What Is Image SEO?
Image SEO is the process of optimizing your images for greater visibility in search engines.
There are several benefits from using SEO optimized images in your content.
- It’s another easy way to enforce your SEO by giving search engines the right signals about your content.
- Your images can rank higher in Google Image Search and get more traffic to your website.
- Your content will be eligible to show in Google Discover.
- Your readers are likelier to share a page with image(s) on social media and gain indirect SEO benefits.
- They enhance the user experience by making content easier to read.

12 Important Image SEO Tips
Follow these best practices to optimize your images for SEO:
- Choose The Right Image Format
- Use Descriptive Filenames
- Set The Max-Image-Preview Tag
- Optimize For Speed
- Use Responsive Images
- Write SEO-Friendly Alt Text
- Customize Image Titles And Captions
- Check Your Page Titles And Meta Descriptions Tags
- Add Structured Data
- Use an Image Sitemap
- Optimize Image Placement
- Add Open Graph Meta Tags
1. Choose The Right Image Format
When using images on your website, there are several image formats to choose from. To keep things simple, use these types:
- JPEG: This is the most commonly used format, ideal for photographs.
- PNG: Use this if you want high-quality images and images with a transparent background.
- SVG: Suitable for icons, logos, or animated elements. This format is vector-based, meaning it's resolution-independent and scales without losing quality, making it perfect for high-definition displays and responsive designs.
- WebP: Use WebP for images that require high quality with smaller file sizes. WebP typically creates smaller files than JPEG and PNG, contributing to faster page load times.
For best results in terms of quality and compression, export your images in PNG and use Squoosh to convert them to WebP.
2. Use Descriptive Filenames
The name of the image is the first thing to check before even uploading to your website. Image Filenames should be informative and accurately describe the image.
When you purchase an image or take a photo using your phone, they usually have names like DC0001IMG.jpg (or similar) that do not make any sense.
Instead, you should rename your image to a more meaningful name, i.e., “iphone-16-rear-view.jpg” or “link-building-guidelines.png.”
In other words, the filename should describe the image in the least number of words possible.
3. Set The Max-Image-Preview Tag
For your images to be eligible to show on Google Discover, the minimum width should be 1200 px, and you should also set the max-image-preview:large robots meta tag.
This instructs search engines to show large image previews of an image in Google search results, Google Image, Google Assistant, Google SGE, and other products.

4. Optimize For Speed
As a general rule of thumb, the smaller the image size (in bytes), the better. Large images take longer to load, negatively impacting the user experience, especially for mobile users.
A good practice is to use image optimization tools that can reduce the file size of an image without losing quality.
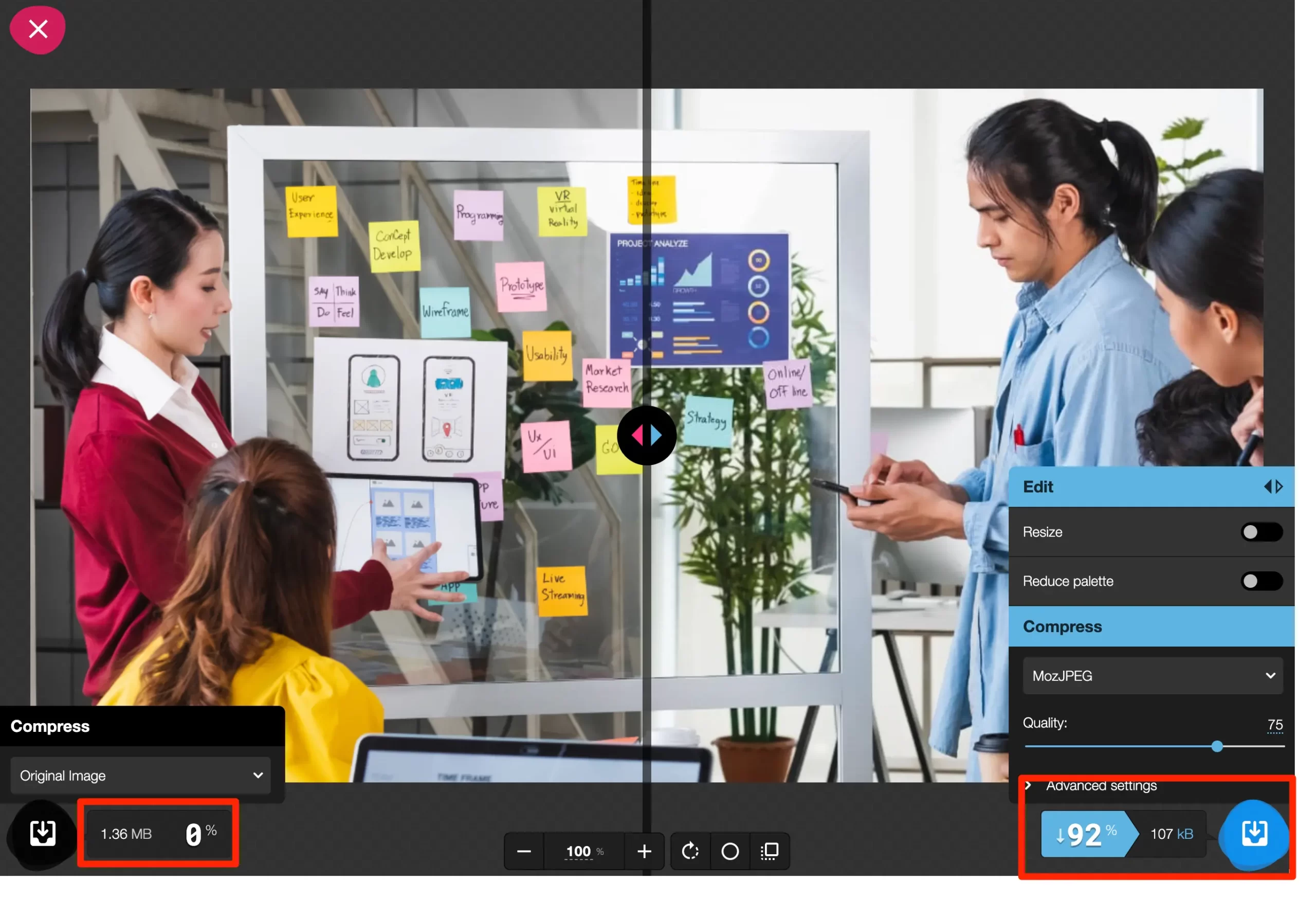
If you use PNG or JPEG, use imageoptim to optimize their size considerably. If you use WebP, use Squoosh. Both tools are free and optimize images without losing quality. Here is an example of a PNG image reduced to 107KB from 1.3 MB when converted to WebP.
5. Use Responsive Images
Responsive images adapt to the size of the viewer's screen, ensuring that your images look good on all devices while optimizing loading times.
WordPress natively supports responsive images. This means that uploading an image automatically creates several images in different sizes and automatically fetches those to users depending on their device.
If you are not on WordPress, you can implement responsive images using CSS. This guide can help you get started: use the srcset attribute in your image tags to define multiple sizes of the same image, allowing the browser to choose the best one to load based on the user's screen size.

Also, use the sizes attribute to indicate the width and height of the image for different screen resolutions. This is important for preventing Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) issues, part of core web vitals.
Here is an example of how responsive images work:
You upload a big image (1000x600) to your post. The file size of the image is 100KB. When users on mobile view your page, they won’t have to download this image and waste their bandwidth, but WordPress will automatically show users an image that is 320x200 in size and only 15KB.
The result is less bandwidth and faster loading speeds.
6. Write SEO-Friendly Alt Text
Alt-text is the most critical element for image SEO.
Search engine crawlers are not so good at understanding what an image is about. And although they are getting better year by year in image recognition, they still need the help of ALT Text.
Why is ALT Text important?
Alt-text is used to describe an image's contents to bots and as a guide for people who are visually impaired and cannot see the image.
When writing ALT text for your images, have the following in mind:
- Don’t use dashes in your alt text. Write normally and try to describe in a few words what the image is about.
- Use keywords relevant to the page's content but don’t overdo it.
- Keep your alt text short and to the point.
- Some people (including me) tend to use the post title as the alt text of the featured image, and although this is not the most efficient way, it is acceptable and common practice.
Here is an example of good and bad alt text.

7. Customize Image Titles And Captions
Besides the ALT text, search engines can use the image title and caption to understand the subject matter of your image better, so it is necessary to provide them with these values. The image title can have the same value as the Alt text.
For the image caption, use text that describes the image to users who see it. Keep it short and descriptive.
8. Check Your Page Titles And Meta Descriptions Tags
Page titles and meta descriptions can indirectly affect your image SEO. If you want images embedded on a page to rank high in the search results, your page titles and meta description should closely relate to the image content.
When your page ranks higher, images from that page are more likely to appear in image searches related to your content.
9. Add Structured Data
Schemas help search engines understand the content of a page better. In the case of images, you can implement the image schema by adding the relevant structured data markup on your pages.
Google can then display your images in certain rich results and drive more traffic to your website.
10. Use an Image Sitemap
An image sitemap helps Google discover your images faster. You can further enrich your XML sitemap to provide information about your images or use a dedicated image sitemap.
If you choose to include images in your existing sitemap, you can use the example below as a guide:

11. Optimize Image Placement
You can position your images anywhere you want on the page, but if you want a particular image to be considered by search engines as an important element of your content, then add it closer to the top with the relevant alt text, image title, and caption.
For example, if you have a unique, original, and useful custom image, you want it to appear in Google Image Search for specific terms.
12. Add Open Graph Meta Tags
Open Graph is a protocol introduced by Facebook. The concept is similar to schema markup, where you use tags to help crawlers identify the important parts of your content and their meaning.
Open Graph tags allow you to specify which image Facebook (and other social networks) will use when users click your website's SHARE or LIKE buttons.
When you have a page with more than one image, you can use the og:image tags to tell FB which image to use.
The best way to add open graph protocol support to your WordPress website is to install the Yoast SEO Plugin.
Conclusion
Images are important from an SEO perspective and vital for making your content more interesting and readable.
From my experience, many people don’t do any SEO image optimization, which is an SEO mistake that must be avoided.
As you have read above, image SEO is a straightforward task. You reduce the file size as much as possible, give it a meaningful file name, provide for an ALT text, write a title and caption, and add it to your sitemap.
It’s not time-consuming, and the benefits are much more than the extra time it takes.



