What Is Search Engine Positioning?
Search engine positioning is the process of optimizing web pages to rank higher in search results for specific keywords. It is different from general SEO, which focuses on optimizing your website as a whole. Search engine positioning refers to the optimization of specific pages.
By leveraging SEO strategies like:
- Focusing on content quality to provide value and relevance.
- Enhancing page experience to ensure fast loading times and mobile-friendliness.
- Optimizing for SERP features, like featured snippets and local packs.
You can get to the top of the search results and benefit from a higher organic CTR and more traffic to your website.
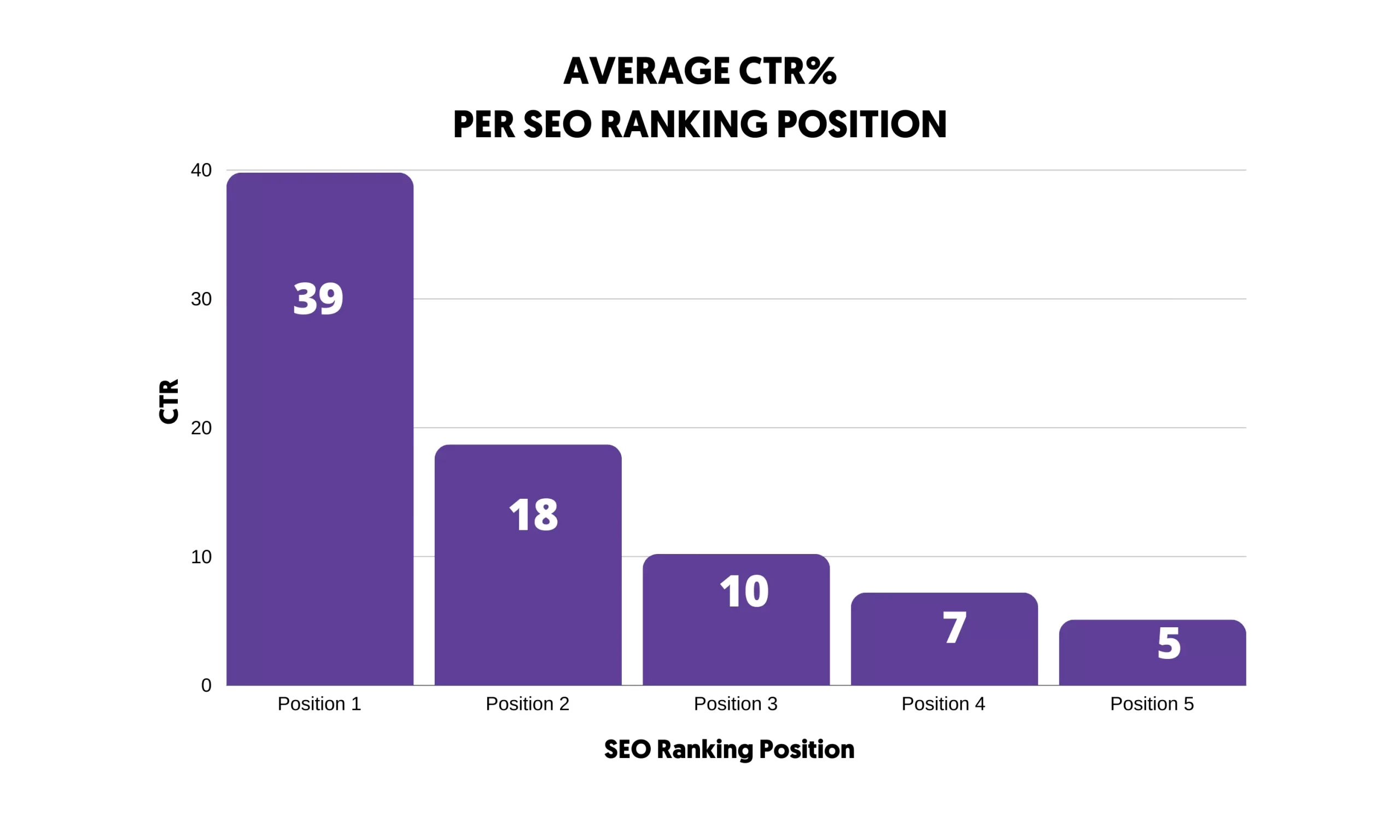
Websites that appear in the top five positions of Google get more than 60% of the clicks.
Why Is Search Engine Positioning Important?
Besides getting more organic traffic, search engine positioning can benefit businesses in several ways:
1. Increased Brand Visibility
The goal of search engine positioning isn't just about being seen; it's about being noticed at the right time. By appearing at the top of the results for specific queries, you ensure your brand is visible when potential customers actively seek information, products, and services related to your offerings.
2. Website Authority and Recognition
Achieving a high rank in search results positions your business as an authority in your niche. Users trust the first few results more, associating top rankings with credibility and expertise.
3. Outrank your competitors
Perhaps the biggest benefit of search engine positioning is comparative advantage. Gaining higher rankings than your competitors allows you to capture the attention of your target audience more effectively.
By positioning your content above theirs, you increase the likelihood of attracting more visitors to your site and position your brand as a leading authority in your niche. This strategic advantage means you have more chances of converting customers before they search for alternative solutions.
What Is The Difference Between Search Engine Positioning And SEO?
Search engine positioning can be thought of as a subset of SEO. It's not something different, but it concentrates more on improving the rankings of individual pages for specific keywords.
Everything that you do to improve the SEO of your website is still valid and needed for search engine positioning to work successfully. Here is an example to help you understand this better.
When doing SEO, you usually follow these steps:
- Perform keyword research to find which keywords to optimize your website.
- Write content to target your primary and secondary keywords.
- Promote your website to get links.
- Work on your technical SEO.
- Improve your page speed and conversions.
With search engine positioning, you concentrate on:
- How do you make the content of a page better than what is already ranking?
- What kind of links do you need for the specific page to improve its position?
- How do you tweak your meta tags to increase CTR?
- For which search features can you optimize your page content?
How Do You Check Your Search Engine Position On Google SERPS?
Before doing any work, you should find out the positions your page appears on Google and for which keywords.
The easiest way to do this is through Google Search Console. If you haven't created an account yet, go to GSC and add your website.
Then click on the Search Results Report (under Performance). To view the results for a specific page, click the +NEW button and select Page.
Enter the URL of the page you want to analyze.
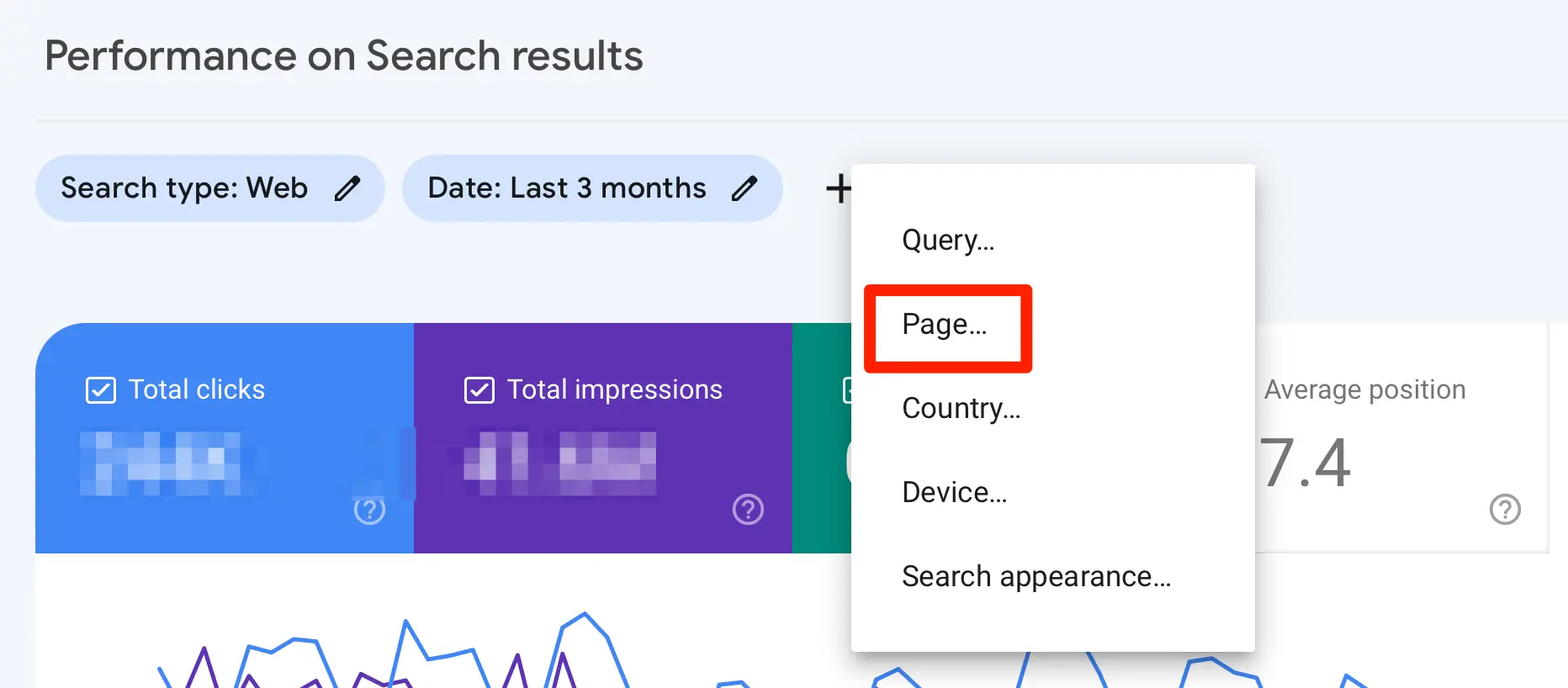
Use the Average Position, Total Impressions, and Total Clicks columns to get an accurate picture of your page's current performance on Google Search.
When you make SEO changes to the page, come back and use the Compare function (under Date) to evaluate your changes between two periods (before and after making changes to the content).
How To Improve Your Search Engine Positioning
Follow these best practices to improve the search engine positioning of a particular page on Google SERPS.
- Create Better Content Than Your Competitors
- Update Existing Content To Match Search Intent
- Optimize Content For SERP Features
- Improve Your Internal Linking
- Optimize Your Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
- Check For Keyword Cannibalization Issues
- Check Your Core Web Vitals Score
- Target Keywords With a Low Difficulty Score
1. Create Better Content Than Your Competitors
The first thing to understand is that to achieve higher rankings on Google for a specific keyword, your content must be better than your competitors. It doesn't have to be perfect, but it should provide more value to users than the existing content.
So, what you should do is visit the top 5 ranking pages and carefully examine their content in terms of:
Topics covered - Write down what topics each article covers. Look at the structure and take note of their H2 and H3 headings. Then compare with your content and spot which topics are included in the top articles, not yours.
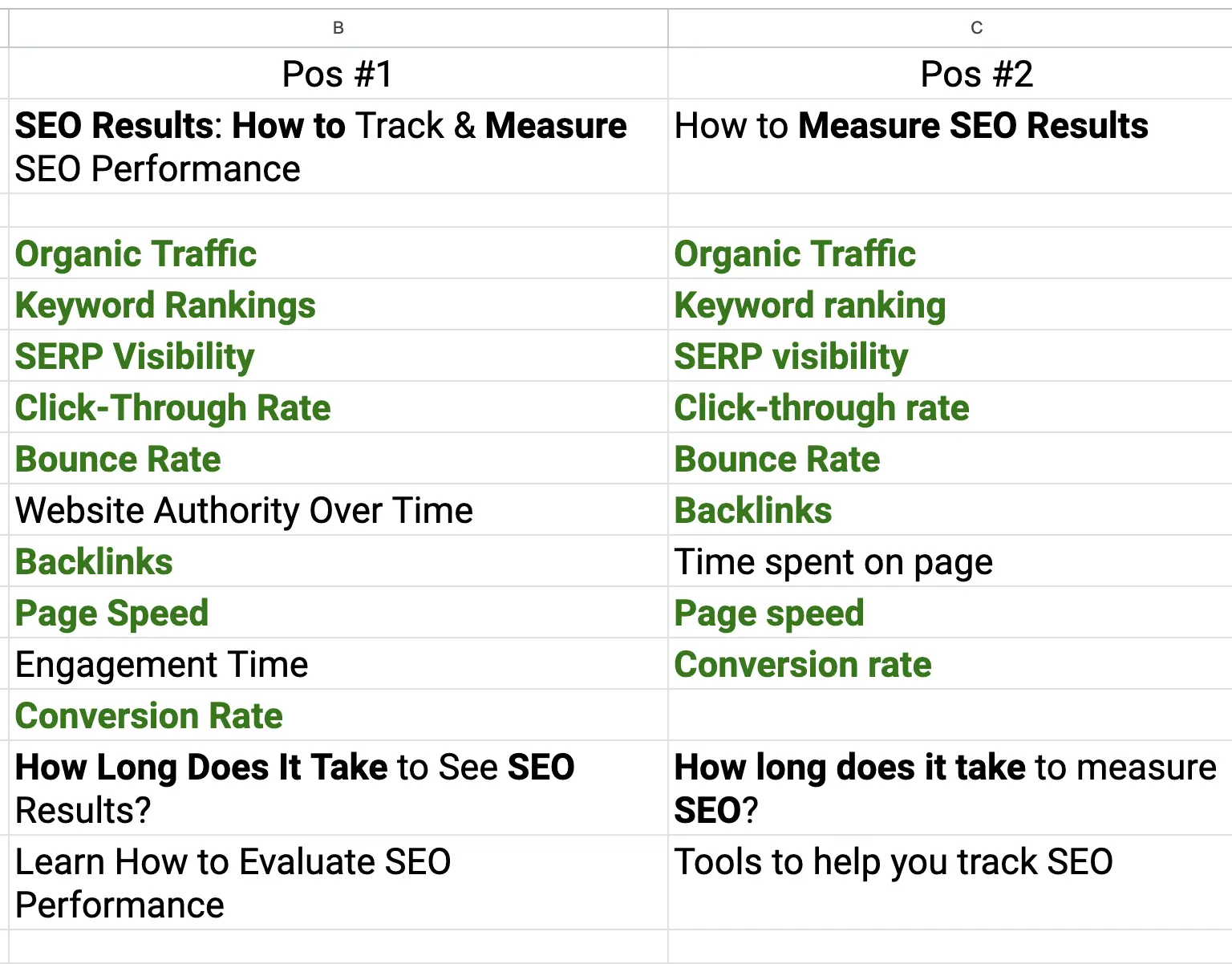
To understand how this process works, consider this example. Go to Google and search for "SEO Results". Follow the above instructions and create the article outlines. You'll end up with something similar to the screenshot below.
Notice how similar the topics for both articles are. If you were to improve the search engine positioning for the keyword "SEO Results", you should definitely include these topics in your content.
Besides looking at the topics, you should also check the length of the articles, the number and type of images, and other elements they might include, like tables, videos, or FAQ sections.
To avoid confusion, your goal is not to make a copy of the existing articles or write the same content using different words but to take their structure as the basis for your content, improve it, and provide different/better advice for the different sections.
2. Update Existing Content To Match Search Intent
The next step is to ensure that your content matches the search intent. By search intent, we mean the user's objective when searching for a keyword on Google.
In addition to what you did in step 1 (which is very important for matching content with the user intent), you should perform the following checks:
- Update statistics and data to reflect the most current research and trends.
- Refresh your images and visuals. If you use stock images, consider replacing them with original images or visuals you create.
- Check for broken links (either internal or external).
- If your content hasn't been updated for a long time, consider rewriting some parts. You can safely use AI for this task (like our AI paragraph rewriter) to give your own work a fresh perspective.
When making several changes to an article, update the "Last Update Date" (if missing from your pages, consider adding this on the top of the page below the main title) to inform users the article contains fresh data.
In addition, use the "Request Indexing" feature of Google Search Console to ask Google to recrawl your content, speeding up the indexing process.
3. Optimize Content For SERP Features
Over the years, Google has enriched the presentation of search results by adding several features like featured snippets, rich results, local packs, knowledge graphs, carousels, and others.
Web pages that appear in these features get more visibility and higher CTRs.
As part of your review process, you should check what Google SERP features are suitable for your content and make the necessary changes to target them. The ones applicable for almost all types of content are:
Featured Snippets
Google featured snippets appear on top of the organic listings and can have different forms (paragraphs, lists, videos, tables). Here is an example of a list featured snippet.
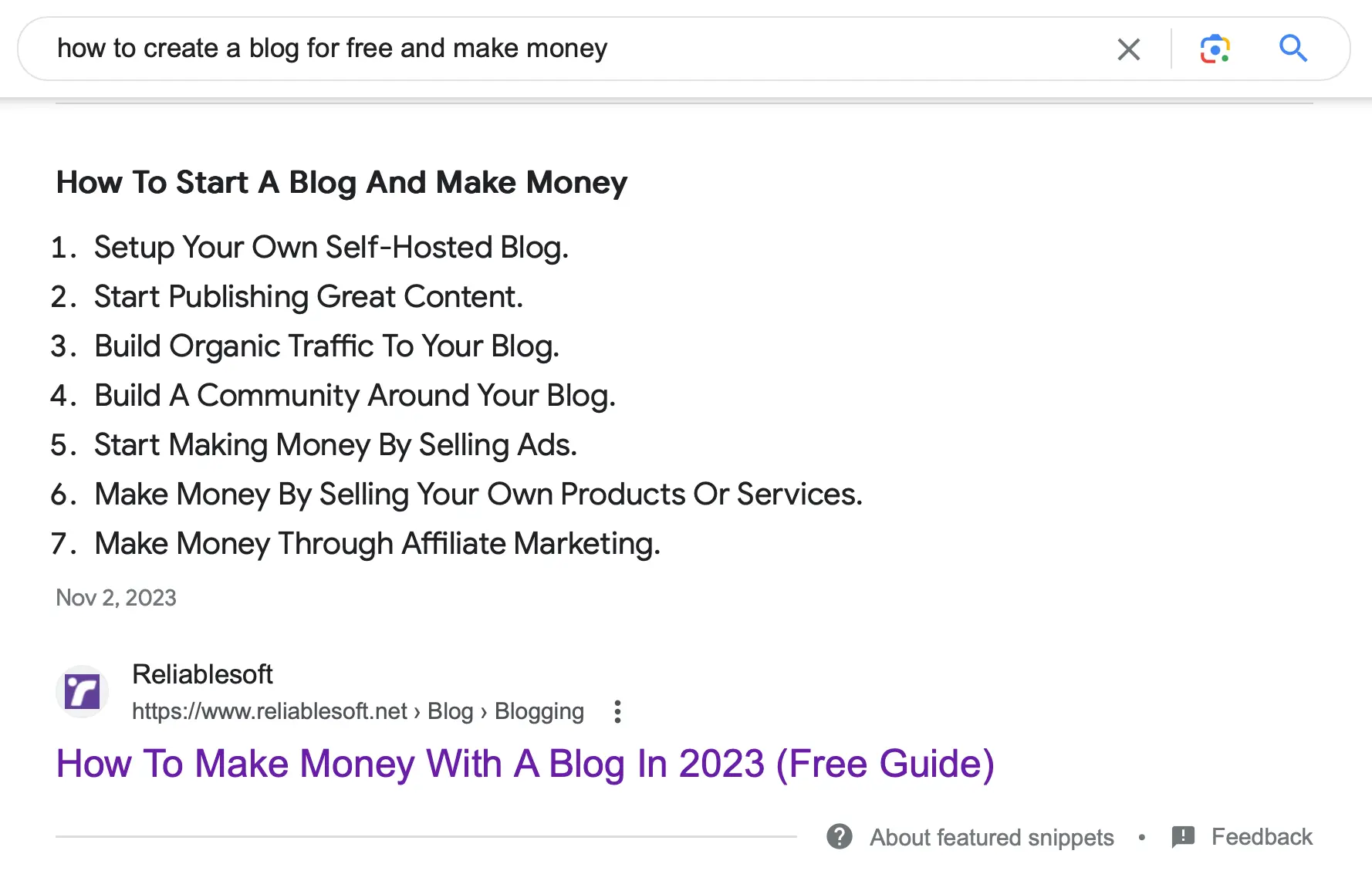
Optimizing for featured snippets usually involves reformatting your content to answer user questions in a formal way and using concise and clear headings.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets, or rich results, add graphical elements like images and review stars to normal search snippets or present data in a completely different format, like carousels.
Here is an example of popular rich snippet types.
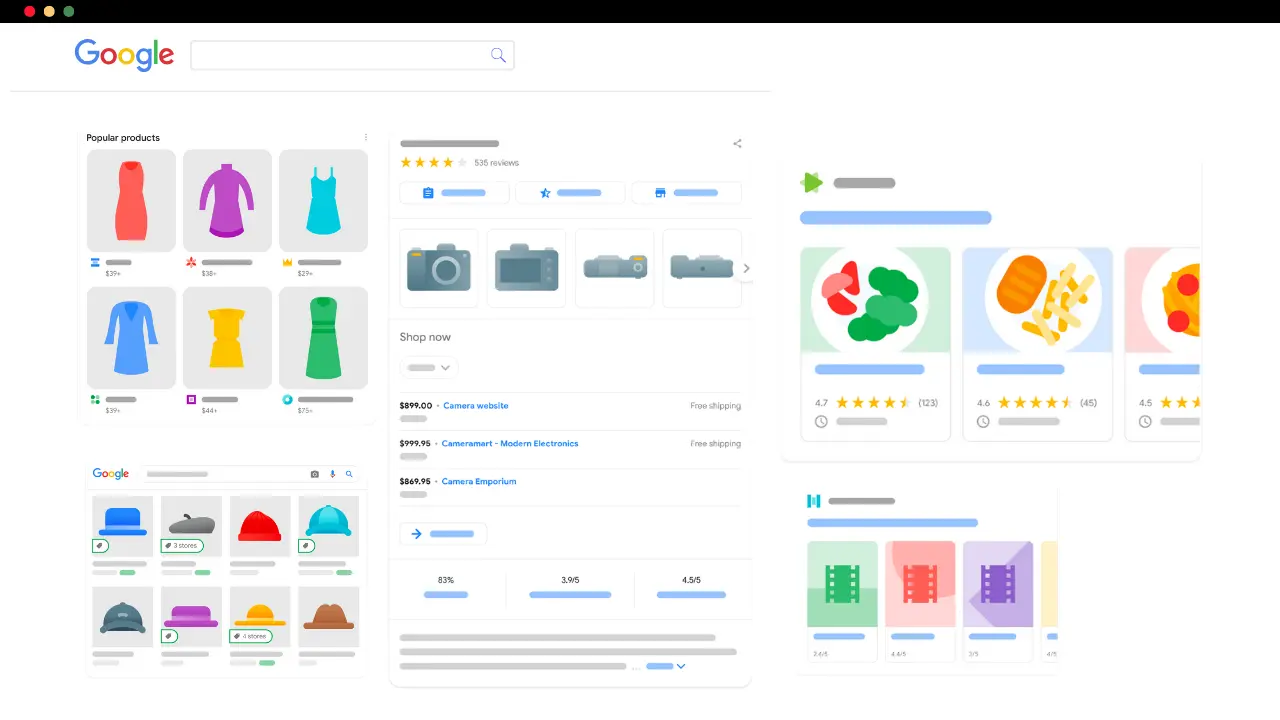
To gain rich snippets, you must add the relevant schema markup to your content and satisfy Google content quality guidelines.
4. Improve Your Internal Linking
Another technique for improving the rankings of a specific page is internal linking. Internal links are links that point to pages within the same site. Good internal links help users find more relevant content, and search engines better discover and understand a site's structure.
Here is what to do:
- Go to Google and use the site:operator ["site:yourdomain.com keyword"] to find pages on your domain relevant to the page you want to enforce its rankings on.
- Edit the page to add an internal link using descriptive anchor text that matches the target page's content.
For instance, if linking to a page about "SEO Best Practices," the anchor text could simply be "SEO best practices," making it straightforward and relevant.
5. Optimize Your Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Next on the list is working on your title tags and meta descriptions.
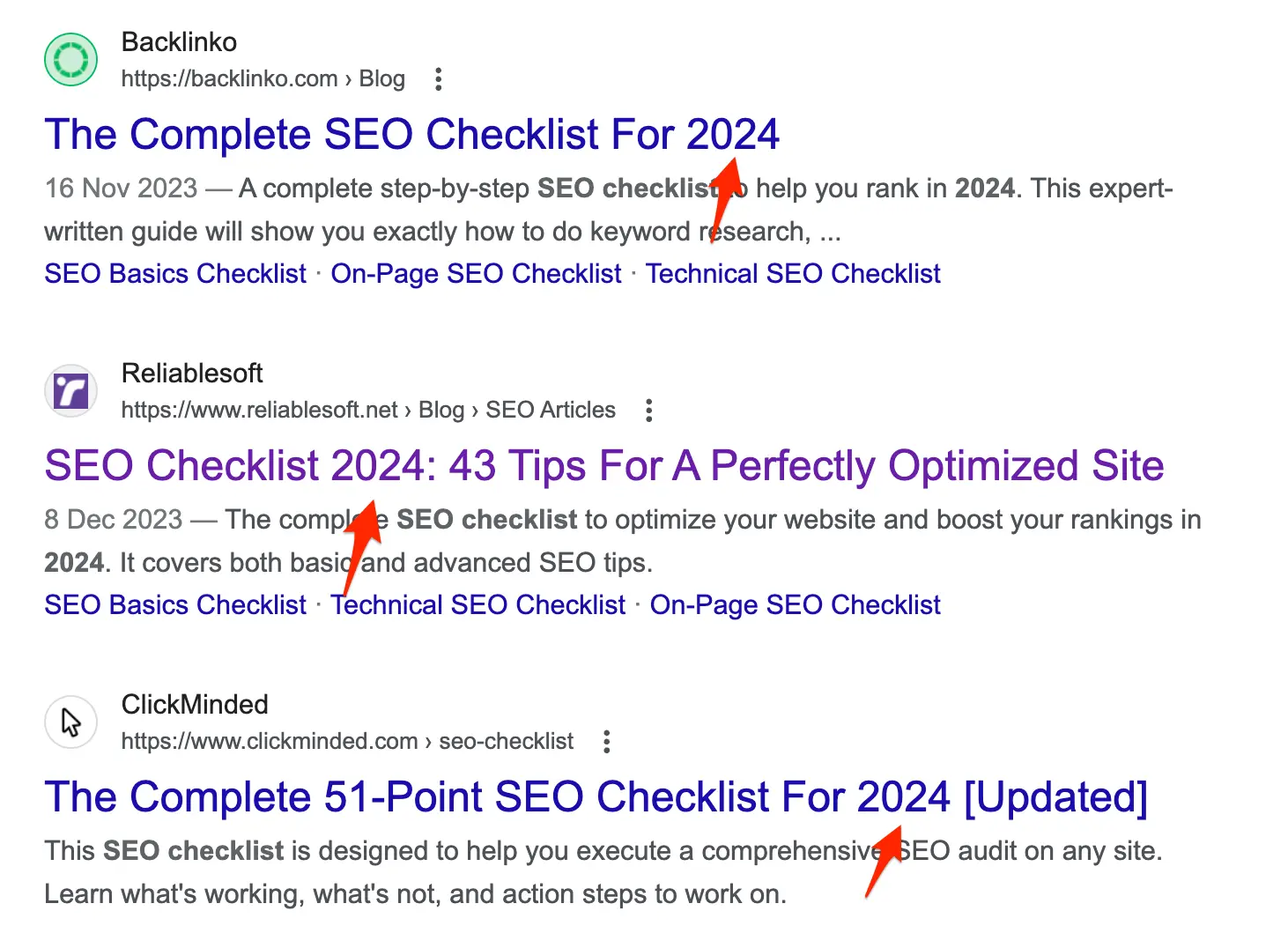
The title tag is shown on the search results and can influence your ranking position and CTR. Look at the titles in the first positions of Google and spot any patterns.
For example, if you notice that all pages include the date in the title to make it relevant, you can do the same (provided that you have changed your content to reflect and support what is suggested in the title).
Don't forget the basic principles of writing good titles, like using keywords and keeping the length to 60 characters.
The meta description is also an element used (sometimes) with your search snippet. Writing a good meta description involves using your keywords and describing in less than 160 words what the page is about and why users should visit.
Here is an example from one of your posts.
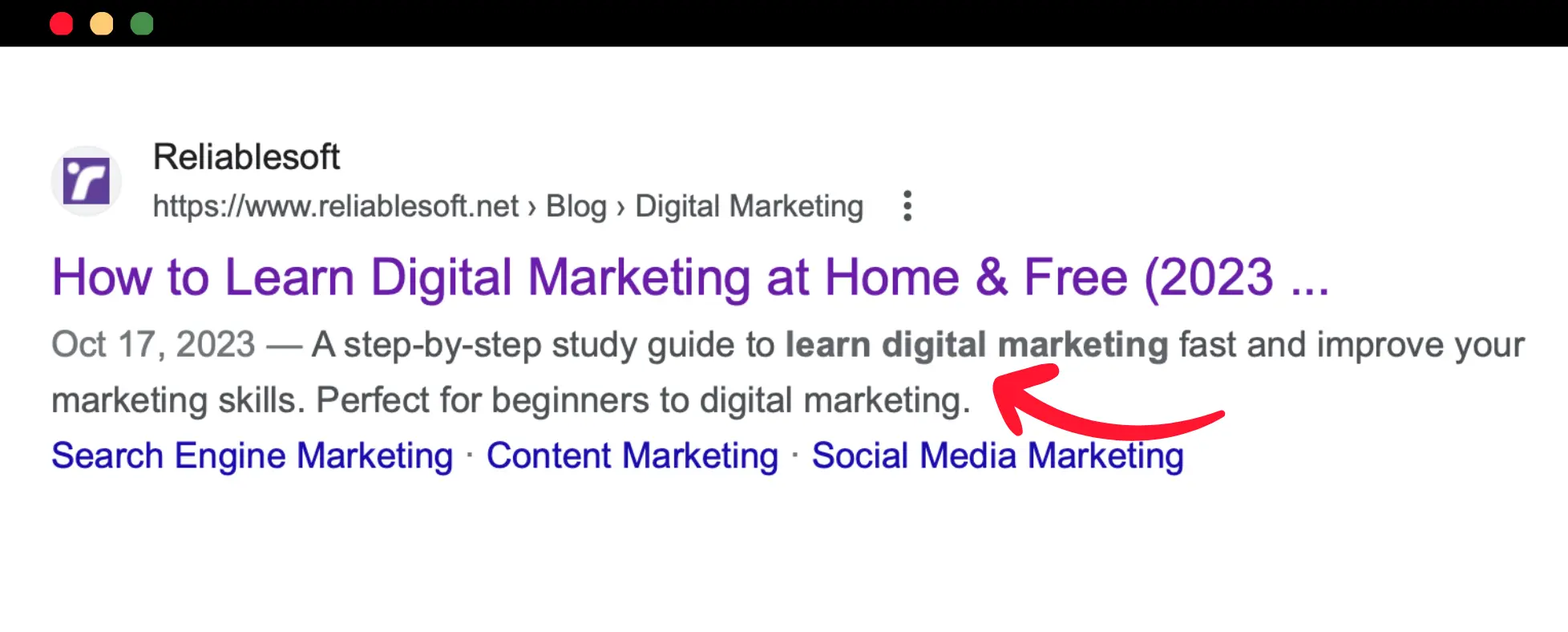
You can safely use AI to help you with crafting engaging meta descriptions. Our meta description generator is free and can give you ideas on creating SEO-friendly meta descriptions based on your content.
6. Check For Keyword Cannibalization Issues
A possible issue that may prevent your web pages from ranking on Google is keyword cannibalization. Keyword cannibalization is when you have more than one page targeting the same keyword on your site.
This isn't good because it confuses search engines as to which page to rank, negatively affecting the rankings of both pages.
What you should do is go through your content to identify if you have different pages targeting exactly the same keywords. You can do this by examining your sitemap, using a tool or the site operator on Google (like the example below).
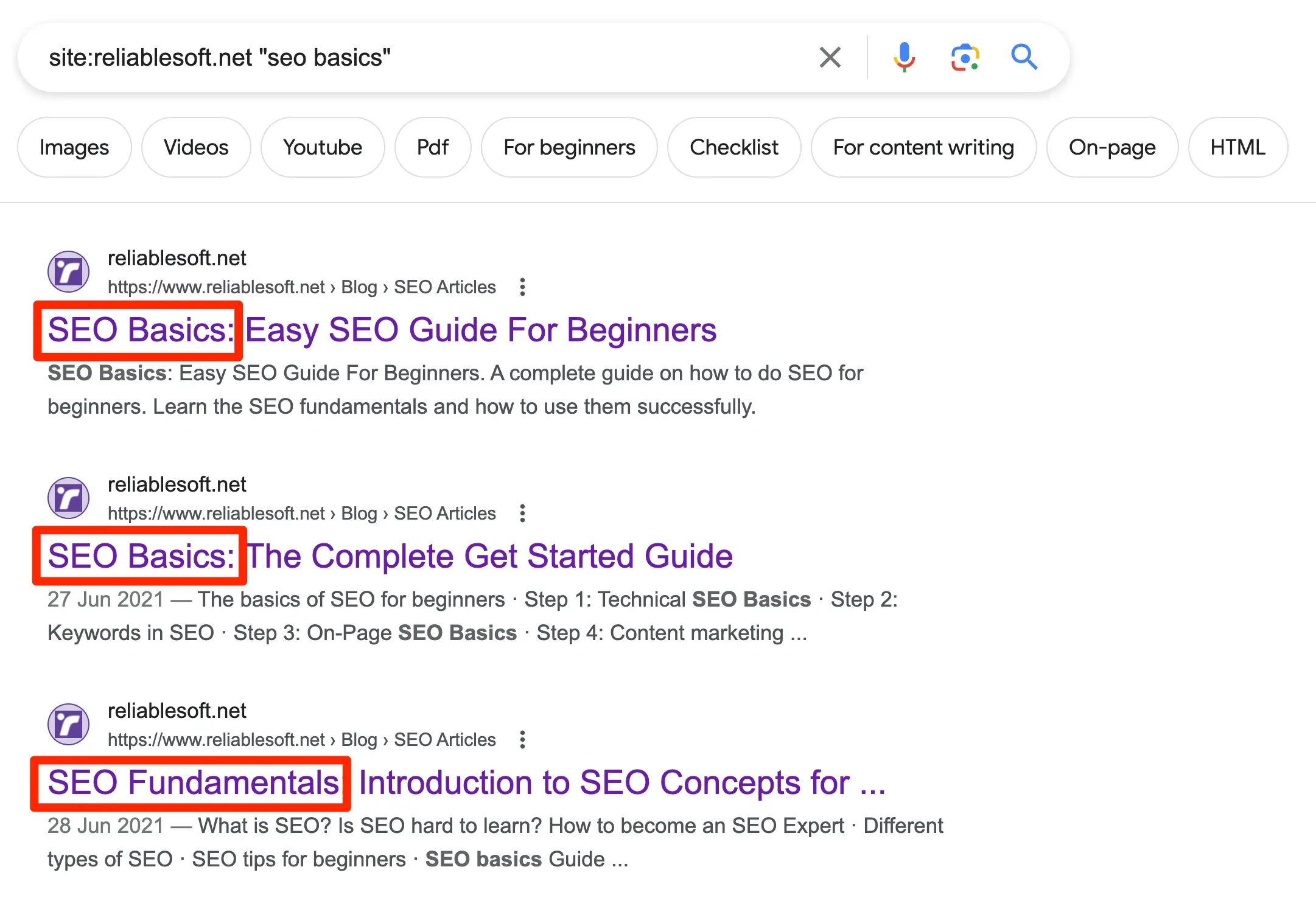
Then you should fix the cannibalized pages by:
- Merging the pages and redirecting the one to the other.
- Setting a canonical tag.
- No-indexing duplicating pages.
Don't worry if this sounds confusing. You can follow the instructions in our keyword cannibalization guide and quickly solve any issues.
7. Check Your Core Web Vitals Score
Another factor that affects your ability to rank higher in the results and user experience is website speed. Search engines and users like websites that load fast, and the metrics to use for this purpose are core web vitals.
Check the Core Web Vitals report in the Google search console to see any errors, and then use Page Speed Insights to analyze the performance of individual pages.
Your goal is to get to these numbers:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) –2.5 sec or less
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – 0.1 or less
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – 200 ms or less
Compressing your images and minifying your CSS and JS files is, on many occasions, all you need to do to get a good web vital score. If making technical changes to your site is not something you feel comfortable with, assign this task to a developer. It will make your website more usable to users and generate many other benefits.
8. Target Keywords With a Low Difficulty Score
The last step for improving your search engine positioning is to evaluate your keyword strategy. It is likely that during keyword research, you identified keywords that have a high search volume and commercial or transactional intent.
Depending on your website's domain authority and content, this might not be your best strategy. Competitive keywords are very difficult to target, especially if big brands and well-known websites occupy the top rankings.
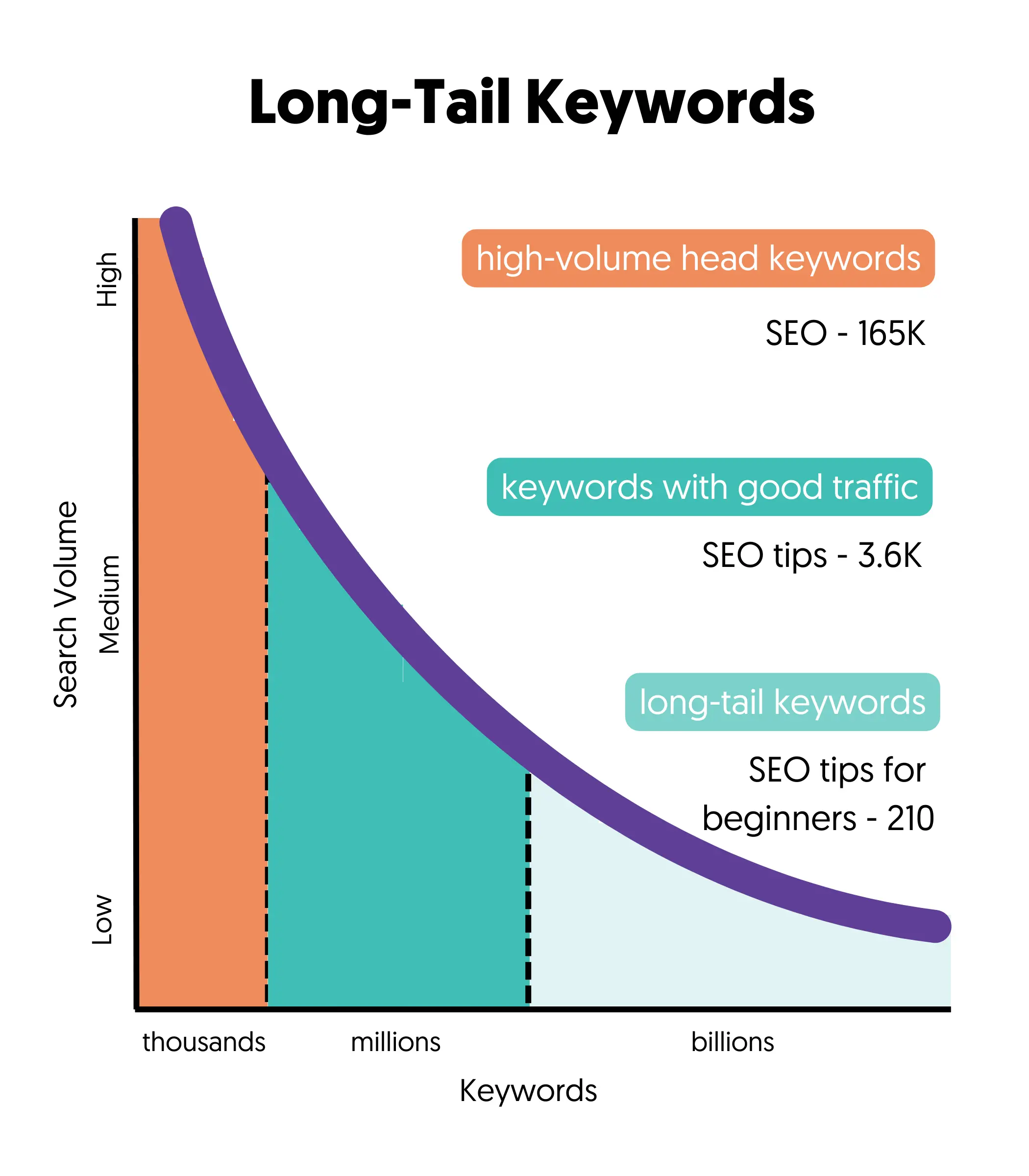
Instead, you should change your SEO strategy and go after keywords with a low difficulty score. These are usually long-tail keywords highly relevant to your products or services but have a low monthly search volume.
The drawback of this approach is that to get to high monthly traffic levels, you'll have to achieve top rankings for several long-tail keywords. It's not impossible, but it will require much effort and patience.
Here is an example of how the search volume changes for high-volume head keywords to low-volume long-tail keywords.
Key Learnings
Search engine positioning is a critical part of SEO. Achieving high rankings for your primary and secondary keywords will bring targeted traffic to your website, translating to more conversions and user engagement.
The key part of the process is to make an effort to keep your content relevant to the user's search intent and fresh. This combination will increase your chances of maintaining your rankings in the long term.



