Understanding crawl budget and how to optimize it is essential if you want search engines to efficiently crawl and index your website.
Many webmasters avoid this technical topic, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this guide, you’ll learn, in simple language, what a crawl budget is (and related terms like crawl rate, crawl stats, etc.), why it matters for SEO, and what actions you can take to optimize it.
What Is Crawl Budget In SEO?
The crawl budget is the number of pages Google crawls and indexes from a particular website over a given period of time.
The crawl budget is affected by site structure, duplicate content (within the site), soft 404 errors, low-value pages, website speed, and other factors.
It should be emphasized from the beginning that crawling is not a ranking signal. This means that crawling does not directly impact the position in which a page will appear in organic search results.
The crawl budget is important for SEO because:
- If search engines do not index a page, it won’t appear for ANY searches.
- If a website has a lot of pages, Google may not index them all (that’s why crawl budget optimization is necessary – more on this below)
- Changes made to a page may not appear as fast as they should in Google search results.
When is crawl budget optimization important?
Crawl budget optimization is not usually an issue with small websites but is more critical for big websites with thousands of URLs.
Nevertheless, as you will read below, optimizing your crawl budget involves following SEO best practices, which can also positively affect your rankings.
PRO TIP: If the terms ‘crawling’ and ‘indexing’ are new to you, reading how search engines work is highly recommended. This will help you understand what crawling and indexing are crucial to SEO.
How to Optimize Your Crawl Budget For SEO
- Provide for a hierarchical website structure
- Optimize Internal linking
- Improve your Website speed
- Solve duplicate content issues
- Get rid of thin content
- Fix Soft 404 errors
- Fix Crawl errors
- Avoid having too many redirects
- Make sure that you have no hacked pages
- Improve your website’s reputation (External links)
1. Provide for a hierarchical website structure
When search engine crawlers visit a site, they start from the homepage and then follow any links to discover, crawl, and index all website pages.
The ideal structure for any website is a hierarchical structure with no more than 3 levels deep.
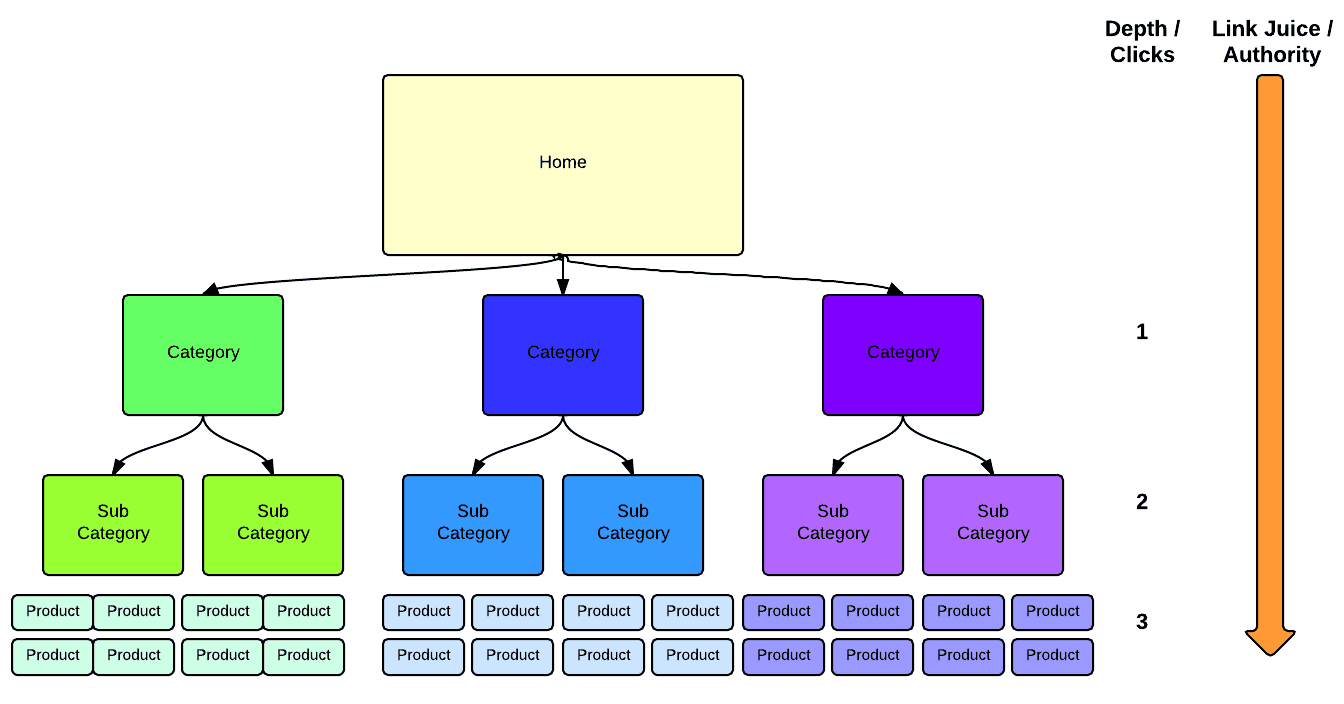
This means that any URL should be accessible from the homepage in three clicks or less.
This simple structure makes crawling easier and faster, and it’s good for the users too.
2. Optimize Internal linking
For any type of website, search engines like to give more priority (when it comes to crawling and indexing) to the most important pages of a site.
One way they identify a site's important pages is by the number of external and internal links on a webpage.
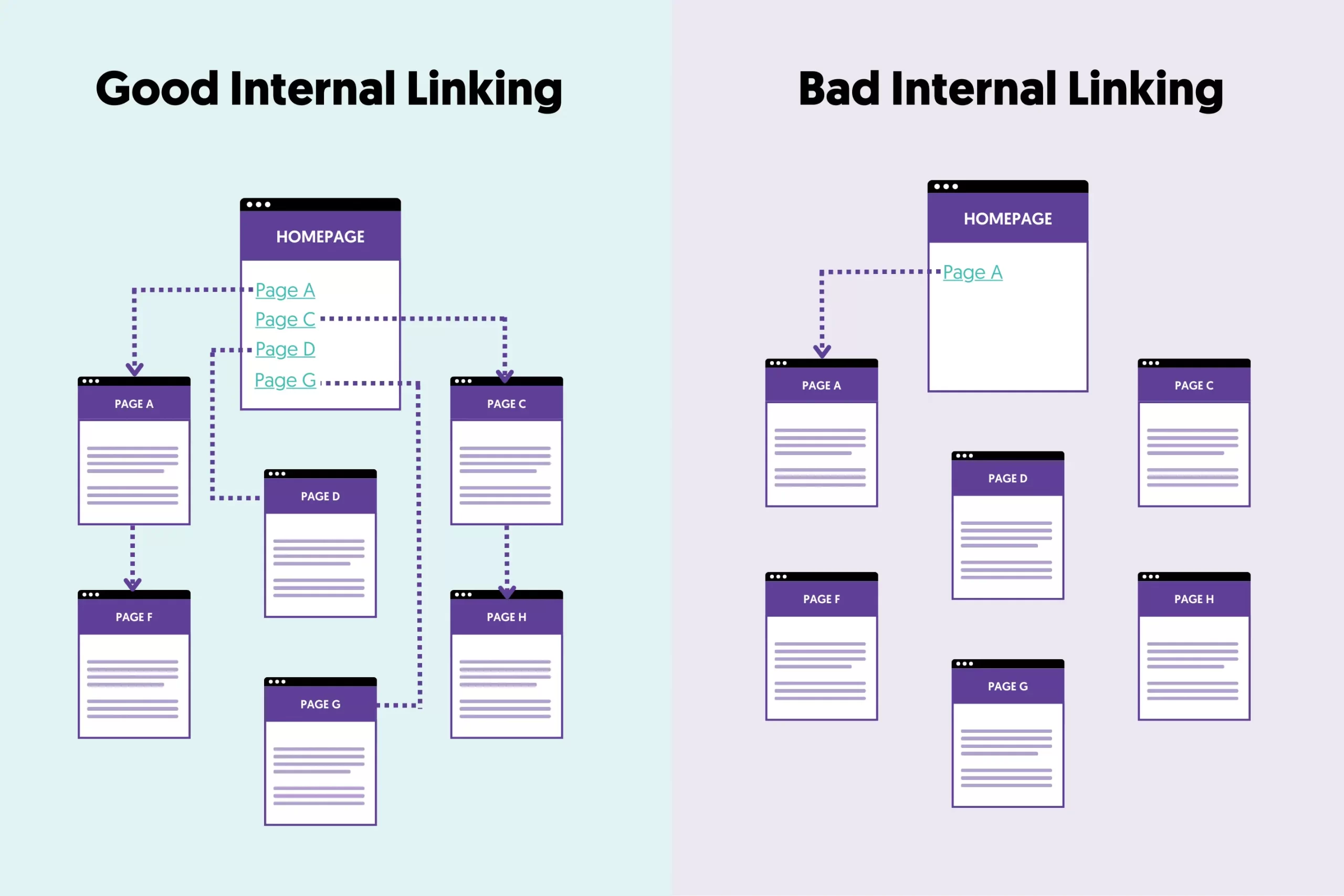
External links are more important but harder to obtain, while it’s easy for any webmaster to optimize internal links.
Optimizing internal links in a way that helps crawl budget means:
- Ensure that your site's most valuable pages have the greatest number of internal links.
- All your important pages are linked to from the homepage
- All pages of your site have at least one internal link pointing to them.
Having pages on your site that have no internal or external links (also called ‘orphan pages’) makes the job of search engine bots more difficult, and they waste your crawl budget.
3. Improve your site speed
Speed is an important ranking factor, a great usability factor, and a factor that affects the crawl budget.
When a website loads fast, Googlebot can crawl more pages of the same site in less time. This is a sign of a healthy website infrastructure and encourages crawlers to get more content from the particular site.
This is what Google mentions about site speed and crawl budget.

As a webmaster, your job is to make every effort to ensure that your web pages load as fast as possible on all devices.
4. Solve Duplicate content issues
One of the factors that can negatively impact the crawl budget is on-site duplicate content.
In this context, duplicate content is identical or similar content appearing in more than one URL on your site.
This is a common issue in eCommerce category pages where similar products are listed in multiple categories.
Besides eCommerce sites, blogs can have issues with duplicate content. For example, if you have a number of pages targeting the same keywords and the content on those pages is similar, Google may consider this duplicate content.
How does duplicate content impact the crawl budget?
It makes Googlebot's job more difficult because it has to decide which pages to index. Crawling resources are wasted on pages that Google will eventually mark as duplicate content.
Pages more valuable to the site may not be indexed because the crawl rate limit might not have been reached.
How do we solve duplicate content issues?

The best way to solve duplicate content issues is to:
- Use canonical URLs to specify the preferred URL for every page on your site.
- Use robots.txt and the noindex directive to block search engine bots from accessing and indexing duplicate content pages.
- Optimize your XML sitemap to specify and help search engines identify which pages from a site they should give priority to.
5. Get rid of thin content
Similar to duplicate content, another factor that can impact the crawl budget is thin content pages.
Thin content is pages on your site with little or no content that add no value to the user. They are also referred to as low-quality pages or low-value pages.
Examples are pages without text content, empty pages, or old published pages that are no longer relevant to search engines and users.
To optimize your crawl budget, you should find and fix thin content pages by:
- Removing them.
- Enhancing their content to add value to users and republishing them.
- Block them from search engines (add the noindex tag).
- Redirect them to a different but more valuable page on your site.
By taking any of the above actions, crawling budget will be allocated to pages that are important to your site.
6. Fix Soft 404 errors
Soft 404 errors can occur for many reasons, and it’s not always easy to determine the exact reason.
The most common causes are misconfiguration of your HTTP server, slow-loading websites, and a large number of thin content pages on your site.
The problem with soft 404 errors (in comparison to normal 404 errors) is that they waste your crawl budget because search engine crawlers keep these pages in their index and try to recrawl them.
The best way to deal with soft 404 errors and optimize your crawl budget is to log in to the Google search console and view the Index Coverage error report.
Click on “Submitted URL seems to be a Soft 404” to view the list of affected pages and fix them.
7. Fix Crawl errors
Another way to increase your crawl budget is to reduce the number of crawl errors. Crawling time spent on errors that shouldn’t exist is wasted time.
The easiest way to do this is to use the Google search console “Index Coverage Report” to find and fix crawl errors.
Our comprehensive guide, "How to fix crawl errors in Google Search Console," has all the necessary information.
8. Avoid having too many redirects
Another issue that may slow down how often Google crawls a website is the presence of too many redirects.
Redirects are a great way to solve duplicate content issues and soft 404 errors, but caution should be taken when creating redirect chains.
When the Googlebot finds a 301 redirect, it may not crawl the redirected URL immediately but will add it to the list of URLs to crawl from the particular site. If a URL is redirected to a URL and that URL is redirected to a new URL, this complicates the process and slows down crawling.
Check your .htaccess and ensure you don’t have any unnecessary redirects and that any 301 redirects only point to the final destination (avoid intermediate destinations for the same URL).
9. Make sure that you have no hacked pages
A hacked website has a lot more to worry about than the crawl budget, but you should know how hacked pages affect the crawl budget.
If your website has been hacked for some time without your knowledge, this will reduce your crawl budget considerably. Google will lose the site's trust and index it less often.
To avoid this unpleasant situation, you can use a security service to monitor your website and check the “Security Issues” report of the Google search console (located under Security and Manual actions) regularly.
10. Improve your website’s reputation (External links)
Popular URLs tend to be crawled more often by search engines to keep their content fresh in their index.
In the SEO world, the most significant factor differentiating popular pages from the least popular pages is the number and type of backlinks.
Backlinks help establish trust with search engines, improve a page’s PageRank and authority, and eventually result in higher rankings.
It’s one of the fundamental SEO concepts that hasn’t changed for years.
So, pages with links from other websites will encourage search engines to visit these pages more often, increasing the crawl budget.
Getting links from other websites is not easy; it’s one of the most challenging aspects of SEO, but doing so will strengthen your domain and improve your overall SEO.
Google Crawl Stats Report
Although you should not become overly obsessed with crawling budgets and crawl stats, it’s good to review the “Crawl Stats” report in the Google search console occasionally and look for abnormal behavior.
The Crawl Stats report is available under "Settings > Crawl Stas".
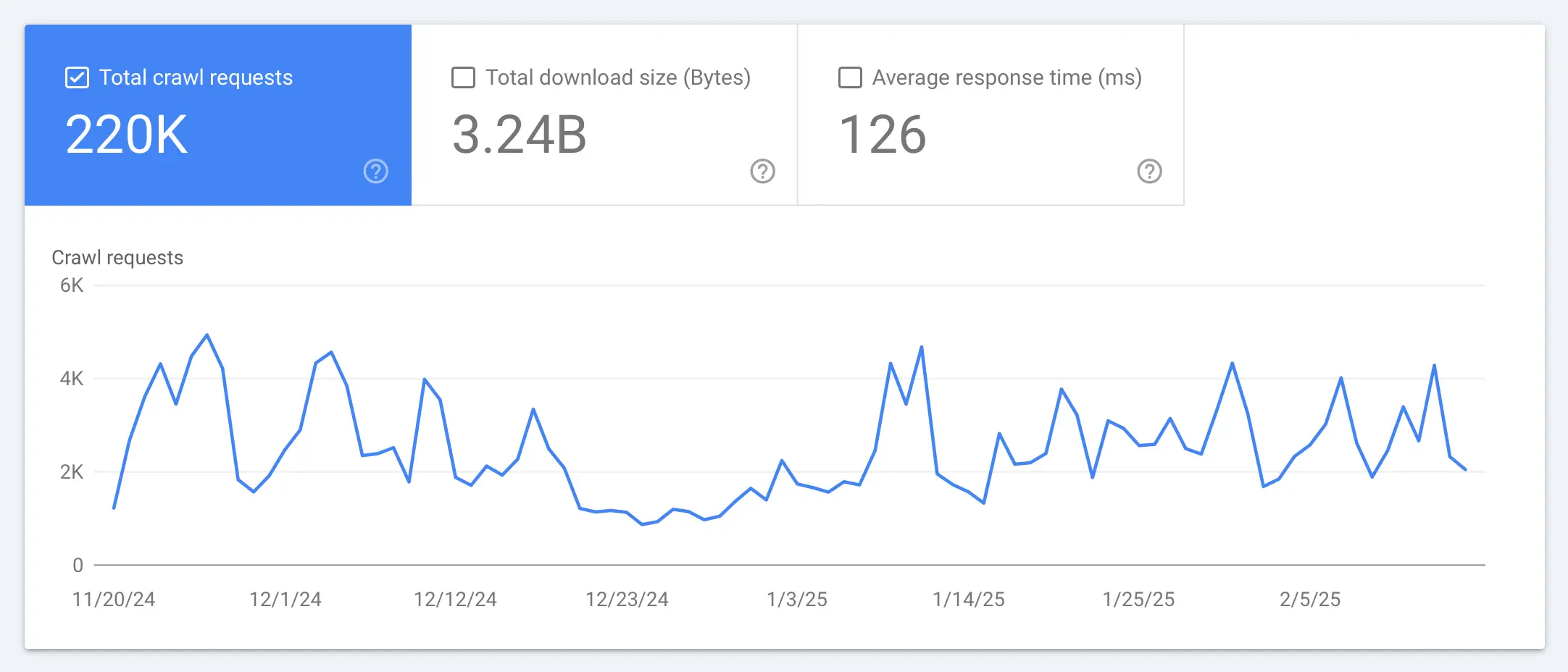
This report provides information about ALL Googlebot activity on your site for the last 90 days.
The report will include any attempt made by Googlebot to access any crawlable asset on your sites, such as pages, posts, images, CSS files, JS files, PDF emails, and anything else you have uploaded to your server.
That’s also why the number of “Pages crawled per day” is bigger than the number of pages you have in the Google index.
What should you look for in the crawl stats report?
When viewing the report, try to spot any sudden drops or spikes in the number of pages crawled daily. Look for a period of two weeks or a month and see if the drop or spike is continuous.
Under normal circumstances, the number of crawl pages should steadily increase over time (provided that you add new content to the site regularly). If you are not making any changes, the pattern should be similar if you compare two time periods.
A sudden drop in crawl rate can occur when:
- You added a rule to block a big part of your pages from being indexed by search engines
- Your website and server are slower than usually
- You have a lot of server errors that need your attention
- Your website is hacked
A crawl rate can spike when:
- You added a bunch of new content to the site
- Your content went rival, and you got new links, which increased your domain authority
- Spammers added code to your site that generates hundreds of new pages
You can visit this link to learn more about the data shown in the crawl stats report, but in most cases, this is not something you should worry too much about.
Key Learnings
Optimizing your crawl budget for SEO is the same process as optimizing your website for technical SEO. Anything you can do to improve your website’s usability and accessibility is good for your crawl budget, good for users, and good for SEO.
Nevertheless, every little step helps SEO, and when it comes to crawling budget optimization, the most important step is to get rid of crawling and indexing errors. These errors waste your crawling budget, and fixing them will improve your website’s overall health.
Other factors, like website speed, duplicate content, and external links, can improve site visibility in search engines, which means higher rankings and more organic traffic.
Finally, it’s a good practice to regularly review your crawl stats report to spot and investigate any sudden drop or spike in crawl rate.



