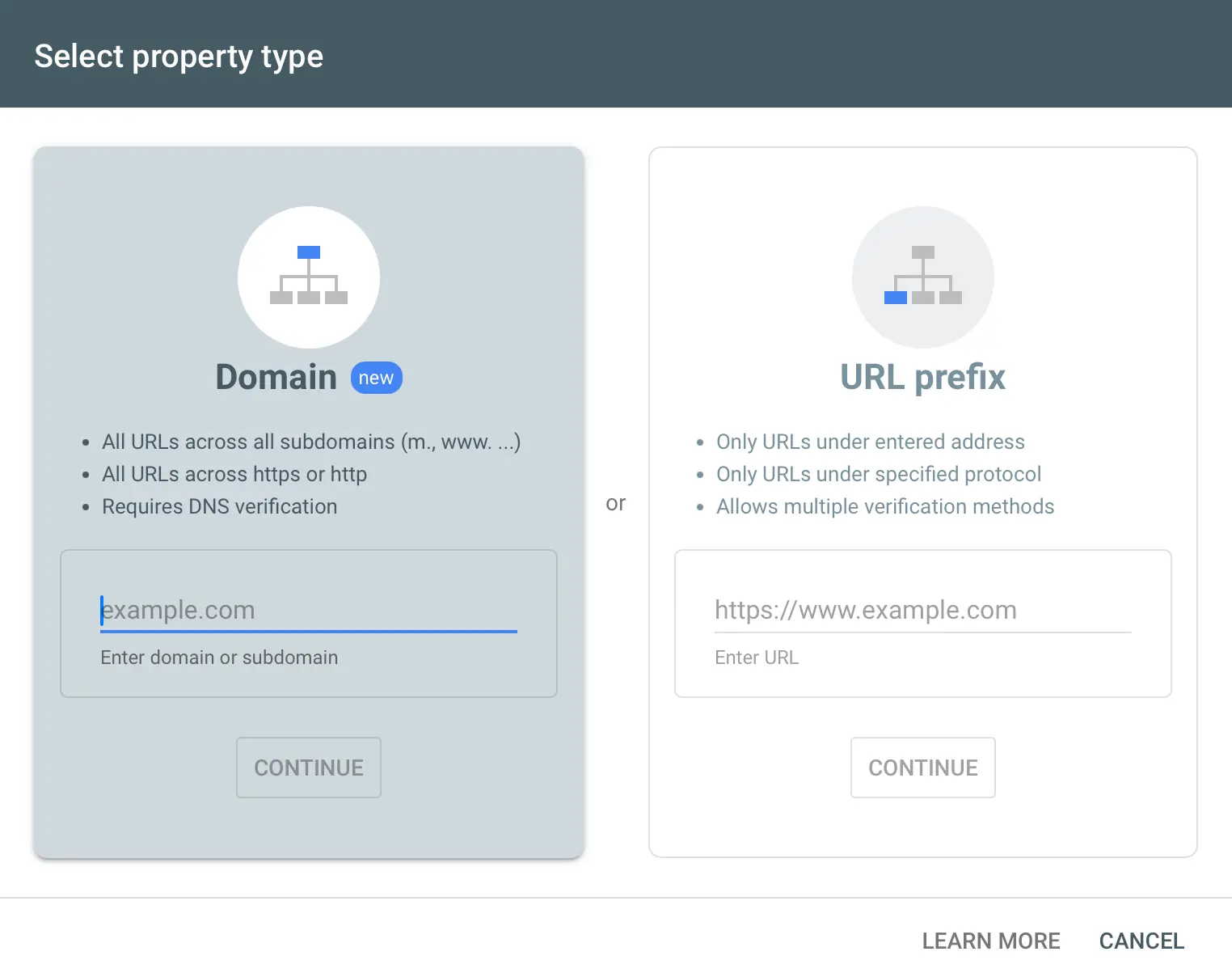
- Go to Google Search Console and login with your Google account (or create a new one).
- Click Add Property by clicking the Search Property dropdown.
- Enter your website’s URL and click continue.
- Verify ownership of your website by following the instructions here (Add website to Google Search Console)
2. Submit an XML Sitemap
Once your website is verified, you should create an XML sitemap and submit it to Google.
A sitemap is an XML file that lists all pages of a website that Google needs to know about and monitor for changes. It includes a page's URL and information on when it was created and last updated.
Even without a sitemap, Google can still discover and index your website. Using a sitemap makes their job easier and you can send them more information about your URLS.
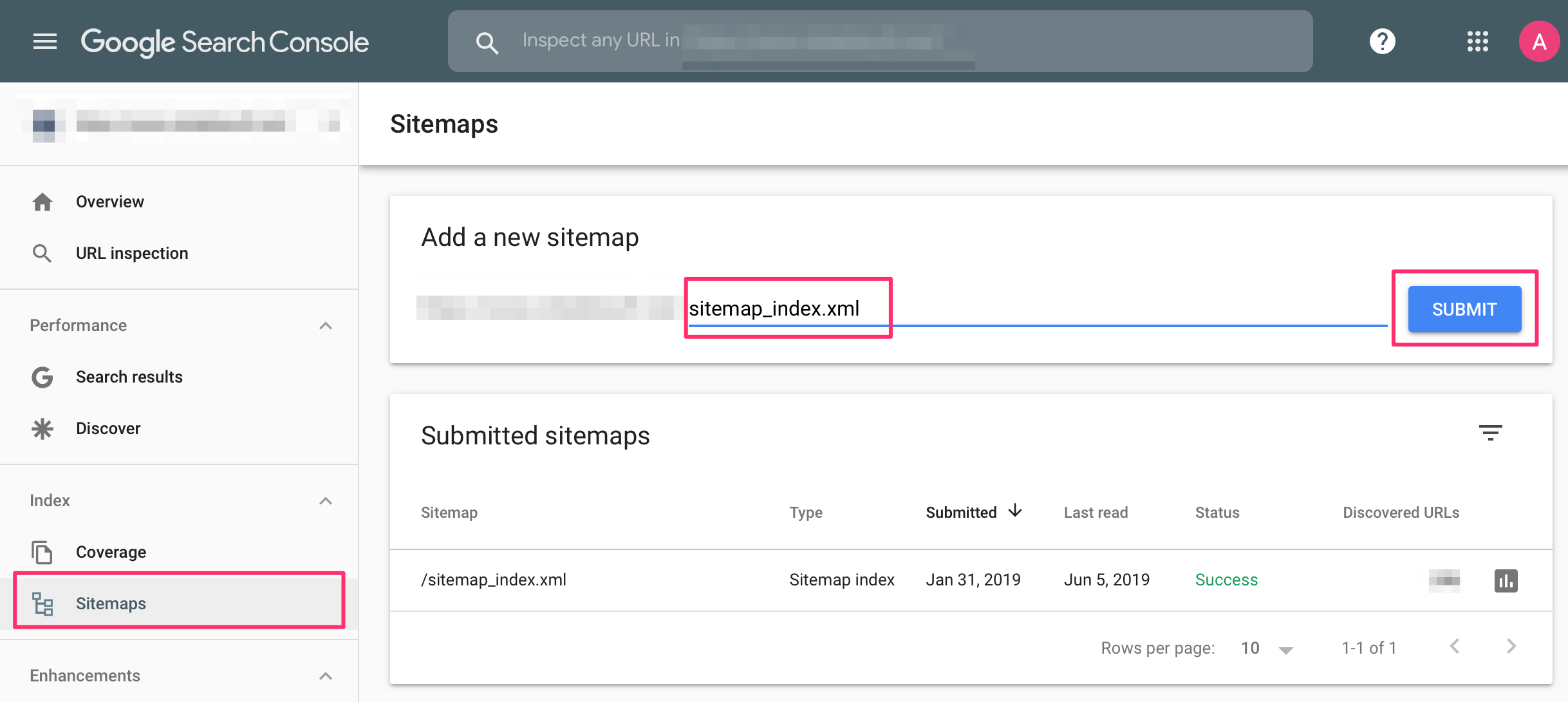
Follow the instructions in this guide: How to submit sitemap to Google
3. Find and Fix Crawling And Indexing Errors
The next step is to check for indexing errors. If a page or a group of pages has problems and is not part of Google's index, it won’t appear in searches.
As a registered user, you will be notified by Google Search Console of any errors, but since you are starting out now, it’s recommended that you go through all the reports to find and fix any errors.
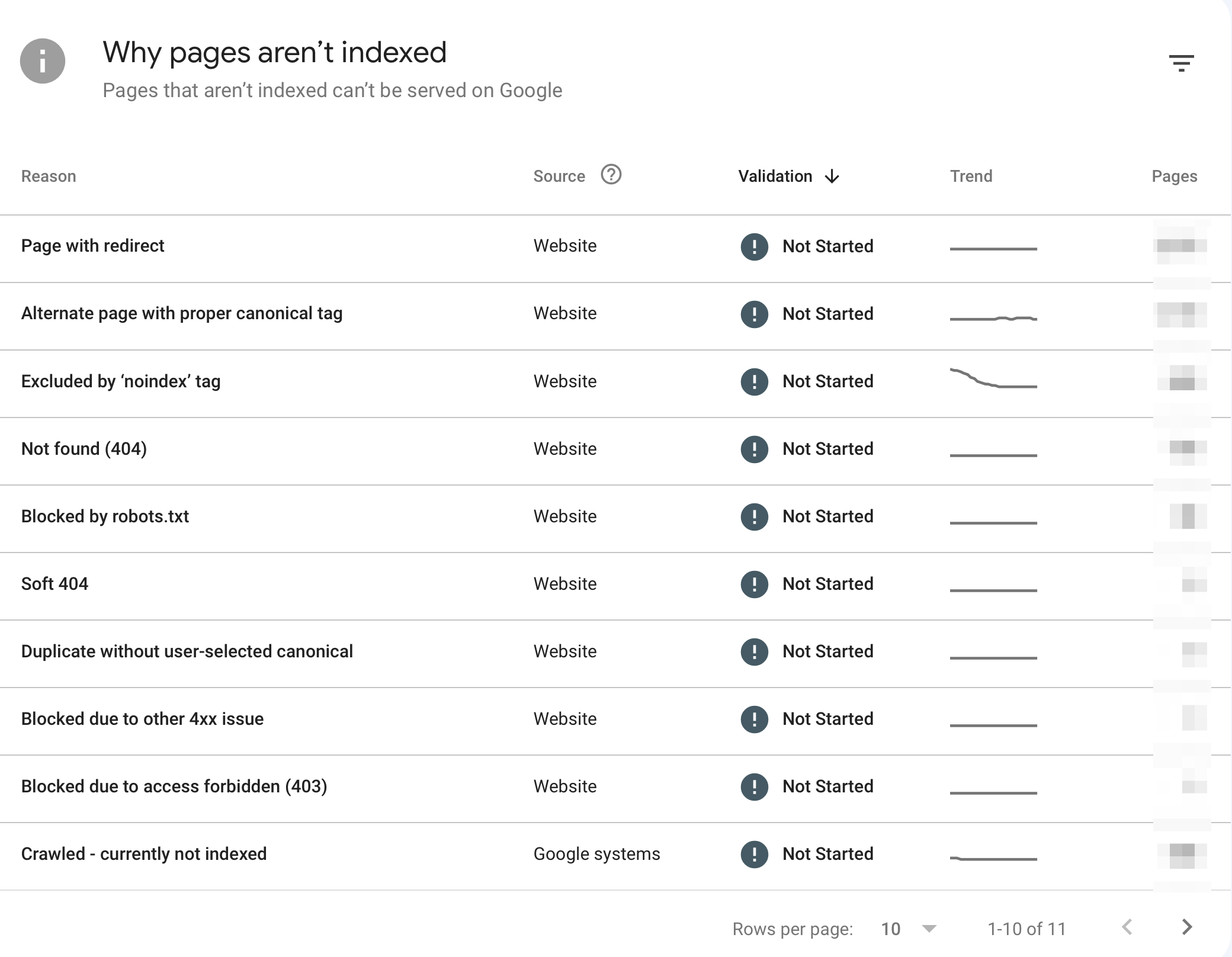
Follow the instructions in this guide: How to fix crawl errors in Google Search Console
4. Check For Manual Actions
The next step is to do a quick check to ensure that your website is not under a Google penalty and that no security issues have been reported.
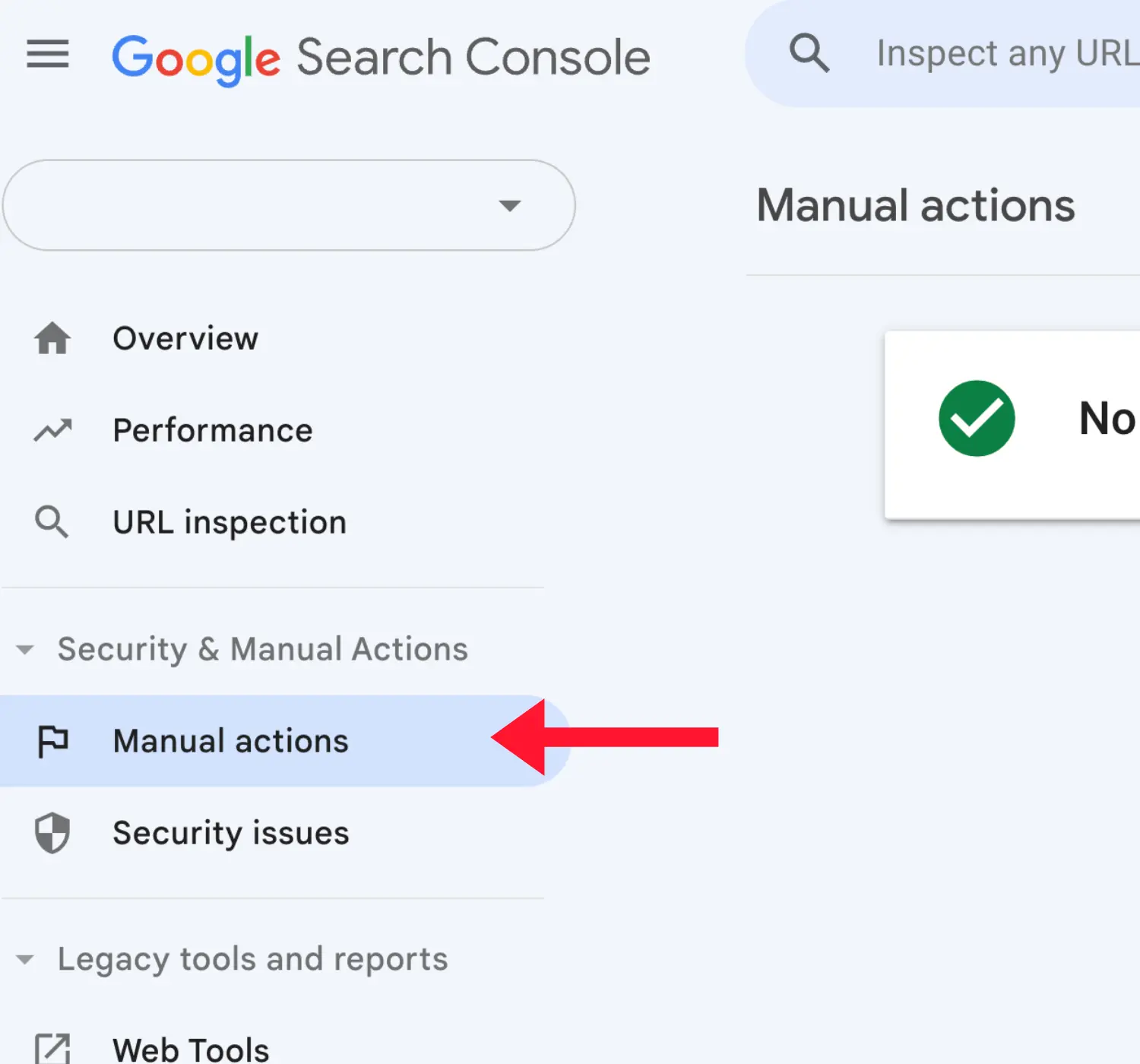
To do so, view both reports under SECURITY & MANUAL ACTIONS.
If there are issues, Google will give you more details on how to address them.
5. Analyze Impact of Google Updates On Your Traffic
Google is constantly changing its ranking algorithm, and it is normal that, at some point, your website will be affected positively or negatively by these changes.
One way to analyze the impact on your traffic is to use the “Search Results” report's compare function.
You can find out when there was a major Google update and compare your search performance seven days before and seven days after the update.
You can use the available filters to find out changes in ranking position by page or keyword.
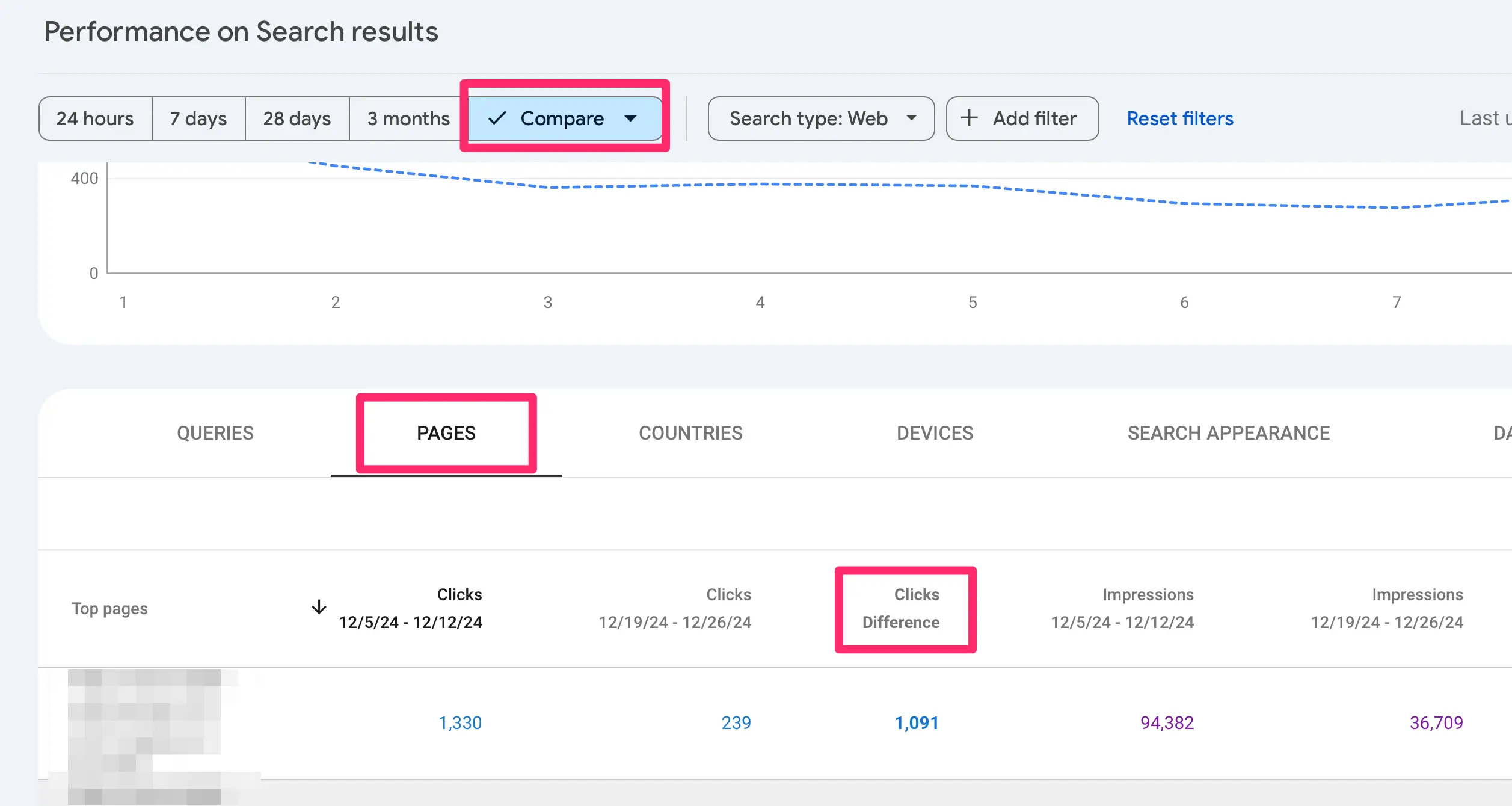
6. Find Pages With A Low CTR (Click Through Rate)
The “Search Results Report” is one report you can use to improve the ranking position of your pages and increase traffic to your site.
In particular, you can use the Average Position and Average CTR filters to identify pages of your website with low CTRs.
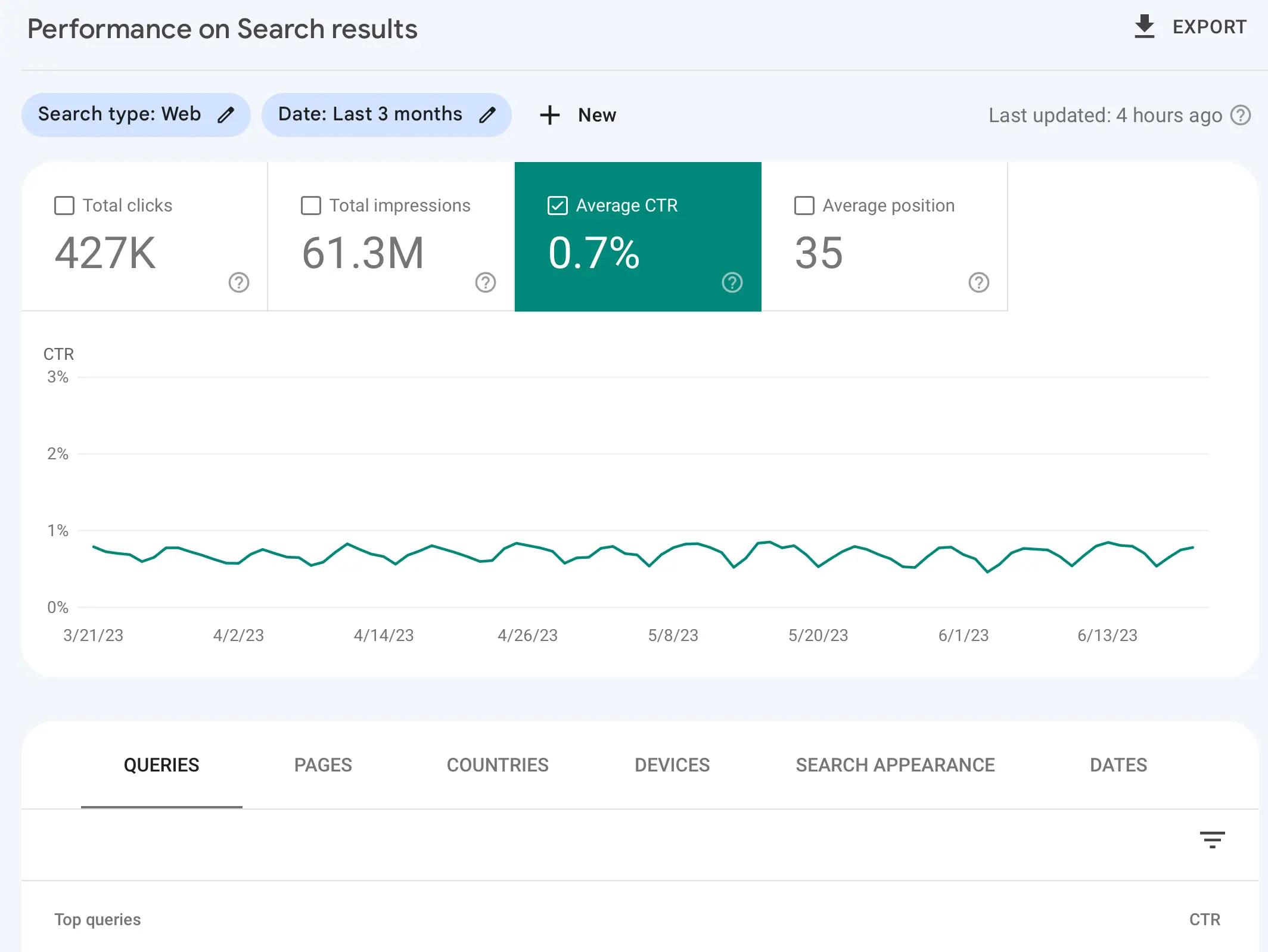
Organic CTR is the rate at which your search snippets are clicked. This number is the percentage of people who view your search listing (Total Impressions) and then actually go on to click the snippet (Total Clicks) and visit your website from Google Search.
A low Click-through Rate can be defined as anything below 3%.
For these pages, you can try tweaking their page titles and meta descriptions to make them more enticing for users to click.
This will instantly generate more traffic to your website and, over time, improve your ranking positions.
When changing the titles or descriptions, make sure to keep a log of when the change was made so that you can compare the performance before and after the change.
Don’t rush into making conclusions, make the changes and give it a few weeks before analyzing the results.
Pro Hint: It is likely that the majority of your traffic comes from mobile devices, so make sure to use the ‘Devices’ filter to separate traffic per device and, if necessary, adjust the meta description length to be optimized for mobile devices rather than desktops.
7. Use Search Analytics To Evaluate Search Performance
The Google search console has several reports that analyze how your website performs in Google search.
You can view the actual keywords driving Google organic traffic to your site and your rankings in Google searches.
The reports have 16 months of historical data and several filters that allow you to compare your performance between different periods and view data by country, device, or even type of search results (rich snippets, amp results, etc.).
- View the search terms that triggered your pages to appear in Google search results (SERPS)
- View for which keywords you received traffic from Google
- Analyze the ranking position your pages appeared on Google for particular queries
- Compare the performance of your website on Google between different periods
- View how many impressions your pages received and how many clicks from Google
- Analyze results by country or device
- Analyze results by type
8. Rank For More Keywords (For The Same Page)
Another way to use Google Search Console is to analyze which keywords a page ranks for and enrich your content to rank higher for those keywords.
The idea is that a page is likely to rank for several different keywords, not just the optimized keywords.
You can use the “Search Results” report with the PAGE filter to find ALL the keywords for which a particular page is ranking.
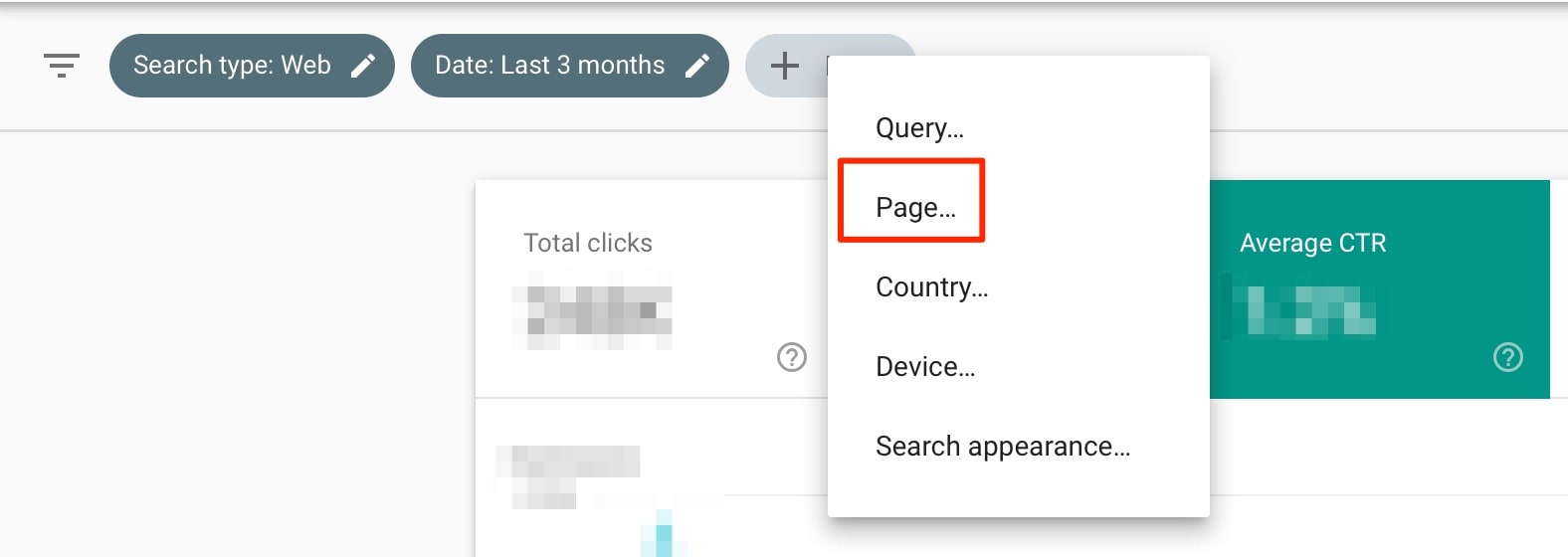
Chances are that the page will rank for keywords that are not included in your content. This is because the ranking algorithm uses AI and other factors (synonyms, LSI keywords) to rank a page for various search queries.
When you intelligently change your content to add missing keywords, over time, your rankings for those keywords will improve, and your visibility on Google will increase.
As mentioned above, keep a log to track your changes, and don’t rush into making conclusions too soon.
9. Analyze Your Pages Using The URL Inspection Tool
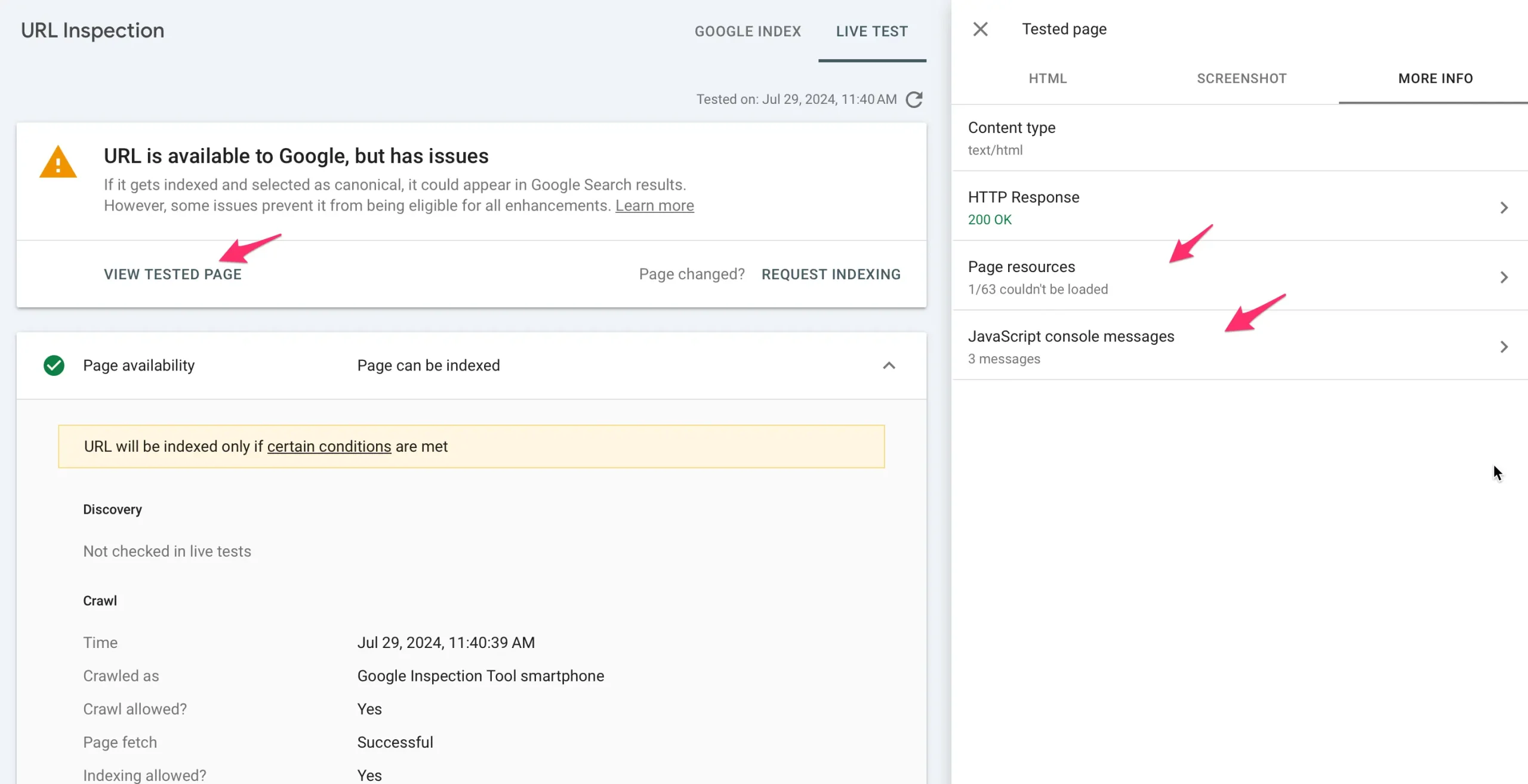
One of the Google search console's most popular functions is the URL inspection tool. This tool analyzes URLs and troubleshoots errors.
This tool is very easy to use. You type in your URL, and Google will tell you everything that they know about the particular page.
- Identify and fix problems related to schema markup and structured data
- Monitor and improve the performance of your rich snippets
10. Analyze Your Backlink and Internal Link Profile
Another helpful feature of GSC is the Links report. In this report, you can see a list of ALL links that Google knows about. These can be inbound (coming from other websites) or internal links.
The list contains both followed and no-follow links.
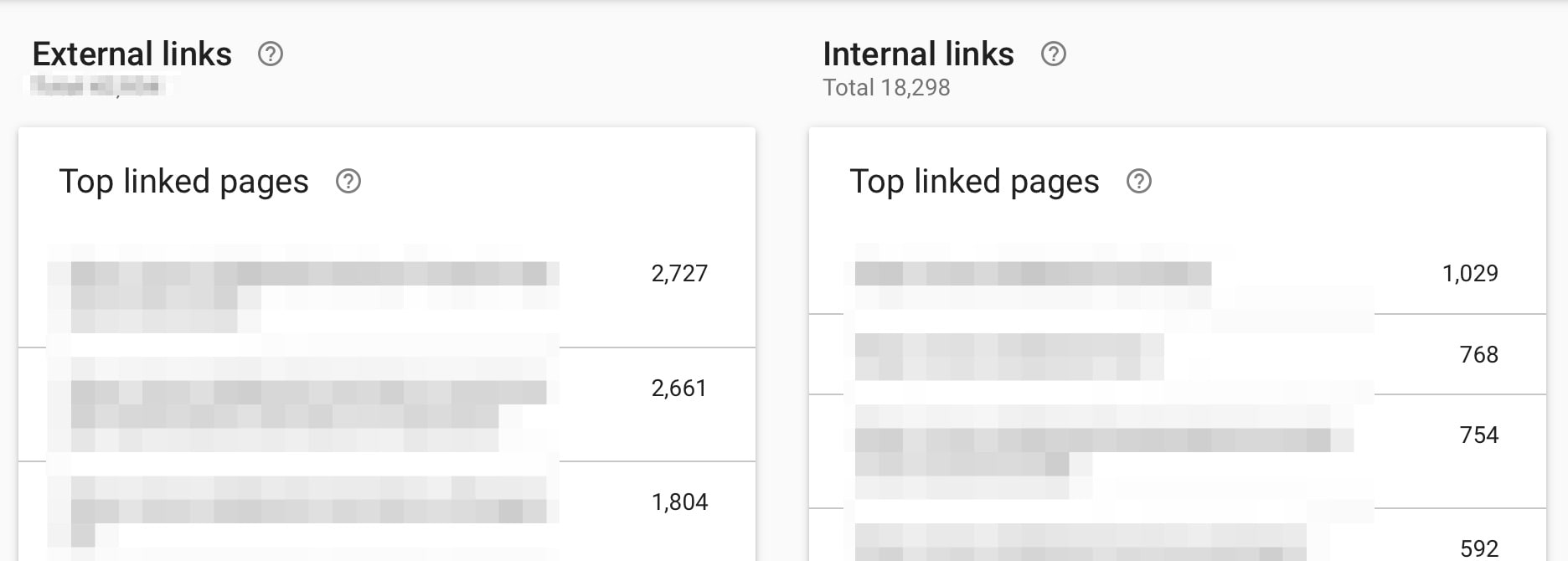
- View all backlinks pointing to your website that Google knows about
- View how Google understands your Internal links
- Remove bad backlinks from Google using the disavow tool (part of GSC)
11. Communicate Important Site Changes to Google
Sometimes, you need to notify Google of changes to your site, such as adding an SSL, migrating to a new domain, or making other significant changes.
Instead of waiting for Google to find out about the changes, you can use the Google search console to notify them and request a re-indexing of your website or particular pages.
- Notify Google of a domain name change
- Force Google to recrawl your site or individual pages

12. Measure Performance in Google Discover
Google Discover is the ‘Google News’ service available through the Google app on both iPhone and Android devices. Through AI, users can get recommendations on articles they can read related to topics they might be interested in.
When your articles appear on Google Discover, you can get more details about their performance in the Google Discover report.
13. View Core Web Vitals Reports
You can find the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console under the “Experience” section in the left-hand menu. This report evaluates your site’s performance based on three key user experience metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Measures loading performance (aim for under 2.5 seconds).
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Measures visual stability (keep below 0.1).
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) - 200 ms or less
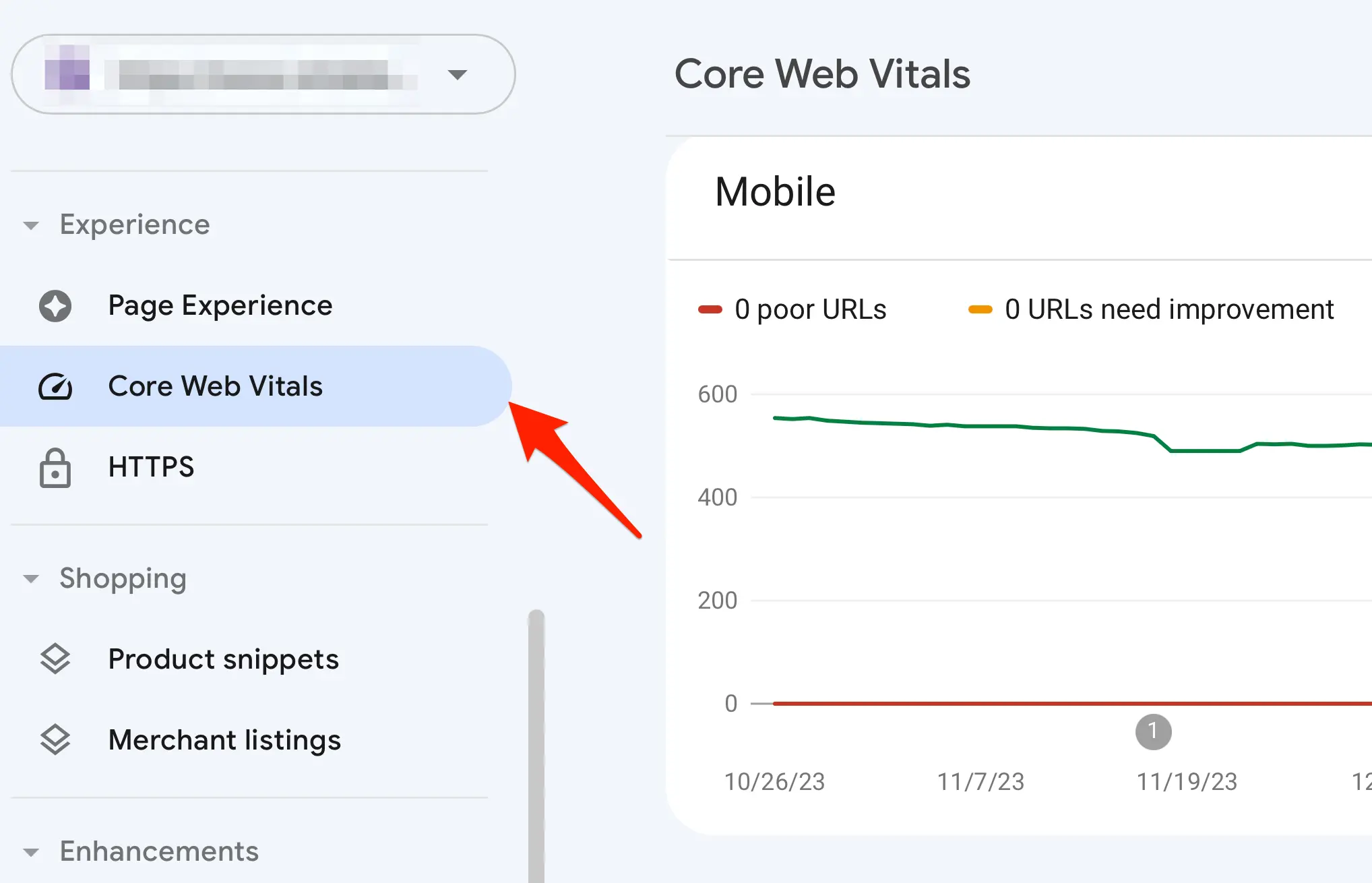
Google categorizes your pages as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor.” If issues are detected, GSC provides recommendations on what to fix. Use this data to improve page speed and user experience, boosting rankings and engagement.
14. View Enhancements Reports
Enhancements in Google Search Console refer to features that improve your website's appearance in Google Search results through structured data.
The Enhancements Report is specific to your website and shows you which enhancement features Google can find on it.
Each report shows whether your enhancements are valid, have warnings, or contain errors. Use the reports to find and fix any errors.
15. Check Crawl Stats
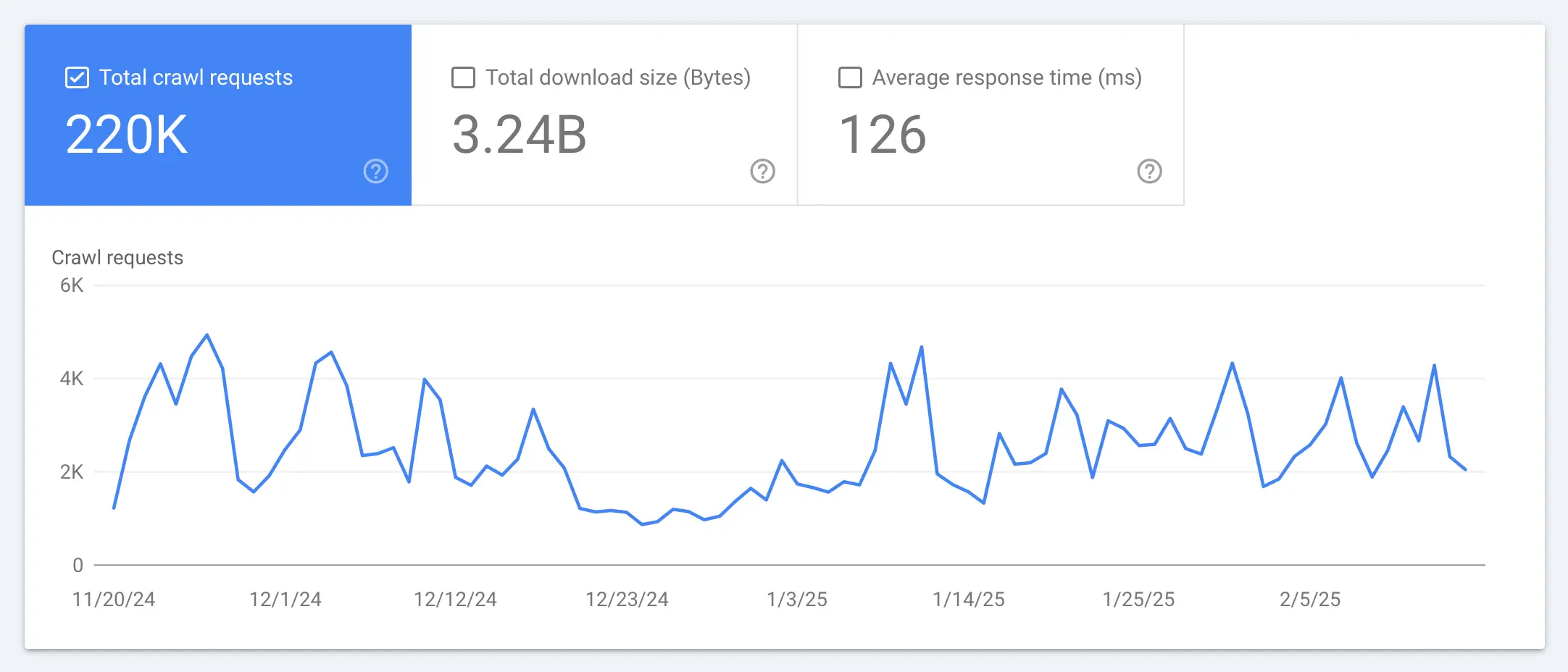
The Crawl Stats Report provides insights into how often Googlebot crawls your site, which pages it visits, and any issues it encounters. Monitoring this data helps ensure Google can efficiently access your content.
To view the report, click Settings, scroll down, and click “Crawl Stats” under the “Crawling” section.
What to Look For:
- Total Crawl Requests – Shows how often Googlebot visits your site. Sudden drops may indicate crawling issues.
- Download Size & Response Time – Large pages or slow server response times can negatively impact indexing.
- Host Status – Confirms if Googlebot can access your site without errors.
If you notice significant changes, such as spikes in crawl errors or decreased crawl frequency, it may indicate technical issues that need attention, such as server problems, blocked resources, or a misconfigured robots.txt file.
For more information read, How To Optimize Your Crawl Budget For SEO.
Google Search Console FAQ
Can I Use The Google Search Console To Contact Google About a Problem With My Website?
No, the Google Search Console does not offer direct communication with Google. You can contact Google through their support forums.
How Fresh Is The Data In The Google Search Console, And How Long Is The History?
You can get data for the last 24 hours up to 16 months. The compare function allows you to view your website's performance over different periods.
Is Google Search Console The Same As Google Analytics?
No, the Google Search Console tells you how your website performs in Google search, while Google Analytics shows you what users do once they visit your website from any online source, not just Google.
With Google Search Console, you can see which keywords generated organic traffic to your website, and with Google Analytics, you can see which pages they visited first, how many pages they visited before leaving, and many other traffic analysis metrics.



