This SEO tutorial will help you better understand how to optimize your website for Google and other search engines.
If you are new to SEO and don’t know where to start or spend your time and energy, get a cup of coffee, take a deep breath, and get ready to teach yourself SEO!
What Is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
The first thing you need to understand is what SEO is and why all the fuss about it.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a framework you can follow to make your website more visible to search engines. Like other frameworks, it has a set of rules, processes, and guidelines.
SEO has two main objectives:
- The first is to make a website friendlier to search engine crawlers so that they can read, understand, and add the website to their index.
- Second, to make a website friendlier to the user. This is one area of SEO that is often overlooked; a website that is SEO-optimized should also be user-friendly and vice versa.
That’s the basic definition of SEO, which is clear and straightforward.
Now consider this: what happens if all websites are properly optimized according to best SEO practices? How do search engines decide which to show first, second, third, etc., in their search results?
This is where the fun part begins. For any search term you can think of, hundreds of websites compete for a top place in the results. The websites that are built on a solid SEO foundation win the race.
Black Hat Vs. White Hat SEO
A solid SEO foundation is based on what is known as ‘white hat SEO’ in the industry.
White hat SEO is a term used to describe optimizing your website without violating any rules.
To be more precise, Google has a set of guidelines for what you can do and what you shouldn’t do to make your website Google-friendly.
If you violate any of those guidelines intentionally or because you didn’t know about them, you risk getting a ‘Google penalty’, which means your website will either be removed from Google or your rankings will dramatically drop.
On the other hand, black hat SEO is a term used to describe actions not according to acceptable standards and practices. The purpose of black hat SEO is to manipulate search engine algorithms using various techniques to trick search engines into ranking a page higher in the results using false signals.
Which way to go?
White-hat SEO is the only way to go. Search engines have intelligent algorithms and spam detection techniques that can track and penalize any websites using black hat SEO techniques to achieve higher rankings.
Don’t believe everything you read online, especially those guides or SEO tutorials that promise you results quickly. SEO takes time to generate good results after you do a lot of work.
If you are looking for a fast way to get traffic to your website, get into Google Ads, Facebook ads, or other paid methods, but if you want to build a successful online business, SEO can guarantee your long-term success.
Why Is SEO So Important?
SEO is important for many reasons, but the primary reason is that it can help you achieve higher rankings, which means more organic traffic to your website.
Search engine traffic is the most valuable traffic source for any website, which can lead to more conversions.
According to statistics, Google receives over three trillion searches per year. Take a moment and think about what this number means and how it can change your business if you manage to get your tiny share of traffic from the billions of monthly searches.
Why does it matter to rank high in the search results?
Most of Google’s organic traffic is distributed among the websites that appear on Google's first page. As you can see in the graph below, more than 80% of the clicks go to the first five positions.
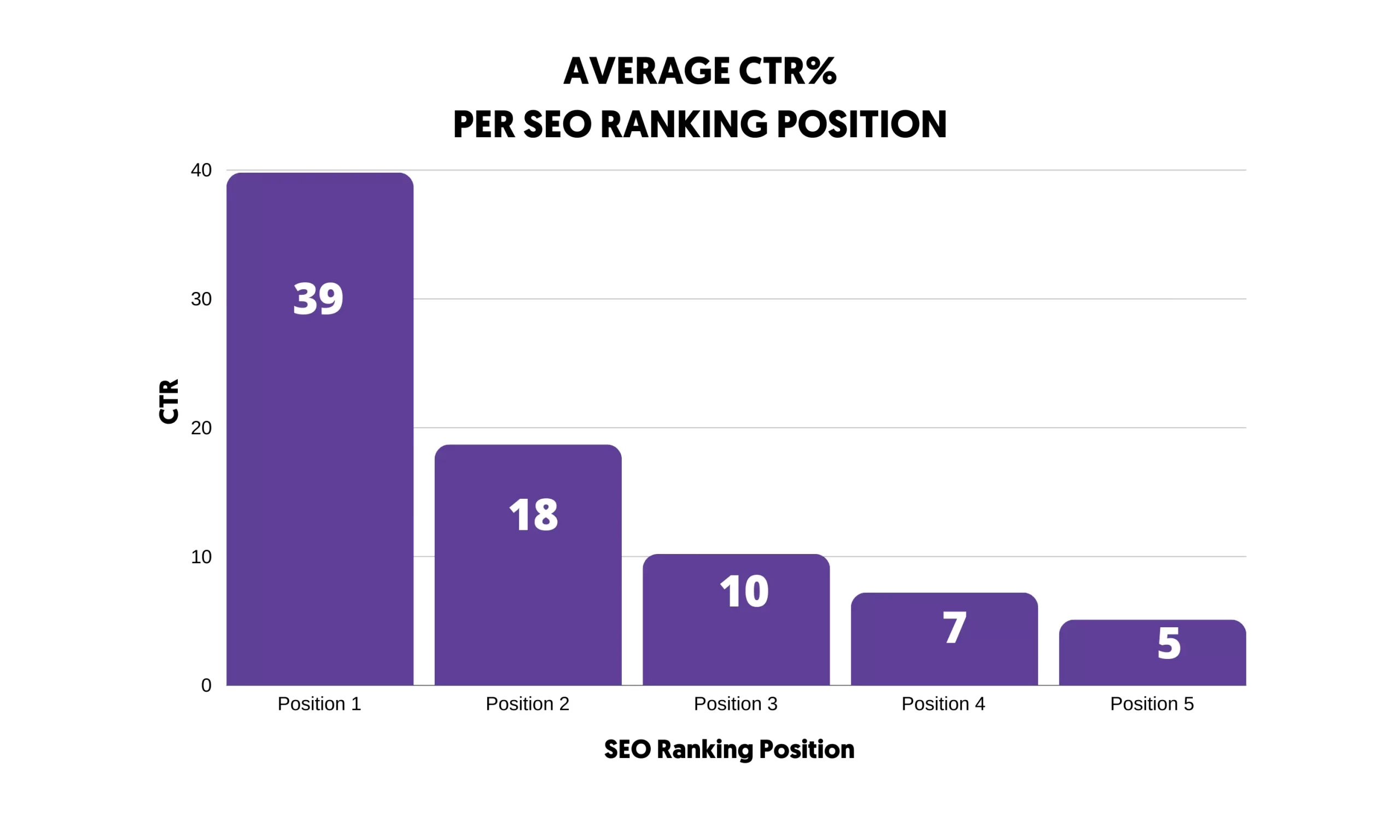
So, to get traffic from Google, you have to rank in one of the top positions or at least on the first page.
How To Do SEO On Your Own
- Understand How Search Works
- Work On Your Technical SEO
- Work On Your On-Page SEO
- Work On Your Off-Page SEO
1. Understand How Search Works
Now that you have a clear idea of what SEO is and why it is important for your online success let’s see how SEO works in more detail.
Since Google is the biggest and most valuable search engine, I will use it in the examples below. But anything you do to optimize your website for Google also applies to the other big search engines.
How does Google Search Work?
Google has a very nice tutorial on how Google works, and if you have never seen this before, I suggest reading it first.
Of course, they don’t reveal all the algorithm details, but you can get a very good idea of how search works, which will help you understand the contents of this SEO tutorial better.
Simply put, Google crawlers search the web to find web pages and add them to their index. When a user types in a search query in Google, their algorithms try to find the best possible match and present those pages in the search results.
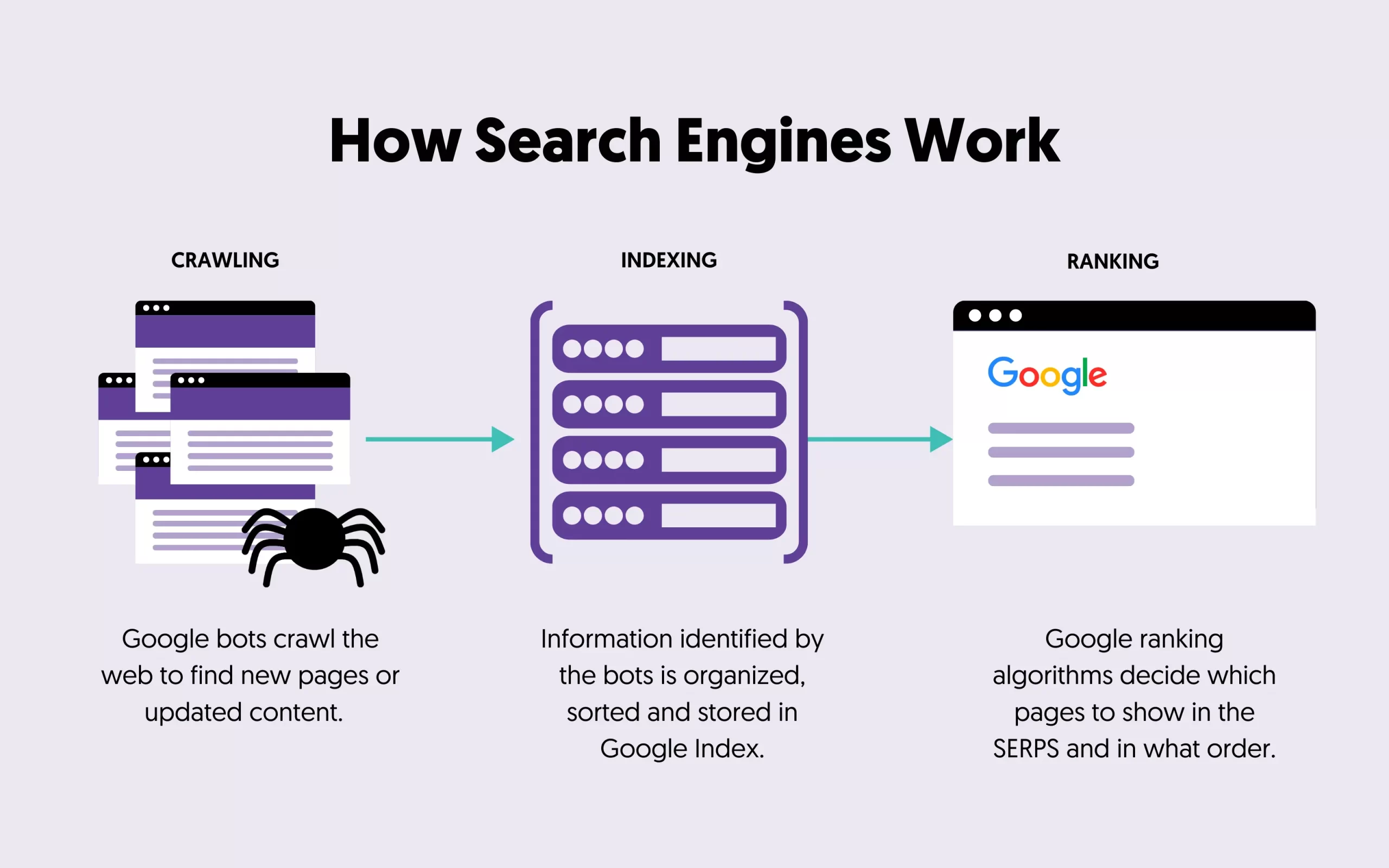
That would not be an issue if only a few pages were available per search query. Google would show those in the first 10 positions. But, as mentioned above, there are thousands of pages about a particular topic, so their algorithm has to decide which is the best match and show those to the user.
Many factors are taken into account by the algorithm, but some are much more important than others.
If you are a beginner at SEO, you don’t have to understand all the theories now; it’s too much information, and I know it gets confusing.
What you need to understand is this:
- Google wants to keep its users happy so that they return and perform more searches.
- Google users are happy when they find what they want in the fastest possible way.
- Google is making a lot of effort to keep low-quality pages out of its index and continually adjusts its rankings algorithms for this purpose.
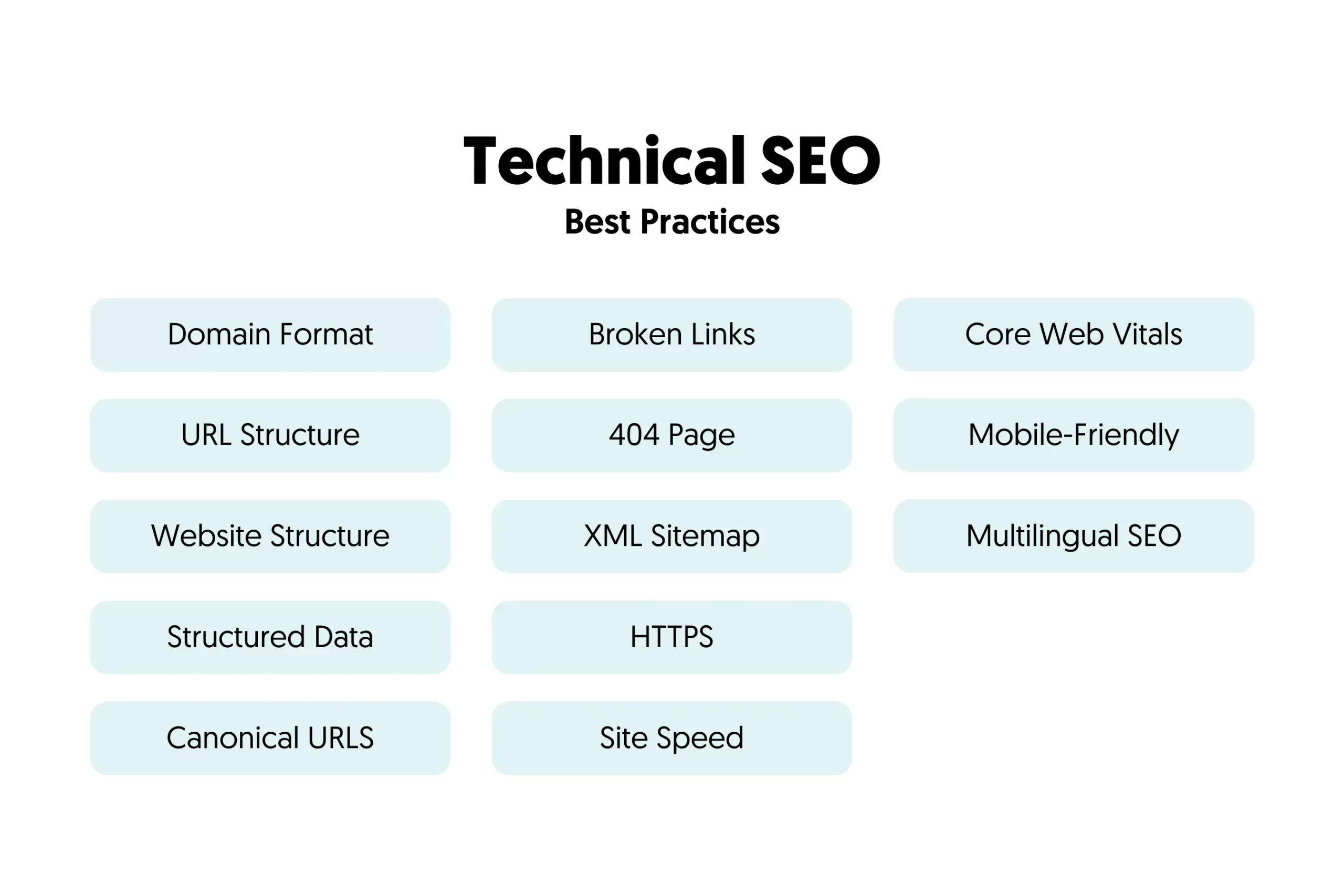
2. Work On Your Technical SEO
Technical SEO has one purpose: to make sure that search engines can discover the important web pages of a website and be able to access them without any issues.
To achieve this, you need to optimize several things, the most important are:
- Website Structure
- User and XML Sitemap
- Google Search Console
- Robots.txt Optimization
- 404 Page Optimization
- PageSpeed
- Mobile-Friendliness
Website Structure
The structure of your website is critical. A good and simple site structure will make the job of search engines and users easier, which has many benefits for SEO and usability.
To make an SEO-friendly site structure, consider the following:
- Group your content into logical categories that make sense. Everything starts with the home page, but after that, you should think of a logical hierarchical structure for the rest of your content.
- Don’t over-engineer, but keep it as simple as possible. Avoid having too many categories or subcategories since, SEO-wise, these don’t offer much value because of duplicate content issues (we will talk about this later).
- Don’t use more than three levels when creating your site hierarchy. Don’t hide your content from search engines and users; make discovery easy.
- Use SEO Friendly URLs. URLs can contain “-” but not underscores or other unnecessary information. Keep them clean and easy to understand.
For example, let’s assume you have a Digital Marketing blog. Your blog posts can be grouped into one of these categories: SEO, Social Media, PPC, and Content Marketing.
Your Website structure can look like this:
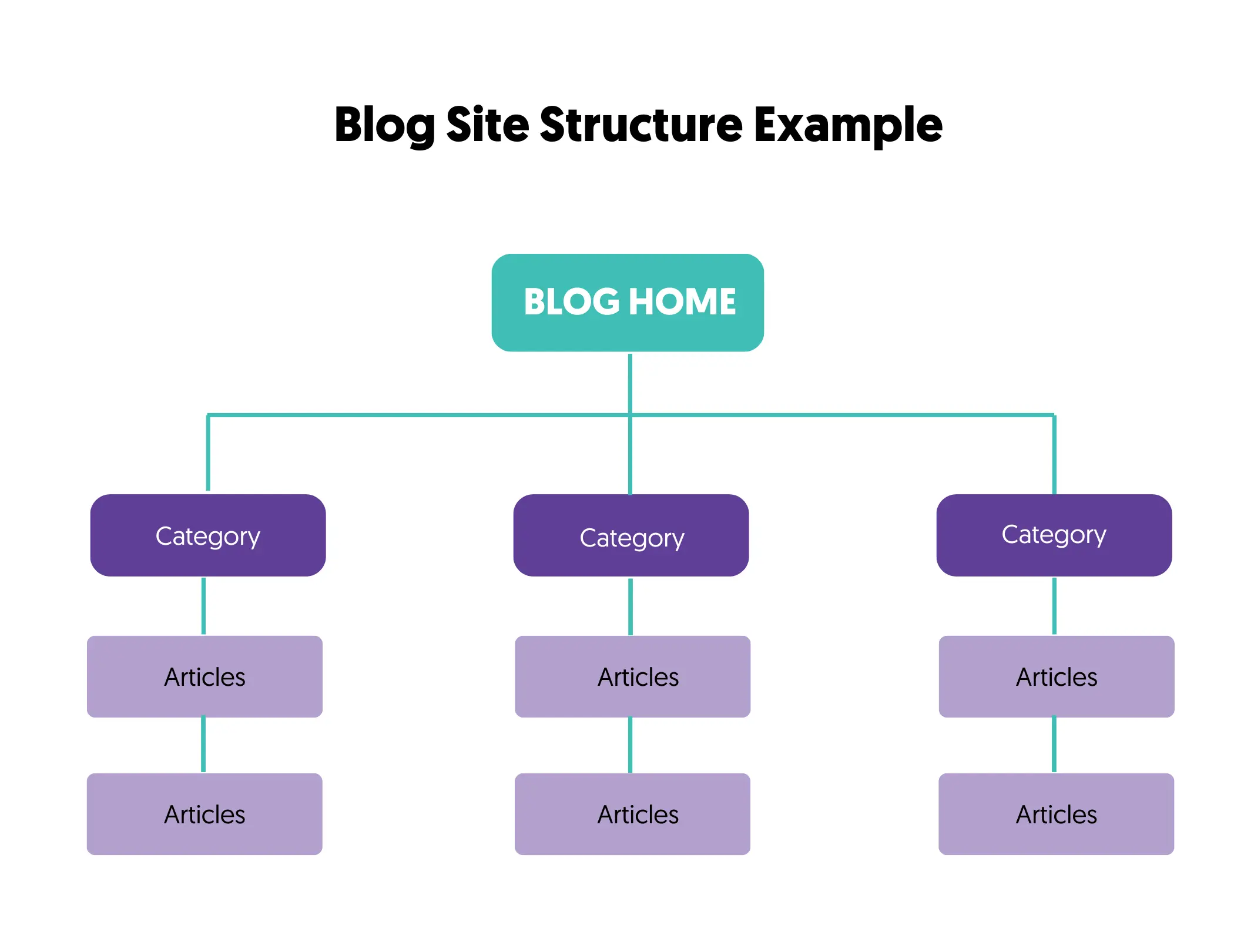
And the URLs like this:
- Sample Category URL: example.com/SEO and example.com/Social
- Sample Blog URL: example.com/my-seo-blog-post
- Sample Page URL: example.com/digital-marketing-services
User and XML Sitemap
Google recommends that you provide users with a simple sitemap page containing links to all the important pages of your website (or to all pages, if possible). You can add this to your main menu or footer.
Besides helping with user navigation, a sitemap page is also used by Google during the crawl process to discover more pages from your website.
Another better way to inform search engines about your website pages and structure is to create an XML sitemap and submit it to Google and Bing.
An optimized XML sitemap should list all pages that search engines should know about, not pages with duplicate content or providing no value to their users.
Submit Sitemap to Google - Three ways to submit your XML to Google.
Google Search Console
One of the ways to check what search engines know about your website is through webmaster tools. Both Google and Bing have made these tools available to their users and are free to use.
You can access Google Search Console here and Bing webmaster tools here.
Webmaster tools can give you a lot of valuable information regarding your website. You can see your ranking position for different keywords, how many links point to your website, how many pages you have in the index, if there are any errors during the crawl process, and much more.
Resources to Learn More
- Bing Webmaster Tools tutorial - A tutorial for beginners to Bing Webmaster tools
- How to use Webmaster tools - A guide on how to get started with Webmaster tools for ALL search engines.
- What is Google Search Console - An introduction to Google Search Console for beginners.
- Add website to Google Search Console - How to add and verify your websites with Google Search Console.
Robots.txt Optimization
Robots.txt is a file that exists on the root directory of every website and can be used to instruct search engines on which directories/files of the website they can crawl and include in their index.
Normally, you will need to deal with robots.txt once, and if everything is ok, you don’t have to change it again.
404 Page Optimization
What is a 404 page? The 404 page is shown to the users if they click a link on your website that leads to a non-existent page.
What is the importance of a 404 page for SEO? Remember that SEO is about usability, and giving users a dead end is not the best approach.
Your 404 page needs to be useful and provide users with alternative ways to find what they want.
PageSpeed
One of the ranking signals that Google has not kept secret is website speed. Websites that load fast have a competitive advantage over websites that are not so fast.
This means that if everything else is the same, Google will rank higher websites faster than slower.
So, even if page speed is a comparative signal and not a direct signal, there are many business benefits from having a fast-loading website.
Numerous statistics show that users are not willing to wait for a website to load for more than 3-5 seconds (especially on mobile), and there is also a direct correlation between website speed and conversions.
To cut a long story short, part of your optimization process should be to improve the loading speed of your website as much as possible.
It’s a technical topic, and you might need the help of a developer to make the necessary changes, but consider this an investment you have to make.
If you want to get your hands dirty, here is the guide: How to increase your page speed.
Mobile-Friendliness
Last, your technical SEO checklist should also include how good or bad your website performs on mobile.
Google confirmed that mobile searches are now more than desktop searches, meaning you cannot reach many potential users if you are not mobile.
A website is considered mobile-friendly when:
- It can be viewed on a mobile device without zooming in and using horizontal scroll bars to access the content.
- It loads fast (preferably more than 2.5 seconds)
- It allows the users to perform the same actions as the desktop using their mobile devices.
3. Work On Your On-Page SEO
Once you’re done optimizing for technical SEO, the next step is to start working on your on-page SEO.
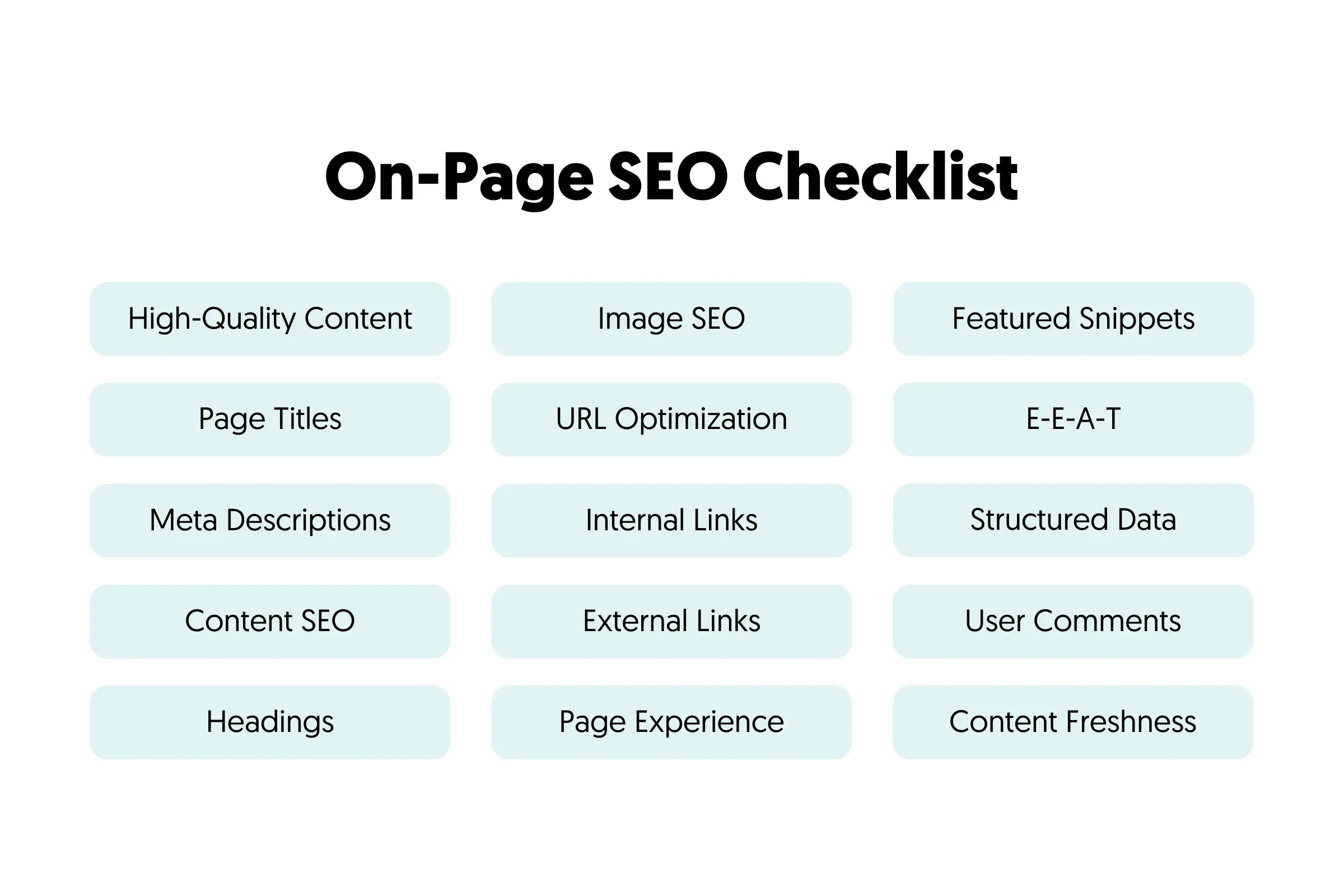
On-Page includes the following tasks:
- Page Title Optimization
- Meta Description Optimization
- Heading Tags and Page Formatting
- SEO Copywriting
- Internal linking
- Rich Snippets and Schemas
- SEO for Multi-lingual websites
Page Title Optimization
A page title (<title>) is the first element that users and search engines see when reading or crawling a page.
Best practices for SEO-friendly page titles:
- Each page of your website needs to have a unique page title
- Page titles should accurately describe the page content
- Page titles are shown in the search results, so they should be attractive and help users understand if the page is relevant to their search so they can click to visit the page.
- Page titles should be brief. In terms of length, it is suggested to go up to 60 characters so that they can fit in the Google search results.
While the above best practices are all related to SEO, there is one more step to take to optimize your page titles further, which has to do with keywords.
Keywords in the page title are important for both users and search engines. Users can easily spot the keywords in the title (sometimes, they are even made bold by search engines), encouraging them to click the link and visit the page.
Search engines ‘read’ the title and determine if this page can potentially satisfy the ‘intent of the user’. If this is the case, they continue to examine the page content and other factors before returning the results to the user.
You should ensure your page titles include your target keywords to win users and bots.
For example, if you are writing a post targeting the keyword ‘SEO Tutorial’, your page title should include this keyword, hence the post's title.
As an additional note, there is no need to add your website name in the title. This is added automatically by Google (if it does not exist).
If you need your website name as part of the title, move it to the end and not the beginning.
The first parts of the title include the important elements (i.e., keywords).
Meta Description Optimization
The page meta description (<meta name="description" content=“your description goes here”) is equally important. Your website pages (including the homepage) should have a unique description that accurately summarizes the page’s content.
Best practices for crafting good meta descriptions:
- Avoid generic descriptions or terms like ‘This page is about...’ but concentrate on why someone should visit your page.
- Include keywords in the description, but don’t do keyword stuffing.
- Keep your descriptions up to 160 characters.
Pro Tip: Unlike page titles, meta descriptions are something you can safely change after a page is indexed.
You can check the description displayed by Google for several terms related to your page and make any changes to the text to make it more appealing to the user. While doing this, you can also ‘spy’ on your competitor’s descriptions and see what message they try to pass to their users.
As a side note, remember that Google may decide not to show your description in their results, but they may show text from the page if they believe this better matches the user’s query.
Resources to Learn More
- Meta Description Length - the ideal length of an optimized meta description (study)
- Meta Description and SEO - More tips on optimizing your meta descriptions.
Heading Tags and Page Formatting
Besides the titles and descriptions seen by bots and shown in the search results, heading tags and page formatting are other factors that directly impact SEO.
As a general rule, headings should be used to guide users on the important sections of a page and thus make a page easier to read and user-friendlier.
Headings can also help search engines understand the content of a page. When reading the HTML of a page, they can identify tags like H1 and H2 and use the text within those tags to figure out the meaning of the page’s content.
Headings should include keywords and have a hierarchical structure. For example, the first heading on the page should be the H1 tag (usually used for the page title), and the subsequent headings can be H2 or H3.

As an example, look at the headings of this article. It’s a long post, so I have used H1 for the post title, H2 for the main sections, and H3 for the subsections.
SEO Copywriting
Maybe you have read many times in the past that content is king, but it is still true. Content is the most important element of any website.
Your content must be high quality, provide answers/solutions to the user intent, and keep the search engine user happy.
If this is not the case, then whatever techniques you use (either white hat or black hat) to increase the visibility of a website in Google searches will all fail.
What is SEO Friendly Content? SEO-friendly content is content that provides value to the user by answering a question or providing insights about a certain topic and, at the same time, can be understood by search engines.
What is a keyword?
To be able to create SEO-friendly content, you first need to have clear in your mind the meaning of keywords and their role in the SEO process.
A keyword is anything that users can type in the search box with a significant value. A keyword may consist of one or more words.
Consider the examples below. Keywords are shown in bold:
- “Marketing”
- “DIY SEO Tutorial”
- “What is SEO?”
- “What is the best Chinese restaurant in Florida?”
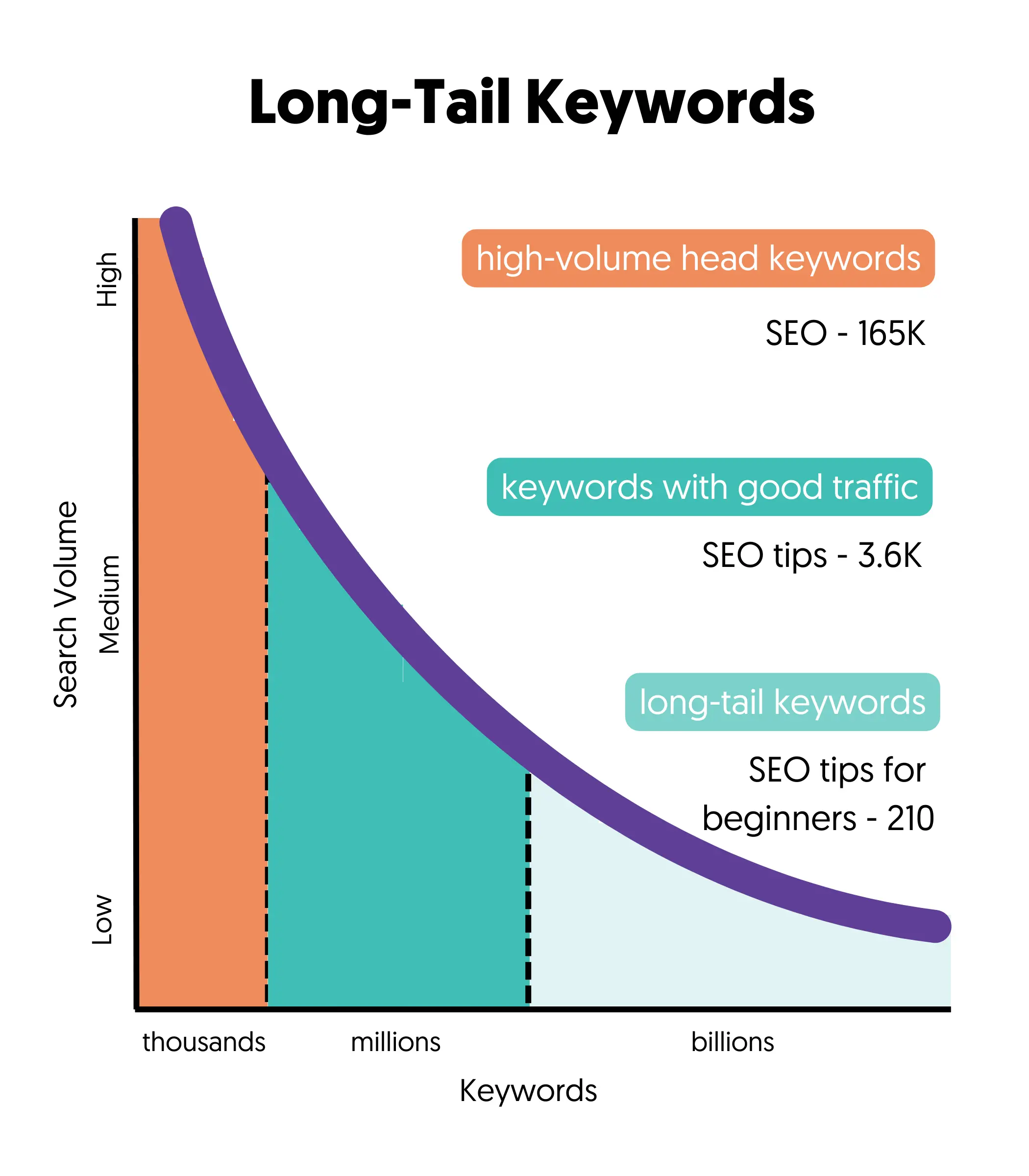
Notice that some keywords are very broad (Marketing), and some consist of 2 or more words, known as long-tail keywords (best Chinese restaurant Florida).
What is the role of keywords in SEO?
Everything online starts with a keyword, whether website content, user search query, or Google Ads.
During indexing, search engines try to match keywords with web pages that can potentially be used as ‘results’ for those keywords.
Your job as an SEO is to ensure that your web page content includes those keywords (or variations) to help search engines index your pages correctly.
Does this mean you will get higher rankings if you have a page full of keywords?
Not at all. Keyword stuffing or content that exists to keep search engines happy cannot achieve high rankings.
What you need for high rankings is high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Resources to Learn More
- Keyword Research Best Practices - Tips to follow while looking for keywords to use in your content
- Keyword Research Courses - These are the best courses you can follow to master keyword research secrets.
Internal linking
What is internal linking? Adding links to your pages that point to other pages within your website. It’s a pretty straightforward concept but sometimes overlooked by webmasters, and this is an SEO mistake.
Internal links serve 2 major purposes:
They aid navigation since they point users to other pages of your website to read more details about a certain topic, and they help search engines discover more pages from your website and also understand the context of your pages better.
Internal linking best practices for SEO.
- Add internal links where it matters and not for doing it.
- There is no limit to the number of internal links you should have per page, but don’t overdo it. Longer posts are more likely to have more internal links than 300-word posts.
- For internal links to have some value, they need to be in the main body of the page. Links in the sidebar or footer are not so valuable (for on-page SEO purposes).
- Use optimized anchor text with your internal links. Unlike external links, internal links can include keywords in the anchor text. There is no penalty.
- Don’t add the ‘nofollow’ tag to your internal links. All internal links should be followed.
Rich Snippets and Schemas
One modern way to give your content more visibility and improve its Google rankings is by using rich snippets and schemas.
What are schemas, and why should you care?
Structured data markup is a formal way to describe your content to search engines. One of the challenges search engines face when crawling a page is understanding the context of a page, and schemas can help them a lot in this direction.
As stated by Google, through structured data markup, you make your content eligible to appear in rich results and knowledge graph cards.
This means eligibility to rank in position 0 of Google (above the normal search results), which has several benefits.
Structured data markup can be implemented by adding tags to your HTML code or a JSON script.
Resources to Learn More
- What is Schema Markup? An introduction to schema markup for beginners.
- Rich Snippets Best Practices - Tips to optimize your content for Google-rich snippets.
SEO for Multi-lingual websites
Many websites have their content displayed in different languages, and while this is normal when it comes to SEO, you need to have a few things in mind:
- Don’t use automatic translators to translate your content into different languages. Your content must be high-quality and readable, without grammar, structural, or spelling mistakes.
- If you want to make your content available to other languages, do it manually page-by-page.
- To avoid any issues with duplicate content, you need to do some SEO configurations, mainly using the hreflang meta attribute.
The hreflang attribute is a way to tell Google that your content is available in more than one language.
Google will use this information and serve the right content to your users (depending on location and language).
Hreflang implementation is an advanced topic and requires technical knowledge to apply the necessary settings to your website.
If you have or are thinking of making your content available in more than one language, read this guide from Google.
4. Work On Your Off-Page SEO

No SEO strategy is complete without off-page SEO. Beginners in search engine optimization should understand that a complete SEO action plan has to include off-page SEO tasks.
While On-page SEO involves optimizing your website and content, off-page SEO is about promoting and getting more exposure and attention to your website.
Why is off-page SEO important?
To understand the importance of off-page SEO, consider the example mentioned above, where several websites target the same keywords, and all have on-page SEO. Which websites will achieve higher rankings?
The answer is simple: the websites that have done a better job in off-page SEO will get higher rankings and traffic.
What is off-page SEO?
Off-page SEO involves methods and techniques to convince search engines that your website is better for its users than others.
In the SEO world, this is translated into incoming links; hence, the term ‘link building’ has been associated with SEO.
Why are links important?
When Google founders wrote the first ranking algorithm, they decided how to rank pages in Google search results.
Besides considering all the factors discussed above, they also came up with a brilliant idea: the websites referenced (linked to) by other websites are more likely to be more important and useful to users, so they deserve a higher ranking.
That’s an oversimplified version of the initial Google algorithm, but the main idea has held up until today. Websites with incoming backlinks from other websites are more likely to rank higher and get more traffic from Google compared to websites that don’t have many links pointing to them.
Over the years, webmasters and SEOs have tried to manipulate this rule by building links to make the Google algorithm happy (black hat SEO), leading to many low-quality sites reaching the first positions of Google.
This, in turn, forced Google to add more rules to its algorithm to consider more quality factors when assessing the quality of a link.
What is a good link?
A good link that can help your website increase its rankings has the following characteristics:
- It is a natural link – A webmaster naturally adds the link because they believe linking to your website will add value to their content and help their users read more details about a certain topic.
- It is coming from a related website – If you have a website about SEO, it’s natural to have links from websites that deal with digital marketing, social media, etc., but it’s not natural to have links pointing from fashion-type blogs or other unrelated topics.
- It’s coming from a website trusted by Google – Not all websites are equal in the eyes of Google. Google loves high-quality websites, and a link from such a website is welcomed.
- It’s not part of an exchange or paid scheme – Links paid for or exchanged (you link to my website and I link to yours) can get you into trouble (see below).
- It’s not coming from a low-quality website - In general, websites that have little or no original content and are full of external links with no incoming links do not offer any value to the user and are considered by search engines to be low-quality websites.
What is a ‘bad link’?
A ‘bad link’ does not have the characteristics of a good link. Usually, bad links are either paid for or injected into low-quality articles for the sole purpose of tricking search engine algorithms.
It may be a surprise to beginners, but several websites exist to publish low-quality content with outgoing links.
What is the problem with that? A lot of bad links pointing to a website can lead to Google penalties, and in simple words, this means loss of rankings, traffic, and Google trust.
What are Google Penalties?
To protect the integrity and maintain the quality of their search results, Google has introduced two types of penalties: manual and algorithmic.
A manual penalty occurs when the Google Search Quality Team imposes a penalty on a website because it violated Google's webmaster guidelines.
When a website is penalized, it loses all (or part) of its rankings. Usually, the webmaster can see the reasons that led to a penalty by viewing the Google search console's ‘Manual Actions’ report.
To return to the Google index, the webmaster must submit a ‘reconsideration request’, manually reviewed by the search quality team. A successful reconsideration request does not mean the website will return to the pre-penalty rankings.
An algorithmic penalty occurs automatically and results from bad practices and violations checked automatically by the Google algorithm. To recover from an algorithmic penalty, you must make the necessary changes and wait for an algorithmic refresh.
Is my website penalized? - How to check if your website is under a Google penalty.
How do you get quality links for your website?
So, good links are important for a website’s SEO success, but how do you get these links without taking any risks?
This is something I explain in more detail in my SEO Courses as it is a huge topic on its own, but to give you some ideas and pointers, consider this:
- Don’t go after links that are too easy to get. It is hard to get links that are usually more valuable.
- Only pursue links from websites that are better than yours in terms of traffic, quality of content, and reputation.
- Don’t believe anything you read about ‘private networks’ or other schemes that exist to give links to any website.
- Use guest posting wisely; don’t spend your energy and time on guest posts that nobody will read.
- Use social media to get your content noticed. Social media shares/likes, etc., are not considered a direct ranking factor, but you can use the exposure you can get from social networks to position your content in front of the people who are more likely to interact with it (comment, share, etc.) and link to it.
In addition to the above:
Don’t be afraid to link out to other valuable and high-quality websites. How is linking out related to getting more links?
Webmasters tend to check their statistics, referral traffic, and links regularly, and if they notice traffic or a link from a website, they will check it out and may return the favor.
To those of you who think that this is a ‘link exchange’, it’s not. First of all, the other webmasters are not obliged in any way to return the favor, and second, this is a method proposed by Google in one of their ‘Audience Engagement Guides’.
Also, another more direct way to ensure that webmasters you’ve linked out to will notice your content is to email them and mention that you like their work and add a link to your articles.
You don’t have to ask for anything in return, but it is certain that a percentage of them will appreciate this action and link back to you.
How Long Does It Take For SEO To Work?
As I explained in a previous article, SEO takes time because any changes you make to your website must be evaluated by Google and then considered.
So, any fixes you do today to make your website SEO friendly may take months until these are properly ‘read’ by Google (and other search engines) and used to improve your ranking positions.
The same is true with link building. When the Google crawlers detect a new link, it must be evaluated before it is awarded a positive ranking signal.
Nobody can give you an exact number of how long it will take to increase your traffic after you do SEO work on your website, but as a general rule of thumb, it may take 3 to 6 months to see the merits of your work.
Thus, being patient and not losing focus is very important. Keep improving your SEO, content, and user experience; you will be rewarded for your hard work sooner or later.
People who are not patient enough tend to get disappointed and quit before they see any results, but those people who work consistently for a long period are those who succeed in the end.
Key Learnings and Next Steps
SEO and Digital Marketing, in general, are disciplines that change constantly. Every week, there are new changes to algorithms and practices that directly or indirectly affect SEO, but the basic ingredients of SEO have been the same for the last 20 years.
If I had to summarize these in one sentence, I would say that SEO is about making your users happy and satisfying their ‘intent’ through high-quality content and easy-to-use websites.
In this comprehensive SEO tutorial, I tried to include pointers to the most important aspects of SEO so that you get the full picture of what you must do to get better rankings in Google.
As I mentioned in the introduction, it’s a lot of work, not a once-off task.
When you decide to enter the world of SEO, you should remember that you are entering a competition with hundreds of people with the same goals. Your competitors are trying to make their content and websites better, aiming to rank higher, and if you are to win this race, you have to do a better job than them in all aspects.
If you have any questions, let me know in the comments below, and I will do my best to answer them.