Measuring your SEO performance will give you an indication of your website's visibility on Google, Bing, and other search engines. You can use this data to make data-driven decisions to improve your SEO results.
10 Metrics To Track SEO Performance
- Organic Traffic
- Ranking Positions
- Impressions and CTR
- Engagement Rate
- Bounce Rate
- Conversion Rate
- Domain Authority
- Referring Domains & Backlinks
- Core Web Vitals
- Number of Indexed Pages
1. Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the most important metric for measuring your website's performance in search engines. It shows how much traffic is coming to your website organically, i.e., without paying for ads.
To use this metric meaningfully, you must know which keywords and pages generate clicks from the SERPs.
How To Measure Organic Traffic
The Google Search Console is the most reliable source of information for measuring organic traffic coming from Google. If you don't already have an account, go to Google Search Console and add your website.
Then go to the "Performance on Search Results" report (Performance > Search Results) and view the following reports:
- Queries - Shows you the keywords that triggered clicks and impressions.
- Pages - This shows you the landing pages that received the most visits.
You can click the +NEW button from the menu and add filters to analyze your data by country, device, specific query, and more.
For more details on navigating through the interface and reports, read our Google Search Console Guide For Beginners.
Google Analytics is an alternative way to measure organic traffic from all search engines, not just Google.
By visiting the "Traffic Acquisition" report, you can see how many visits are coming from organic search and useful metrics (like engagement rate, page views, events, and conversions) that can help you understand how valuable the traffic is.
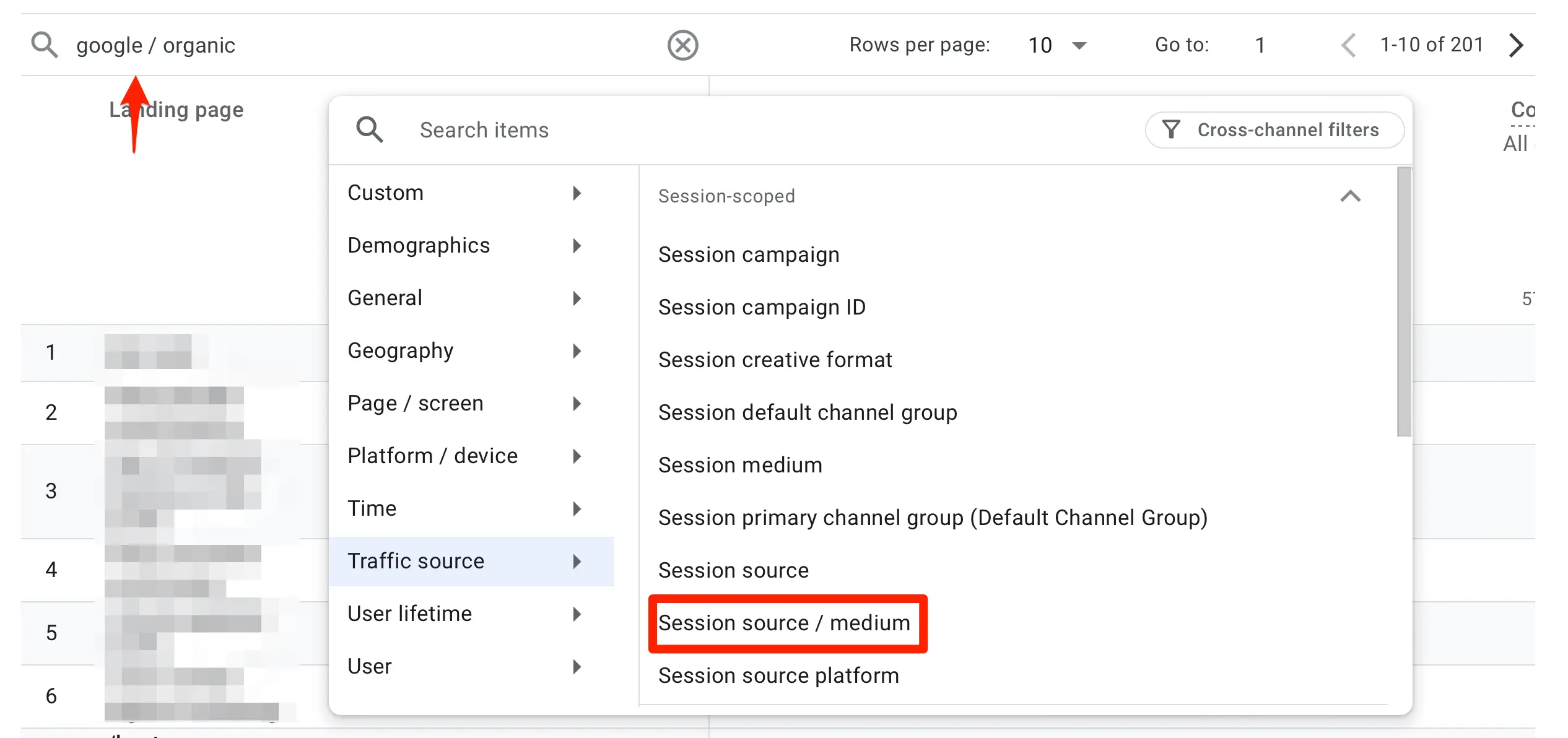
You can analyze the traffic by search engine by selecting "Session source/medium" from the dropdown menu.
What To Look For When Analyzing Your Organic Traffic?
Use Google Search Console or Google Analytics to view your Google traffic over a long period and compare that with the dates that Google updated its ranking algorithms.
If you notice any traffic gains or drops during that time, it's a strong sign that your website has been affected by Google updates. In such cases, you should investigate further to understand what contributed to the change and take action to recover your traffic or build on what is already working.
For more information, see How To Check For Google Penalties.
2. Ranking Positions
Landing on the first page of Google doesn't happen overnight. You should track keyword rankings to monitor how your SEO improves over time and if you're on the right track.
When you publish new content, it takes months to find its final position in the SERPs, and in 90% of cases, it won't get any good rankings or traffic. By monitoring your rankings, you can spot the 10% of your content that has potential and work on improving it further.
How To Check Your Keyword Rankings
One of the best ways to check your keyword rankings is to look at Google Search Console reports (as explained above).
Other ways include using dedicated tools that are easier to use and have more features. Rank Tracker is a great option with powerful features and reasonable pricing (it comes with a free trial).
For more tools, visit our 5 Free Tools To Check Your Keyword Rankings in Google guide.
What To Look For When Analyzing Your Keyword Rankings?
Look for pages that rank in positions 5-15 on Google. There are good candidates to optimize their content further and achieve higher rankings.
If the pages were published at least 6 months ago, you can optimize them for featured snippets, review them for search intent, and add more internal links.
For more information, read How To Improve Your Search Engine Positioning.
3. Impressions and CTR
Another set of metrics that impact your SEO results are impressions and CTR.
Impressions refer to the number of times a user saw a link to your site in search results. Organic CTR (click-through rate) is the percentage of searchers who click through to your website from the search results.
How To Check Your Impressions and CTR
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Navigate to “Search Results Report” under Performance
- Check the boxes that say Total Impressions and Average CTR.
What To Look For When Analyzing Your Search Impressions and CTR?
Look for queries with the highest impressions but the lowest number of clicks. Click on the "Pages" tab to view the affected pages.
Work on those pages to improve CTR by optimizing page titles and meta descriptions and making the content eligible for Google-rich snippets.
4. Engagement Rate
The main goal of SEO is to get website traffic, but it's equally important for users to interact with your website and engage with your content.
If users visit your website from Google and then click the back button to return to the search results, this is a sign that they are not happy with the content. Over time, Google algorithms will consider that, and your rankings will be negatively affected.
One of the metrics to measure this is engagement rate. The engagement rate is the percentage of engaged sessions on your website.
As defined by Google Analytics, an engaged session is a session that lasts longer than 10 seconds or has at least 2 pageviews or when users perform a key action (such as clicking a button).
How To Check Your Engagement Rate?
The engagement rate is available in Google Analytics. To add it to your reports:
- Go to Pages and Screens” report under Life Cycle / Engagement. Click the ‘Customize Report’ button (top right corner) and then click METRICS.
- Select Engagement Rate and Bounce Rate and click the APPLY button.

Once added, you can view the engagement rate per page, traffic source, device, or other report filters.
What Is a Good Engagement Rate?
The higher the engagement rate, the better. There is no minimum value for a good engagement rate. You should view the engagement rate of all your pages to find the ones with a low engagement rate.
Examine the pages' content and find ways to improve it. Look at the pages ranking at the top of Google for the same terms and compare them with your content. Identify any content gaps or features missing from your pages.
Sometimes, improving user experience factors (like page speed, reducing ads, and better content formatting) is what it takes to keep users on your website for longer.
Review our 15 Landing Page Best Practices for actionable tips on increasing user engagement rate.
5. Bounce Rate
The opposite of the engagement rate is the bounce rate. It's the percentage of users who landed on a webpage and then exited without interacting with the page. In other words, those users were not engaged with your content. The lower the bounce rate value, the better.
Like the engagement rate, the bounce rate indicates how happy users are with your content.
How To Check Your Bounce Rate?
You can check your bounce rate using Google Analytics (as explained above).
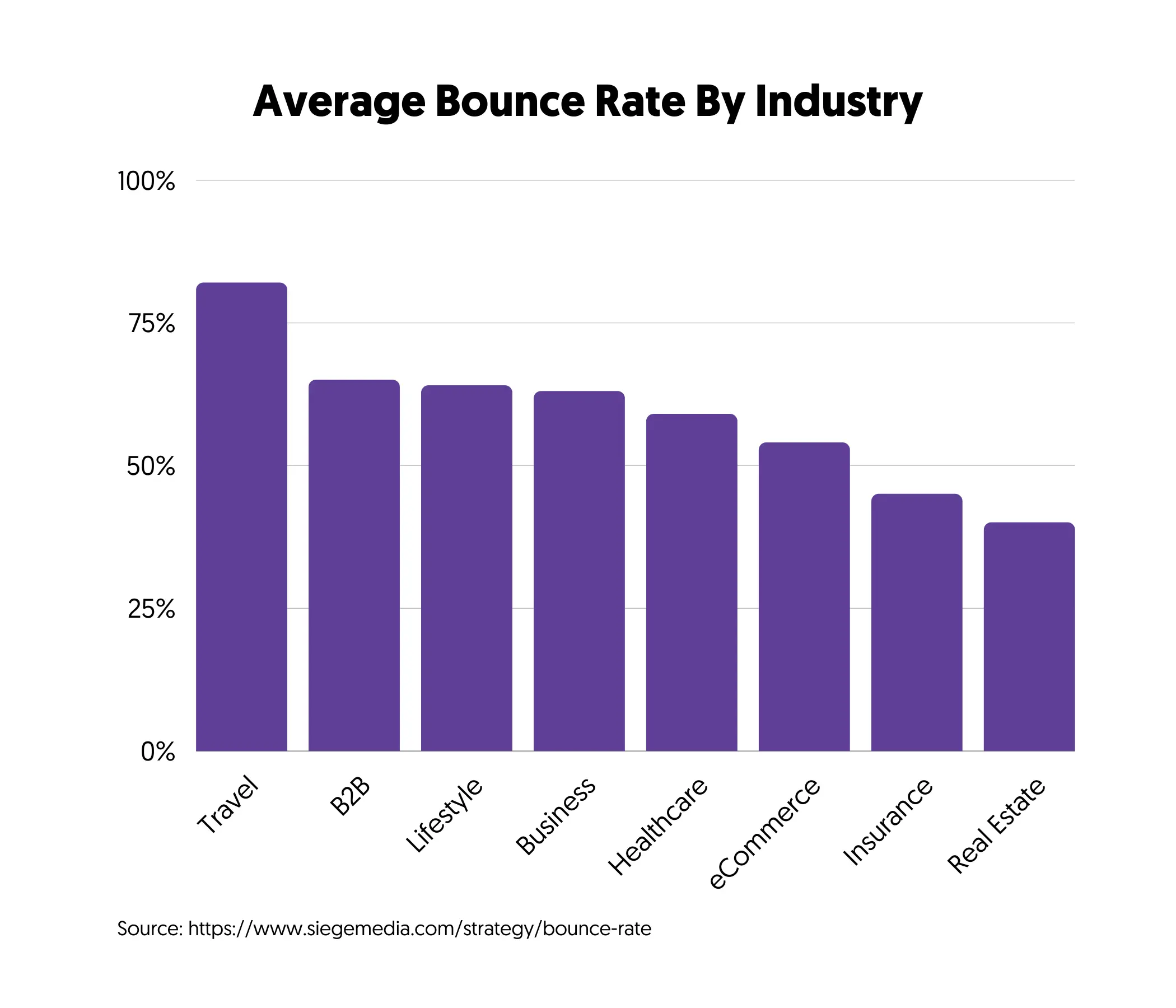
What Is a Good Bounce Rate?
A good bounce rate varies per industry, but a bounce rate below 50% is generally considered good. The graph below shows the average bounce rate by industry, which you can use as a general guide.
For tips on reducing your bounce rate, read 10 Best Ways to Reduce Bounce Rate (Tried & Test).
6. Conversion Rate
When we measure SEO results for our clients, the most important metric we look at is the conversion rate. Getting SEO traffic to a website that does not generate conversions has no value, so it's necessary to monitor this KPI closely.
A website conversion is an important action you want users to take while on your website, like subscribing to a newsletter, filling out a contact form, or purchasing. A conversion rate is the percentage of people who visited your website and performed an important action.
How To Calculate Your Conversion Rate?
To calculate your conversion rate, use the following formula: (Number of conversions / Total number of visitors) x 100
For example, if you get 1000 website visits and 20 of them buy a product from your store, your conversion rate is (20 / 1000) X 100 = 2%.
What Is a Good Conversion Rate?
As a rule of thumb, a conversion rate above 2% is considered good. However, whether this is good for your website depends on several factors, such as the type of conversion, industry, traffic type, and more.
7. Domain Authority
Domain authority is a metric that doesn't directly impact your SEO performance but is always good to monitor. It is a number between 0 and 100 that tries to predict how well a website will rank on search engines.
Google does not use domain authority in any way. It is used by various SEO tools, and each tool calculates it differently.
You should decide which tool to use to measure domain authority and monitor it once a month. If you notice any big spikes or decreases, it might be worth investigating more to discover what caused the changes.
In normal situations, your DA should also increase as your website grows (content, traffic, and links).
How to Check Your Domain Authority?
Many da checker tools exist, but I recommend using Ahrefs DA metric. It's the most recognized when comparing websites. Go to Website Authority Checker and enter any website to check its DA.
8. Referring Domains & Backlinks
Backlinks are still important for SEO. Despite the debate about whether they are in the top-ranking factors, we should count the total number of links as part of your SEO results.
Good, high-quality links will always positively impact your rankings and domain trust.
How To Monitor Your Backlinks?
You can get an idea of how many links and unique domains link to your website in the "External links" report of the Google Search Console, but the data is unreliable. Google only shows you a portion of the links, and the numbers fluctuate frequently.
A better way to find who links to your site is to use a tool like Semrush or Ahrefs. With these tools, you can see how many unique domains and links point to your domain, get historical data, analyze the links (follow, nofollow), and many other useful metrics.
9. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a set of metrics for measuring user experience, including page speed, interactivity, and visual stability. Although Core Web Vitals is a lightweight SEO ranking factor, having a fast website that provides a good user experience is great for your business.
How To Measure Your Core Web Vitals?
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to analyze your website aim for these values:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) –2.5 sec or less
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – 0.1 or less
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – 200 ms or less
You can also monitor the "Page Experience and Core Web Vitals" reports in Google Search Console.
10. Number of Indexed Pages
Another metric that impacts your SEO performance is the number of pages in the Google Index. During the crawling and indexing process, search engines add to their index pages that meet their quality criteria. These pages are used by the ranking algorithms to decide which ones will show up in the top positions for a given query.
If your website doesn't have any technical SEO issues, the number of indexed pages will increase as your website grows.
How To Measure The Number of Indexed Pages?
The "Page Indexing" report in Google Search Console will tell you how many of your website pages are indexed and why some pages aren't indexed.
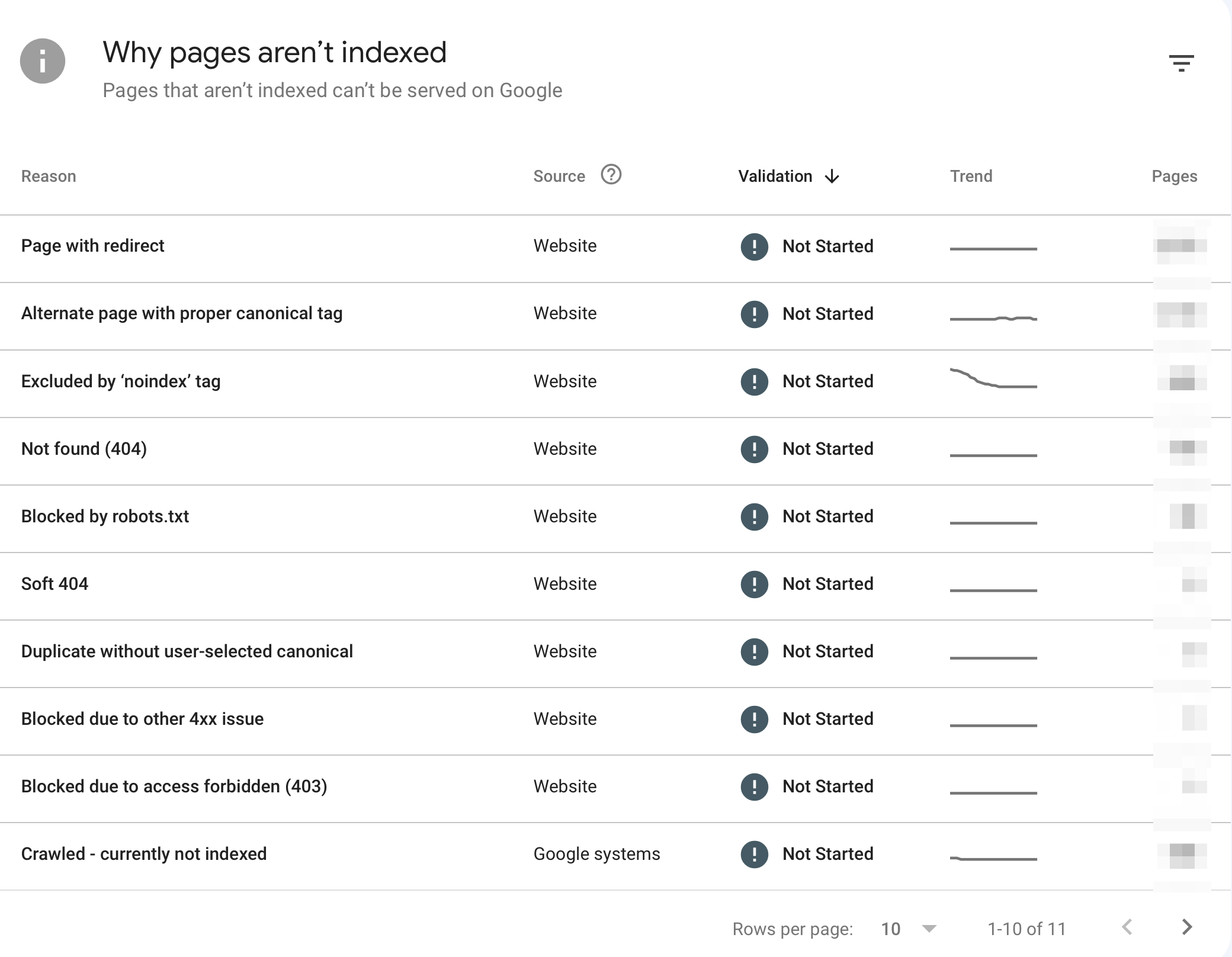
You should regularly check the reports to find and fix any indexing errors.
How Long For SEO To Product Good Results?
When you start tracking your SEO performance, you'll notice that it takes time to get good results with SEO. With 'good results' we mean to achieve high rankings for the keywords that matter for your business.
How long it will take depends on competition, your website's domain authority, and the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
In my experience, if you're starting with a new website, it generally takes about six to twelve months to see noticeable improvements in your rankings.
For established websites looking to improve, the timeline can be shorter, often around three to six months. Remember, SEO is a marathon, not a sprint, and consistent effort is key.
How To Evaluate Your SEO Performance
To evaluate your SEO performance correctly, start by setting clear, measurable goals based on the metrics you're tracking. For example, if your focus is on increasing organic traffic, set a specific percentage increase as your target. Ensure this is realistic to achieve, taking into account competition levels and your ability to create the required amount of content in the specified timeframe.
Use tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics to monitor these metrics over time, not just in isolation but also in comparison with previous periods.
Next, consider the context of your data. For example, a drop in traffic could be alarming, or it might coincide with seasonal trends in your industry. Analyze your SEO traffic to understand whether changes are due to Google changes or external factors.
If Google's algorithmic changes affect your SEO performance, you may have to take a different approach. Instead of creating new content, you may have to improve your existing content.
Lastly, don’t forget to evaluate the quality of traffic brought in through SEO. High traffic numbers are welcomed, but if they don’t convert into leads or sales, you may need to refine your SEO strategy.




