- What is Keyword Difficulty?
- Why is Keyword Difficulty an Important Metric?
- How to Estimate How Difficult Is To Rank For A Keyword
- How to Check Keyword Difficulty With A Tool
- What Is a Good Keyword Difficulty (KD) Score For a Keyword?
- Long-Tail Keywords and Keyword Difficulty
- Learn More About Keywords And SEO
What is Keyword Difficulty?
Keyword difficulty (KD) is a common SEO metric that estimates how difficult it may be to rank on the first page of Google for a specific keyword or phrase. In most tools, this metric is ranked on a score of 0 to 100. The higher the number, the harder the ranking will be.
Various factors help determine keyword difficulty in SEO, from the website's domain authority to the number of referring domains (backlinks) and content quality on competing sites.
Why is Keyword Difficulty an Important Metric?
While doing keyword research, finding relevant terms with a decent search volume is simple enough.
Determining how easy it will be to rank for them is much harder.
If you consistently target keywords with a high “keyword difficulty” score, then you’re unlikely to appear on the top of Google. This means wasting time and resources on content that doesn’t deliver the right results.
Alternatively, if you choose keywords that are too easy to rank for, you might miss out on valuable opportunities to earn traffic and conversions.
Measuring keyword difficulty helps you find the perfect balance between overly competitive keywords and terms that are easier to rank for but have a decent search volume.
How to Estimate How Difficult Is To Rank For A Keyword
Here is how to determine your chances of ranking for a keyword:
- Analyze Your Competitors
- Check Search Intent
- Evaluate Content Depth and Quality
- Check the Number of Backlinks
1. Analyze Your Competitors
The starting point for measuring keyword difficulty is to find out who's competing for the particular keyword. If the websites ranking in the top position of Google have low authority, ranking for that keyword will be easier.
Go to Google, search for your target keyword, and start analyzing the top-ranking pages using the following factors:
Assess each page’s brand authority. In other words, how well-known is the site? It’s unlikely you’ll be able to outperform big-known brands or well-known sites (like government domains) when attempting to rank for a keyword.
Check the rest of their content. If a site has a lot of content connected to a specific topic, it will generally be harder to outperform that site in the search engines for a related keyword.
Analyze their domain authority and rankings. Use your preferred tool and find out their domain authority, which other keywords they are ranking for, and how many pages they have in Google's index.
For example, if you want to rank for the keyword "kitchen knives," you'll notice that super authoritative websites occupy the results with millions of traffic and links.
This is a strong signal that unless you have a website of similar size and authority, it is impossible to rank high for this keyword. In practice, this means that you should look for keywords that are realistic to target.
Remember, when accessing your competitors, always compare their performance and metrics with your website.
2. Check Search Intent
Next, it’s important to consider why people search for a specific term. In other words, what do they want to get out of the content they’re searching for?
Search intent determines why someone is typing a query into Google or any other search engine. Satisfying “search intent” is the best way to ensure you rank higher on Google. You increase your chances of ranking if you can address a customer’s needs more effectively than your competitors.
There are four different types of keyword intent:
- Informational: Users want educational insights into a topic.
- Commercial: People research options when making a purchasing decision.
- Transactional: Someone wants to buy something or complete an action.
- Navigational: The searcher wants to find a specific page (such as a brand’s website or product page).
Look at the top results again and the type of content they provide. Establish what each result tries to do (drive a sale, provide insights, etc.), and ask whether you can create something more valuable.
In our example, "kitchen knives" presents articles comparing and listing the best options. So, if you decide to target this keyword, your content should be a list of products users can buy.
If you're not sure what the intent of the user is, look at the Intent column in your keyword research tool. You can also use the filters to find keywords that align with your business goals.

3. Evaluate Content Depth and Quality
While many factors can influence keyword difficulty and how challenging it might be to rank, Google always prioritizes content that delivers genuine value.
Quality content is content that’s relevant, helpful, and trustworthy.
When assessing the top-ranking pages on Google for a specific term, ask yourself how valuable each page is to its intended audience.
Though famous methods like the Skyscraper technique have prompted many content marketers to believe longer, more detailed articles will rank higher, that’s not always the case.
Making an article longer doesn’t necessarily improve its quality unless you can offer something the other top-ranking pages don’t.
When browsing through ranking pieces, ask:
- Does this article provide accurate, up-to-date information?
- Is the piece written by a subject matter expert with clear authority?
- Is there unique information available?
- Is the content well-written and grammatically correct?
- How easy is it to read the content on mobile (based on formatting and design)?
If you can’t deliver more value to your audience than the top-ranking pages, you won’t rise above them in the search results.
4. Check the Number of Backlinks
SEO tools like Ahrefs frequently focus on the number of domains linking back to a website when evaluating domain authority.
Backlinks validate a site or page, demonstrating that it offers valuable insights and information. Search engine algorithms use this validation to determine the ranking position of a page for a particular search query.
The more backlinks a website has, the harder it will be to out-perform them. A backlink checker tool is the easiest way to determine how many backlinks point to a website or page.
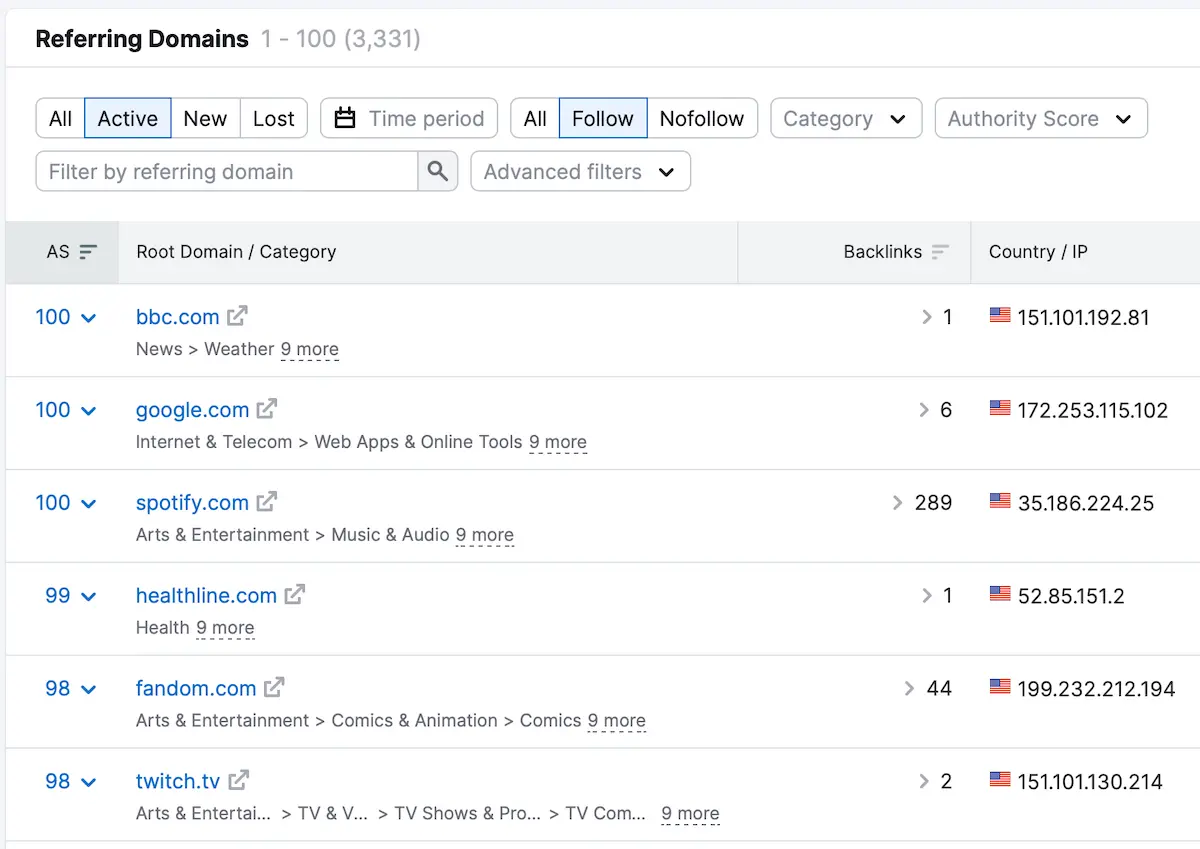
You can see the authority of a domain and the number of “do follow” and nofollow links.
If a page ranking number 1 for a specific keyword has many "do follow" links from high-authority websites, your chances of outperforming them are minimized.
How to Check Keyword Difficulty With A Tool
All popular SEO platforms offer free tools for checking the keyword difficulty of a keyword.
How to Measure Keyword Difficulty With Semrush
Semrush analyzes the Google SERPs to find which websites rank in the top 10 positions.
The tool then examines each URL to look at the SERP-related qualities for each keyword, the median number of referring domains for the URL, nofollow/dofollow links, and URL authority score.
To determine a keyword’s difficulty score, go to Semrush Keyword Overview and type a term into the search bar.
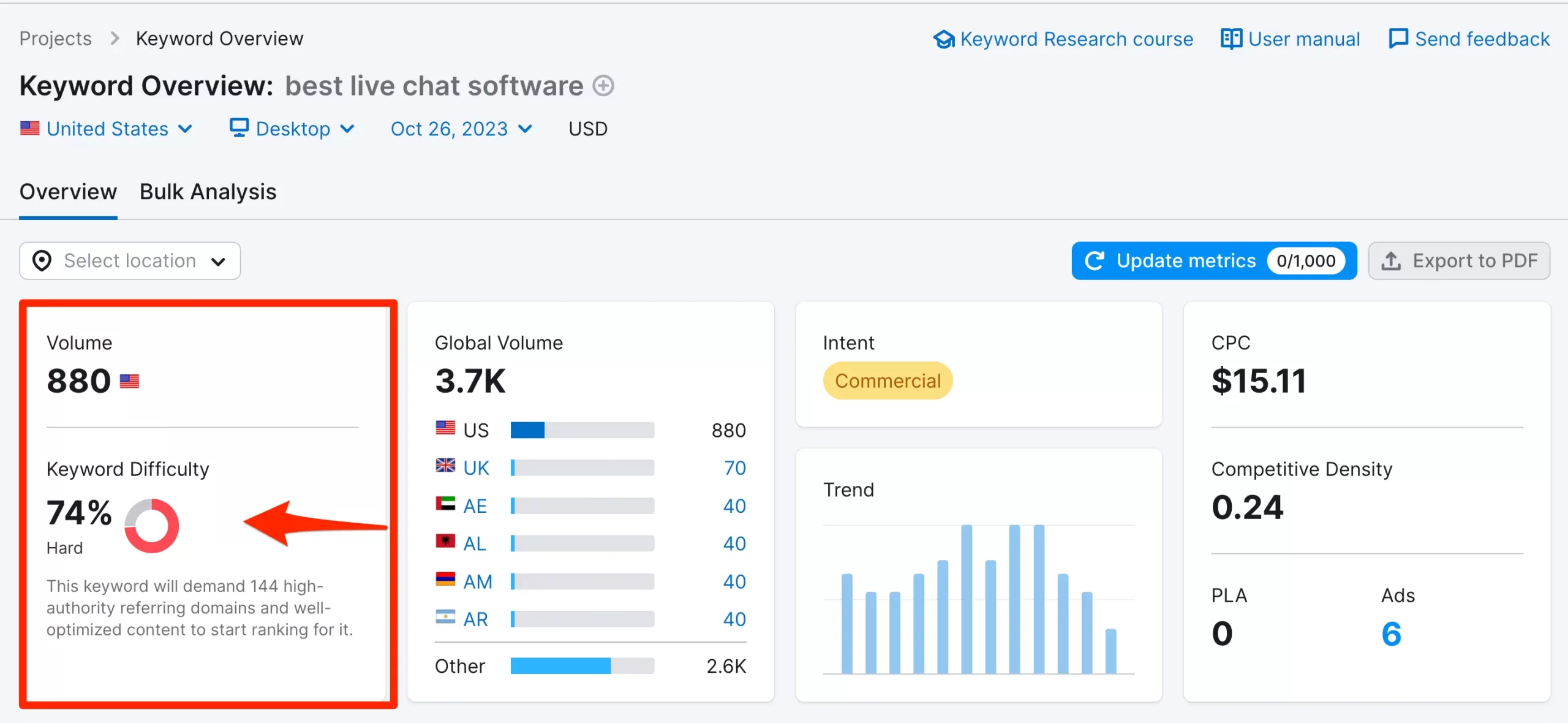
The keyword difficulty will appear in the KD% column alongside a term’s search volume and other metrics.
How to Measure Keyword Difficulty With Ahrefs
Ahrefs uses a similar method to Semrush to determine keyword difficulty. The system pulls the top 10 ranking pages for a keyword and looks at the number of referring domains and backlinks connected to those pages.
To discover a keyword’s difficulty using Ahrefs, go to the free keyword difficulty checker and type a term you want to check.
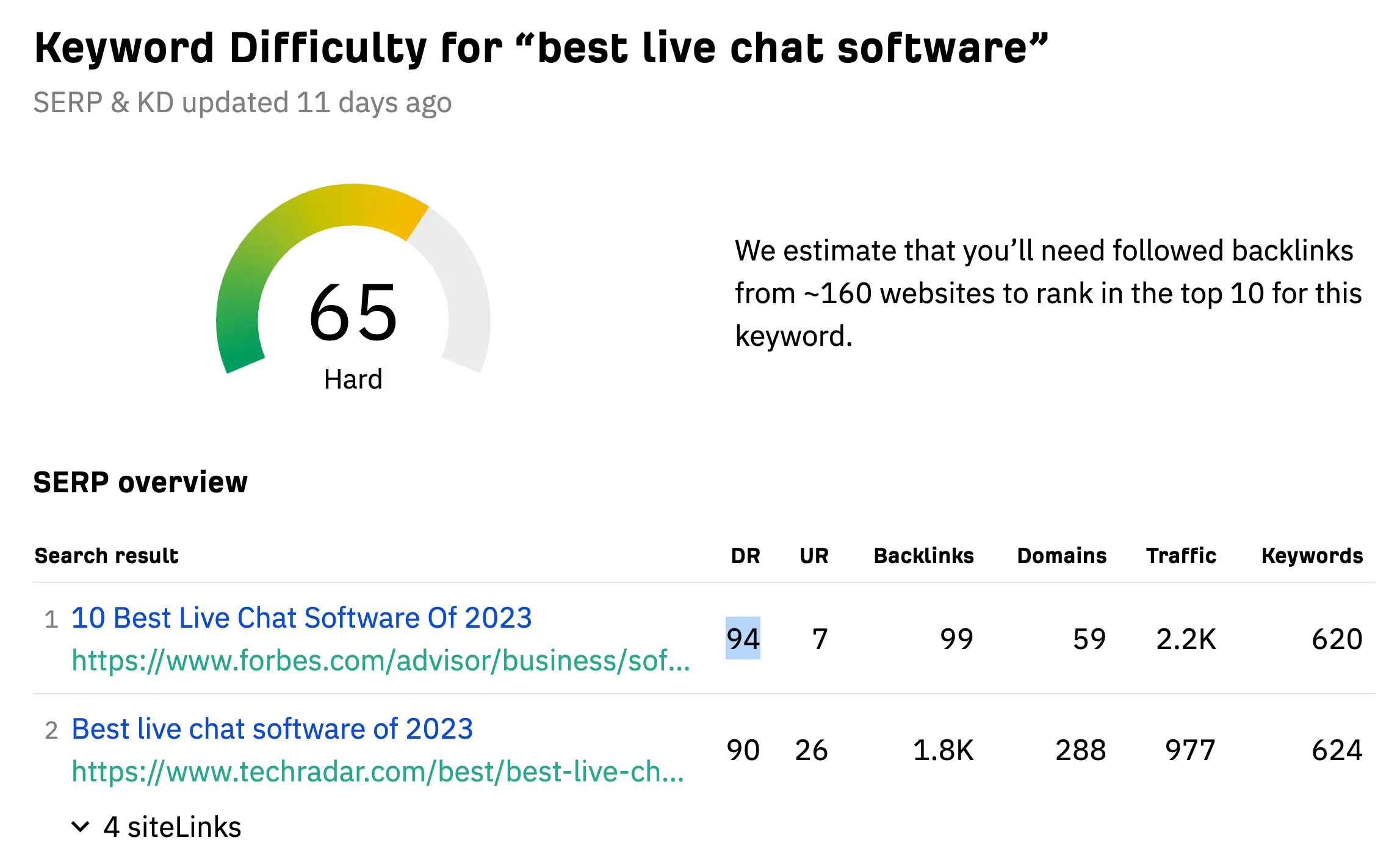
Alongside the KD score, Ahrefs gives you an estimate of how many followed backlinks you’ll need to rank in the top positions of Google for the particular keyword.
How to Measure Keyword Difficulty With MOZ
To determine the KD of a keyword using MOZ for free, you need to go to the Moz Keyword Explorer, and create a free account.
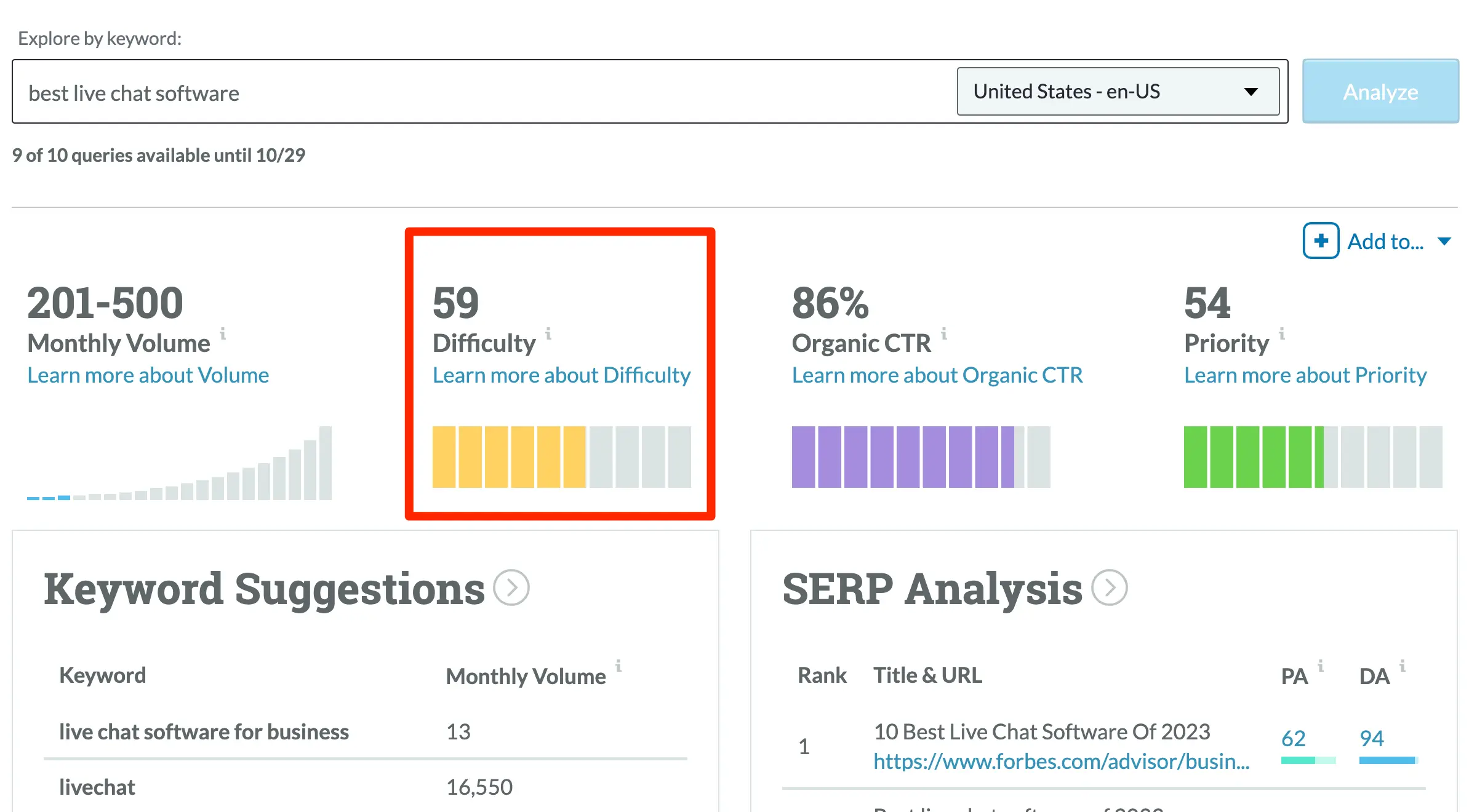
What Is the Problem With The KD Score of Tools?
Keyword research tools provide a general insight into ranking potential through keyword difficulty scores. However, these tools all use different methods to evaluate the ranking potential of a keyword. This means relying on the information available through these tools alone isn’t a good idea.
In the example below, we’ve analyzed the KD score of the “best live chat software” keyword.
Each tool showed a different score and estimate of what it takes to appear in the top positions of Google for that keyword.
| Tool | KD Score |
|---|---|
| Semrush | 74% |
| Ahrefs | 65% |
| Moz | 59% |
That’s a problem and why it’s crucial to do your own research to ensure you fully understand how much work you’ll need to put into ranking for your term.
What Is a Good Keyword Difficulty (KD) Score For a Keyword?
A good keyword difficulty score depends on your website's authority and how it compares with other websites targeting the same keyword.
Your website's authority combines your domain authority and topical authority.
If Google considers your website authoritative about a topic, ranking for keywords with a high difficulty score will be easier.
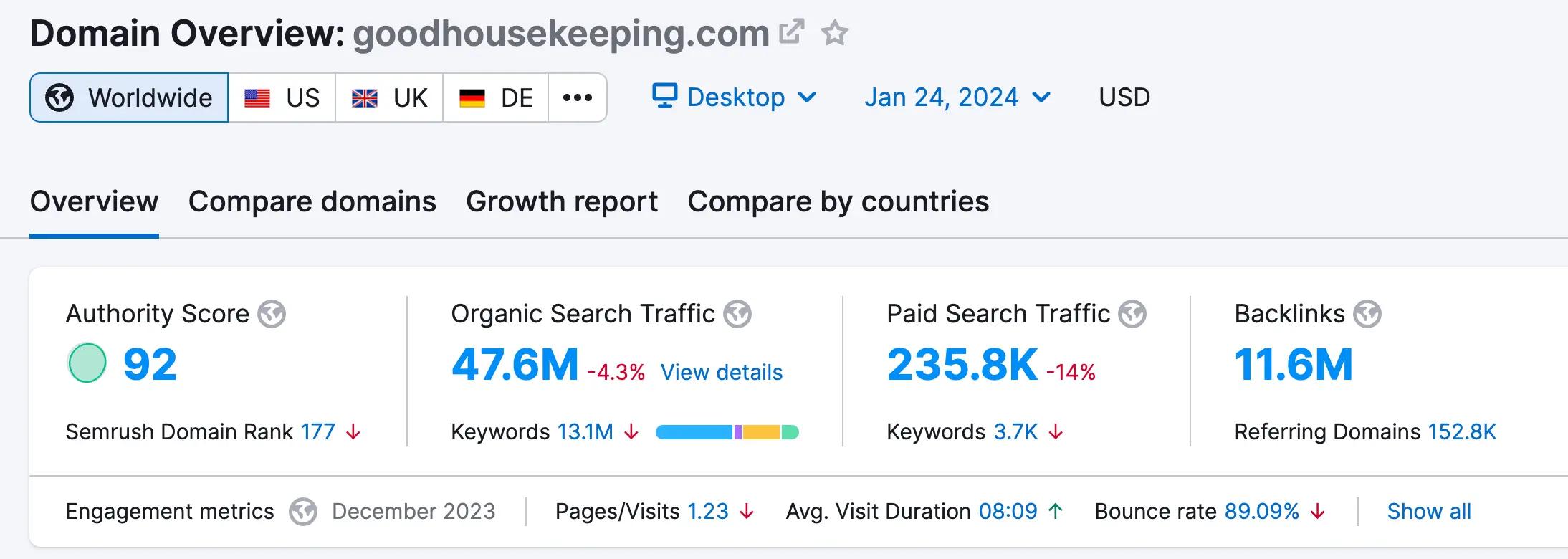
Here is an example of what we mean by domain authority. Forbes has a domain authority of 94 (according to Ahrefs). In practice, this means that any article Forbes publishes that is high-quality and satisfies the search intent has many chances of ranking on the first page of Google. This is happening because it has a very high domain score.
Here is an example of what we mean by topical authority. Goodhousekeeping.com already ranks for several keywords related to "knives". Any articles they publish related to "knives' are likely to rank on top of Google, regardless of the KD score.
So, when accessing the KD of a keyword as good or bad, always compare your website with the websites you'll have to compete with. Use the keyword difficulty score provided by tools and all the information you’ve gathered about the top-ranking pages to figure out if the particular keyword is a realistic target for your SEO strategy.
Long-Tail Keywords and Keyword Difficulty
Regardless of your industry, one way to find keywords you can actually rank for is to look for long-tail keywords.
Long-tail keywords usually have a lower search volume than head keywords, but they can be much easier to rank for. Targeting long-tail keywords also means you can focus on attracting a more specific audience.
Once you’ve pinpointed potential long-tail keywords you may be able to rank for, go through the same process outlined above again to ensure these terms are worth your time.
You may have to publish many articles targeting long-tail keywords to get the desired traffic levels, but sometimes, it's the only effective way to get organic traffic for your chosen topics.



