In this post, you will learn what content SEO is and how to optimize your content for search engines and users using best practices.
What Is SEO Content?
SEO content is content created with the goal of attracting search engine traffic. It is useful to users and optimized around a specific keyword. The most common types are blog posts, product pages, and landing pages.
Why Is SEO Content Important?
If you want your content to rank high and get targeted traffic from search engines, it has to be SEO-optimized. The most important advantages of SEO content are:
- Increases visibility and traffic: SEO content helps your website appear in top search results, attracting more visitors actively looking for information related to your products or services.
- Enhances user experience: Content produced with users in mind creates a better experience and higher user engagement.
- Builds trust and credibility: High-quality, relevant content that ranks high in search results establishes your site as a credible and authoritative source in your niche.
- Provides lasting value: Unlike paid advertising, the effects of good SEO content are long-lasting.
Types of SEO Content
Content can have different forms. It can be text, images, videos, audio, infographics, or a combination. In general, the different types of SEO content are:
- Blog Posts: The most widely used format. It can be a combination of text, images, and video. It can be news types of articles, lists, how-to guides, press releases, or general information.
- Static Pages: Content found on static pages of your website, like the ‘About Us’.
- Product pages: Pages promoting specific products or services.
- Landing pages: Pages explicitly designed for PPC campaigns or as the first page users see when they visit your website.
SEO Content Best Practices
Follow these guidelines to create SEO content:
- Start With Keyword Research
- Use Keywords In The Content
- Satisfy The Search Intent
- Cover The Topic Adequately
- Add Internal And External Links
- Work On On-Page SEO
- Add Schema Markup
- Group Content Into Categories
- Optimize Content For Conversions
1. Start With Keyword Research
Before you get your hands dirty and start thinking about your introduction, you need to do your homework first, and in this context, we mean performing keyword research.
Knowing what keywords are typed by users in the search box can serve two primary purposes:
- You will know what type of content to create to make users happy
- You will know how to optimize your content and increase your chances of getting noticed by search engines. In the long run, this means higher rankings and traffic.
The outcome of your keyword research should be three things:
- A decision on what is the main keyword you are targeting.
- A set of long-tail keywords related to your primary keyword.
- A set of keywords related to your primary keyword.
You will use these as part of the content SEO process. To be more specific:
- Your target keyword should include your URL, page title, and h1 heading.
- Long-tail keywords can be included in your subheadings
- Other related keywords can be included in your subheadings and the body of the content.
2. Use Keywords In The Content
Use your primary keyword above the fold.
Everybody knows that your main keyword should appear in your title and h1 heading, but what is equally important is to mention your keyword once or twice in the first couple of paragraphs.
There is a rule of thumb stating that the important content of a page is the one found on the top part of the page (above the fold), so make sure that within that content, you give search engine spiders more clues on what the rest of your content is all about.
Here is an example from one of my posts. The target keyword was learn digital marketing.

Use long tail-related keywords for subheadings.
When you target a specific keyword, you don’t just repeat that repeatedly, but you use variations of that keyword in your content.
A great way to do this is to find long-tail keywords related to your main keyword and use those in your sub-headings.
Start typing your main keyword in the Google search box and take note of the different suggestions. These are great keywords to include in your subheadings and content.
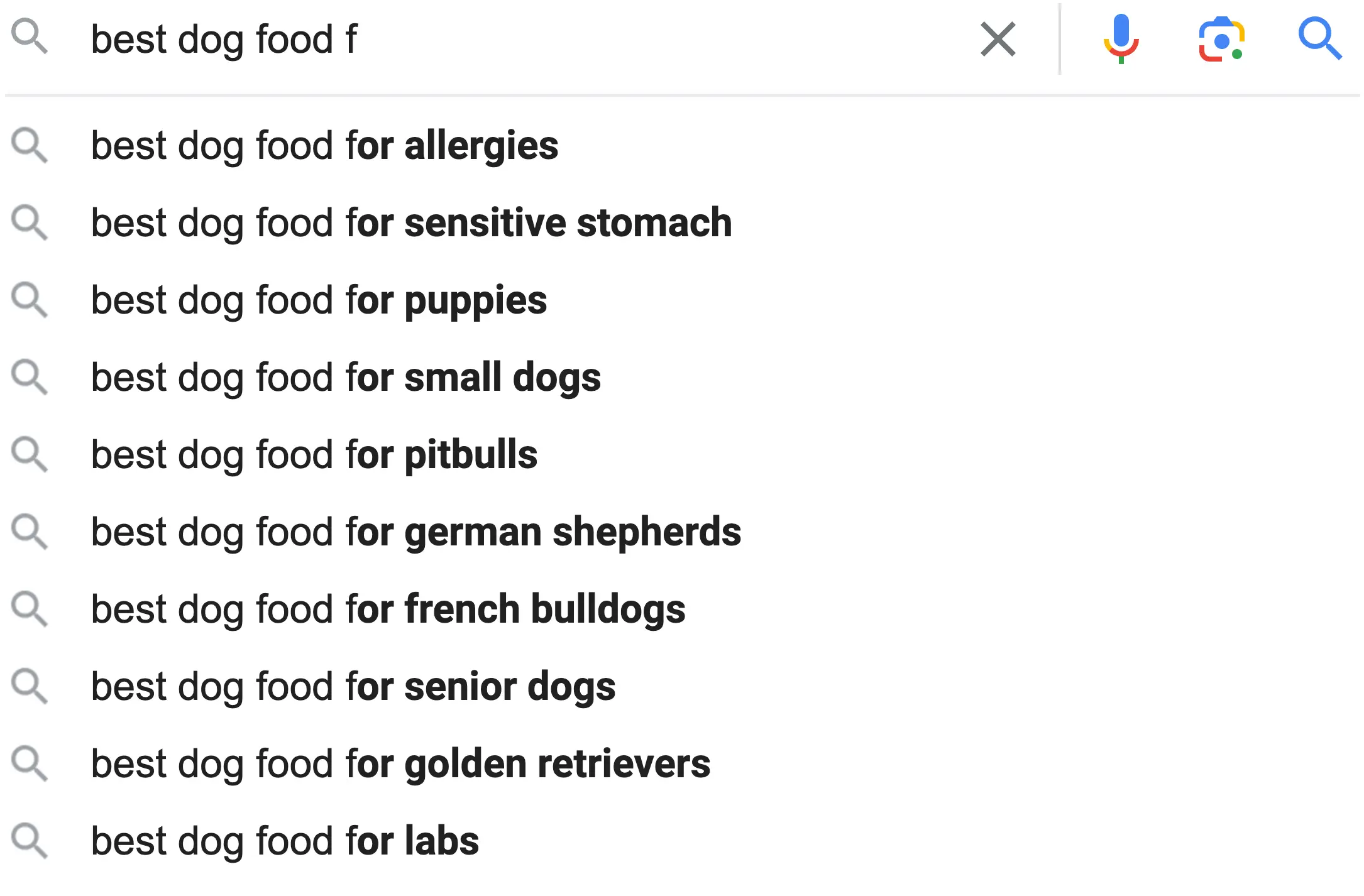
Another way to find related keywords is to search for the main keyword in Google and look for the ‘People Also Ask’ section.
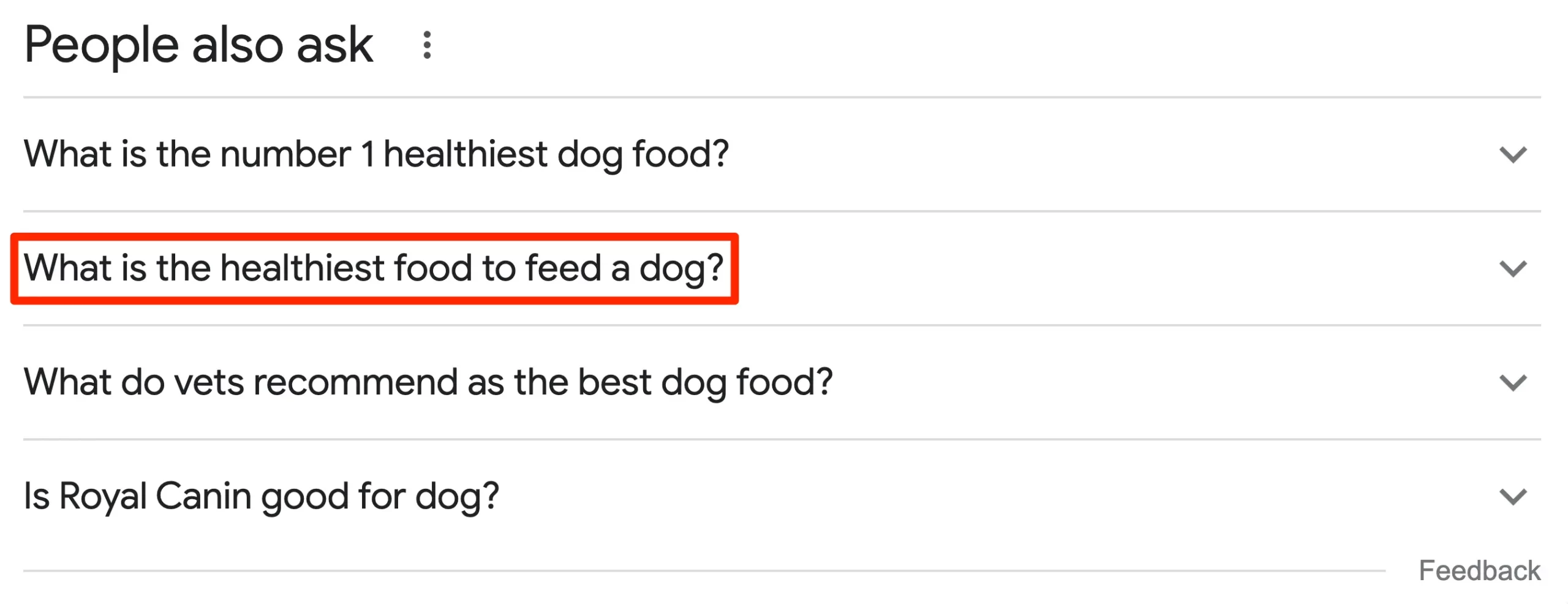
Use related keywords in your content.
LSI stands for Latent Semantic Index; in simple terms, these are word phrases with the same meaning as your primary keyword.
Why are LSI keywords important? With the introduction of Rank Brain (Google’s machine learning technology used as part of the ranking algorithm), Google is trying to understand the broader meaning of keywords, which is taken into account in rankings.
How do you find LSI keywords?
The easier way is to search for your main keyword in Google and look at the “related searches” section.
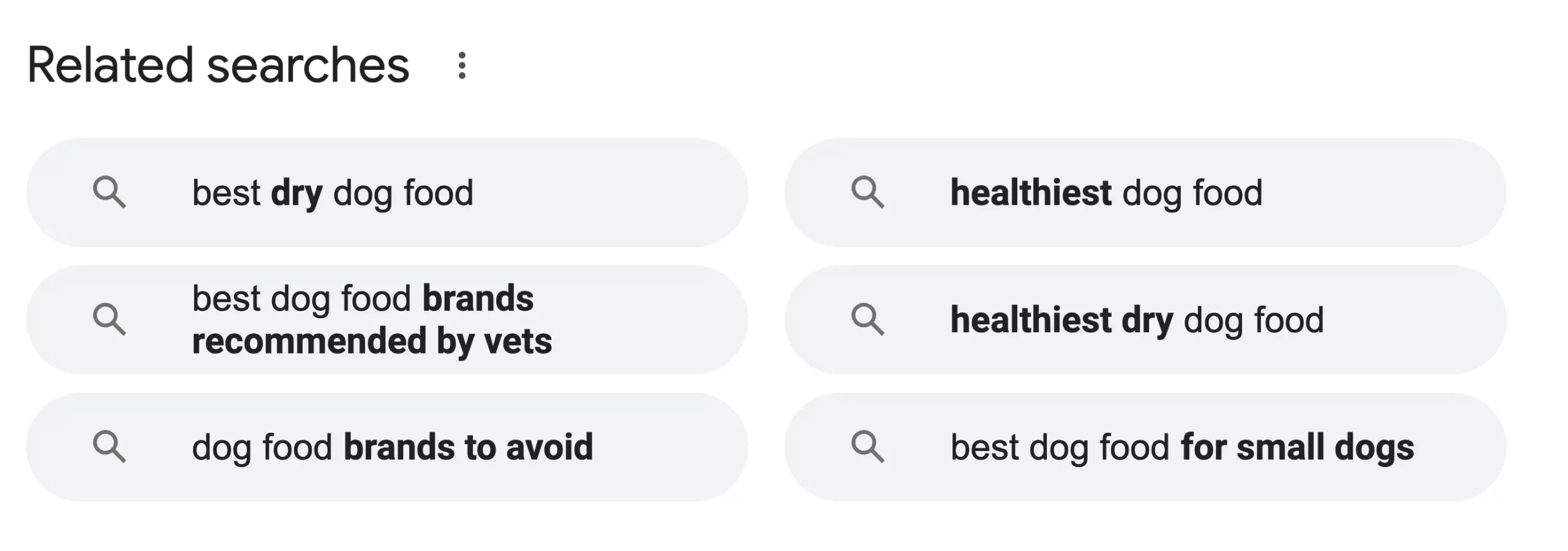
3. Satisfy The Search Intent
Before publishing content on your website, you must understand the search intent. In other words, what type of content do users want to see for a given search query?
The easiest way to do this is to take advantage of Google because (Google) has already understood what users like for different searches.
Here are the steps to follow:
Let’s say you are writing an article about ‘what is off-page SEO’. The first step is to search Google for this term and look for the featured snippet and the meta descriptions of the first 10 results.
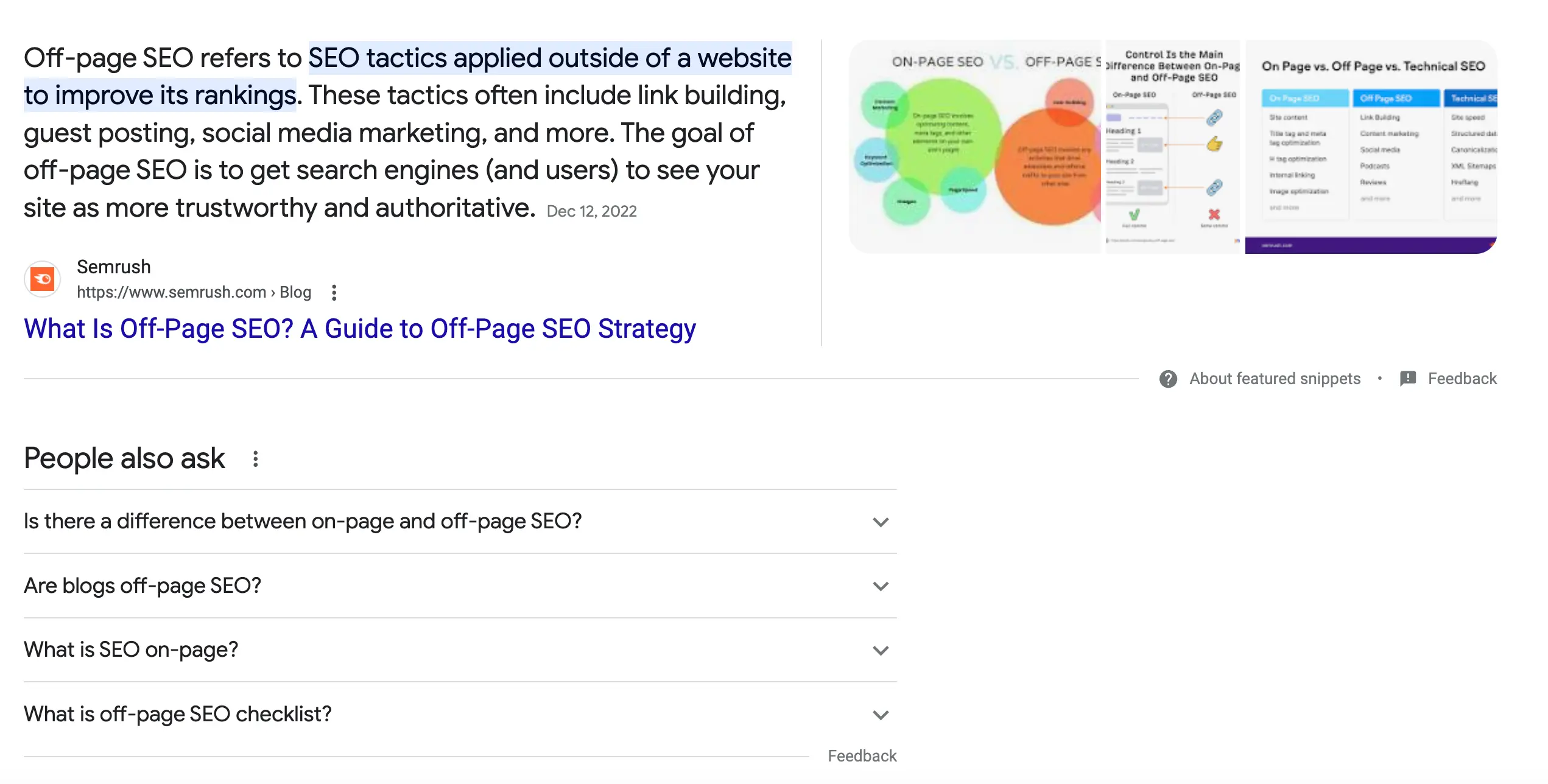
If you take a closer look at the above screenshot, you will notice that Google is trying to give a direct answer to the question “What is off-page SEO?” in both the featured snippet and the description of each snippet.
This pattern tells us that if you want to rank high for this term, you need to give a direct answer to that question.
In other words, the intent of the user for the particular query is to read a definition of what we mean by ‘off-page SEO’.
What you should learn from this?
For search queries related to questions, how-tos, or lists, try to answer the top part of your page, and then you can give more details within the post and not vice versa.
In the past, we used to write lengthy introductions so that readers could spend more time reading them before getting to an answer, but this is no longer the case.
Give the answer first, satisfy the initial user intent, and then expand your article to give more information.
4. Cover The Topic Adequately
Several studies show that long-form content performs better in search and social media networks. While this is true, it does not mean you should write thousands of words to get to a word limit.
The quality of the content is always more important than quantity. If your writing is good and attracts shares and links, it can rank high on Google even if other posts are longer.
I prefer to publish long-form content because it makes sense for SEO articles. This is what readers want and what my competitors are doing.
Optimize long-form content
A nice tip for optimizing long-form articles is to use a table of contents at the top of the post to help users navigate the content.
Besides making navigation easier, you also increase your chances of getting sitelinks to appear with your snippet in the Google search results.
For example, my SEO checklist post is 4000 words long because it covers all aspects of SEO. To help users navigate through the content, I have included a table of contents.
5. Add Internal And External Links
Another element of content SEO is internal linking. Within your content, link to other pages of your website to help users find out more about a certain topic, and search crawlers are another reason to index more pages from your website.
Internal links create what is called ‘content relevancy,’ something that helps Google understand the meaning of the content better.
When adding internal links, use meaningful anchor text so that crawlers can get a good idea of what the linked page is all about.
Add external links to other high-quality websites.
Besides linking to your articles, it’s a good practice to link out to other high-quality websites or sources provided that:
- They will help users read more about a topic.
- You trust the website you will link to.
- You do it with getting compensation (that’s selling links, and it’s not allowed).
Don’t overdo it with external links, but don’t be afraid to link out when it makes sense.
6. Work On On-Page SEO
will help you make your content SEO-friendly. Follow these tips:
Always use text to accompany your non-text content.
Search engines can understand text content more than any other type of content, so make their life easier by having text content on your page, even if you promote other types of content.
For example, you created a nice infographic about a topic and want to publish it on your blog. Don’t just add the infographic and hit publish; try to have text content on the page explaining the infographic.
You can follow the same concept when publishing images, videos, or audio. For example, if you are running a podcast, you can have the description of the podcast and even a text transcript so that both users and search engines can better understand what the audio is all about.
Make your content easy to read.
Don’t just throw text on a page; apply formatting styles to make reading more accessible, especially for users who like to skim-read.
- Use short paragraphs
- Use bold and italics to highlight parts of the content that matter
- Use lists to outline steps
- Use short sentences
- Use a font that is easy to read (and large enough) on all devices
- Add enough white spacing between your paragraphs
Optimize non-text elements.
As mentioned above, content can have many forms and is not necessarily text. When adding other non-text elements to your content, make sure that it is optimized. The most common is images, and all images included in your content should:
- Have a friendly filename (i.e., LSI-keywords.jpg and not 345afg.jpg)
- Have an appropriate ALT Text
- Include a line of text below the image to describe what the image is all about.
7. Add Schema Markup
In addition to the above, you can use structured data to describe your content to search engines in a way they can understand.
There are a number of schemas you can implement depending on the type of content you are publishing. There are schemas for articles, videos, podcasts, products, recipes, reviews, and more.
Structured data has been gaining more importance in the last couple of months, and according to Google, it’s here to stay for the long term.
8. Group Content Into Categories
While this is not directly related to content SEO, it is good for overall SEO.
Google, when crawling a page, is primarily interested in the content found on that page, but it also takes into account where the page belongs.
In other words, you should create categories and group your pages to ensure your site structure is reflected in your menu and breadcrumbs.
Follow these simple rules:
- Create several categories.
- Add articles to categories.
- Optimize your categories.
- Add categories to your main menu (name them topics or anything else).
- Ensure that your breadcrumb menus allow users to navigate to the parent category.
9. Optimize Content For Conversions
I have mentioned above that the main goal of content SEO is to satisfy the user intent, but equally important is to satisfy your goals as a publisher.
Every piece of content published on your website should have a purpose. By purpose, we mean, “What do you want users to do once they read your content?”
- Do you want to get more email subscribers? Then, ensure that you have a sign-up box below your posts.
- Do you want people to buy your products and services? Then, add CTA (call to action) within your content to direct traffic to your sales pages.
- Do you want to get clicks on your ads? Then, ensure that ads are visible while users read the content.
- Do you want users to engage and stay on your website for longer? Add a related articles section below the post.
Whatever your purpose is, it should be clear to users what the next step is in continuing their journey.
What’s Your SEO Content Strategy?
You should follow the above best practices every time you publish new content, but you must also have a content strategy in place.
What do we mean by content strategy? To have a plan that will include the following:
- What type of content to publish
- Which keywords to target
- When to publish it
- How to promote it
- To whom to promote it (The target audience for each piece of content)
When discussing content SEO, it is important to understand that optimizing your existing content is not enough. You need to have a way to produce new content regularly.
The competition is tough, and if you want to reach or bypass your competitors, you need to create a content marketing plan and follow it without excuses.
Consistently publishing high-quality content is the best way to improve your ranking on Google.
It is also proven that companies that blog regularly get more leads than those that do not.
What’s next?
So, what’s next? You know how to optimize your content and have a content marketing strategy. That’s great, but it’s definitely not the end of the story.
Your ongoing SEO process should include the following:
- Ways to promote your content.
- Link-building strategies.
- Monitoring rankings for keywords and individual pages.
- A plan to do content enhancements (on existing posts).
- Rinse and repeat.
Conclusion
Content SEO is a very important component of the on-page SEO process. Your goal is to give users and search engines the content they seek. As stated by Google, know what your readers want and give it to them.
The process starts by discovering what users seek and creating content satisfying their intent.
Before hitting the publish button, you should ensure that your main keywords are included in the top part of the page and related keywords (including LSI) in your subheadings and body.
Beautify your content, make it easy to read and navigate, and then promote it to get in front of the eyes of as many people as possible.
Don’t worry if some of the above concepts are difficult to understand now. As you get more experienced with SEO, everything will make better sense.



