Running a small business is not an easy thing to do. As an owner, you have to deal with many things, and if digital marketing or SEO is not something you are familiar with, things can get tricky.
In this guide, you'll learn how to use SEO to grow your business online in simple terms and everyday language.
What Is Small Business SEO?
Small business SEO is the practice of optimizing a small business's website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines like Google. It's a subset of SEO tailored to attract organic traffic and customers by making the business more searchable and competitive online.
Difference Between Small Business SEO And Local SEO
You may come across other terms like Local SEO when dealing with small business SEO. Both are subsets of general SEO targeting small businesses. Local SEO refers to several techniques you can use to optimize your website for location-aware searches.
When users add a location to their search query, Google shows a local pack of businesses operating in the particular area on top of the organic results (and in Google Maps).
So, if your business operates in a specific geographical area, you can use the tips in this guide (applicable for all kinds of small businesses) and get extra tips in our Local SEO guide.
Importance of SEO For Small Businesses
SEO has many benefits to offer to small businesses. The most important reasons why you should do SEO are:
- Increase organic traffic - SEO will help you rank higher in Google's organic results and get more targeted traffic to your website.
- Get more customers - By optimizing your site for relevant keywords, you attract visitors who are more likely to convert into customers.
- Boost brand awareness - High rankings in search results enhance your brand's visibility, making your business more recognizable and trusted.
- Open your business 24/7 - With a well-optimized website, your online presence works round the clock, drawing in customers even outside of business hours.
- Cost-effective - SEO is an effective channel with the highest ROI compared to other marketing channels.
In addition, SEO will help your small business compete with bigger companies and grow over time without spending money on paid advertising.
16 SEO Tips For Small Businesses
- Set Up Google Search Console
- Set Up Google Analytics
- Register With Google Business
- Find Your Target Keywords
- Analyze Your SEO Competitors
- Review Your Site Structure
- Optimize Internal Links
- Utilize Schema Markup
- Create Content To Match Your Customer's Search Intent
- Optimize On-Page SEO
- Perform a Technical SEO Audit
- Get Links From Partners
- Register Your Business With Online Directories
- Get Positive Online Reviews
- Work On Brand Awareness
- Monitor Your Rankings
1. Set Up Google Search Console
One of the first SEO tasks is registering your website with the Google Search Console and submitting your XML sitemap.
It’s the best way to inform Google about your website and future content updates, and it’s also a great way to find out how your website is performing in Google Search. You can use Google Search Console functions to:
- View which keywords your website showed up for on Google.
- Find and fix any issues related to crawling and indexing of your content.
- Analyze your website's organic CTR (click-through rate) for various queries, enabling you to optimize your titles and meta descriptions for better engagement.
- Inspect individual URLs to ensure they're properly indexed and to view detailed information about their search appearance and indexing status.
- And many more.
You can learn all the details in our Google Search Console Guide for beginners.
2. Set Up Google Analytics
While the Google search console can give you information from a search engine's view, Google Analytics can give you more information from the user’s view.
It is necessary to understand how users interact with your website to improve the quality of your content and offer them a better user experience.
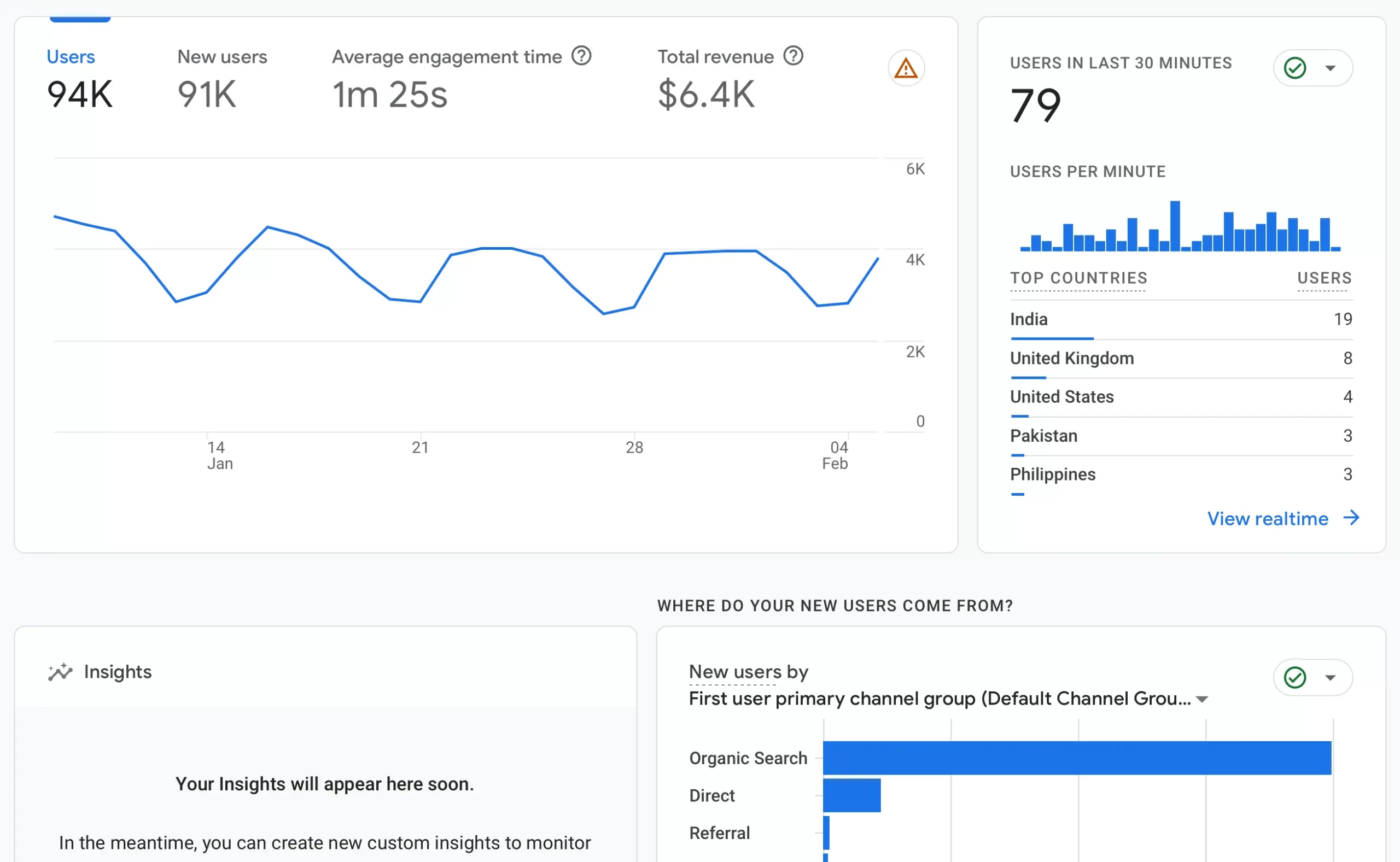
With Google Analytics, you can:
- Track user behavior on your website, including pages visited and time spent on each page.
- Measure the effectiveness of your SEO campaigns by monitoring organic traffic, conversions, bounce rates, and many other useful SEO metrics.
Registering for a Google Analytics Training Course is the fastest way to learn the ins and outs of Google Analytics.
3. Register With Google Business
One of the main goals of small business SEO is to make it easier for people to find you online, and Google Business Profile does exactly that.
Registering your website with Google Business is free, and the benefits are a lot, including:
- It’s easy to set up – You don’t need special knowledge to set up your account.
- Great for local SEO – Google will show your business in the local search results.
- Users can find out where your business is located, how to contact you, etc., without visiting your website.
- Interact with your customers – Customers may add a review about your products or services, and as a verified business owner, you can respond back.
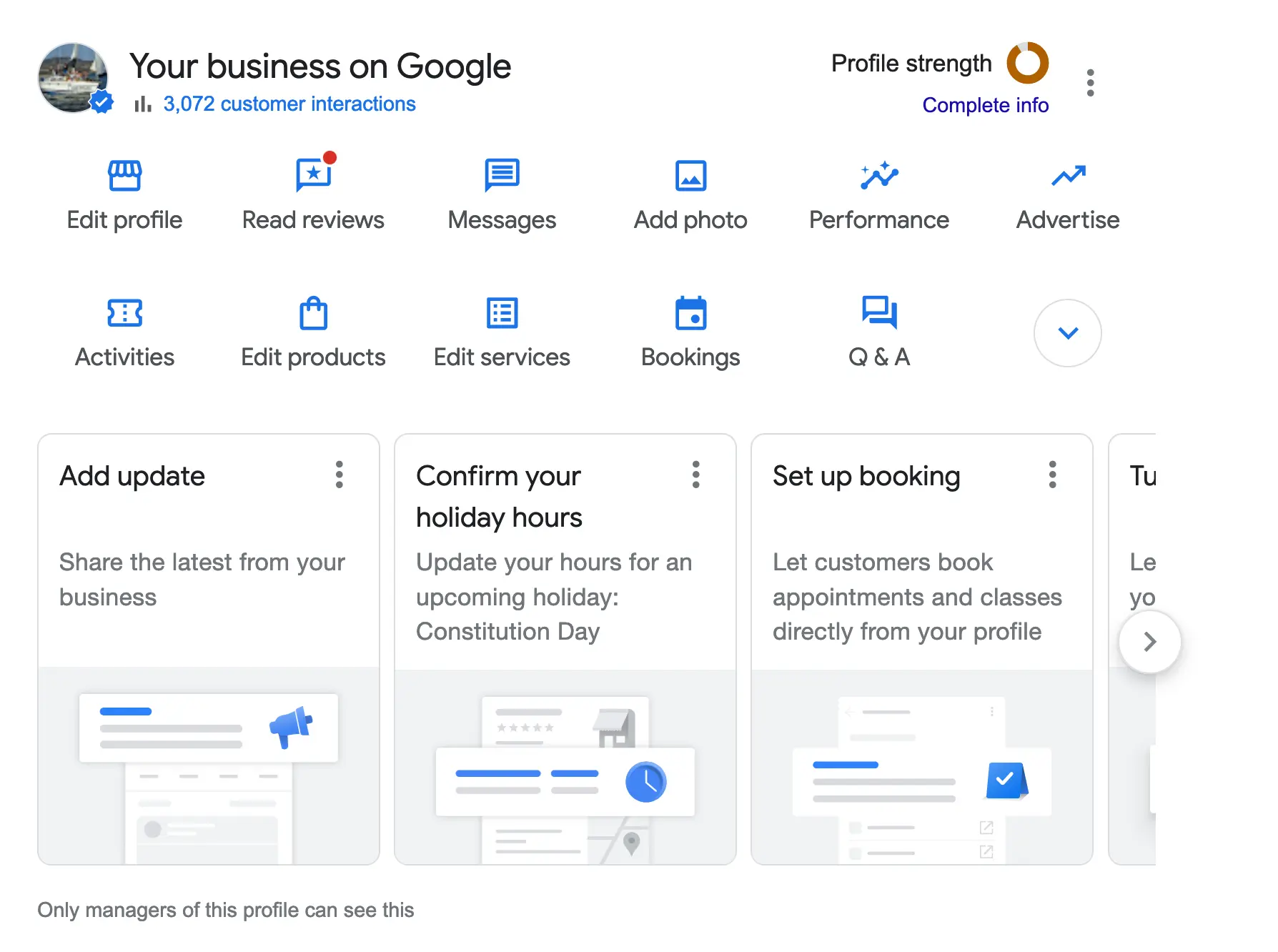
Google Business Profile suits brick-and-mortar, service-based, and any business. If you haven't yet created a business profile, this should be the top item in your SEO checklist.
4. Find Your Target Keywords
A critical component of a successful small business SEO strategy is to find which keywords or phrases your customers type in search engines when looking for related products and services.
This SEO process is called keyword research, and the outcome is a list of keywords to optimize your website, Google Business Profile, and other online properties.
Here is the process to follow:
Begin with listing search terms related to your products or services that a customer may enter in Google search.
Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner or Semrush to analyze your keyword list to find monthly search volume, keyword difficulty, and other related terms.
Examine the search intent behind the keywords to ensure they align with your business offerings and the content on your website.
For example, a small bakery business specializing in gluten-free products might start with basic terms like "gluten-free bakery" or "gluten-free bread".
Using Google Keyword Planner, they may discover related terms with significant search volumes, such as "gluten-free cakes near me" or "grain free bread".
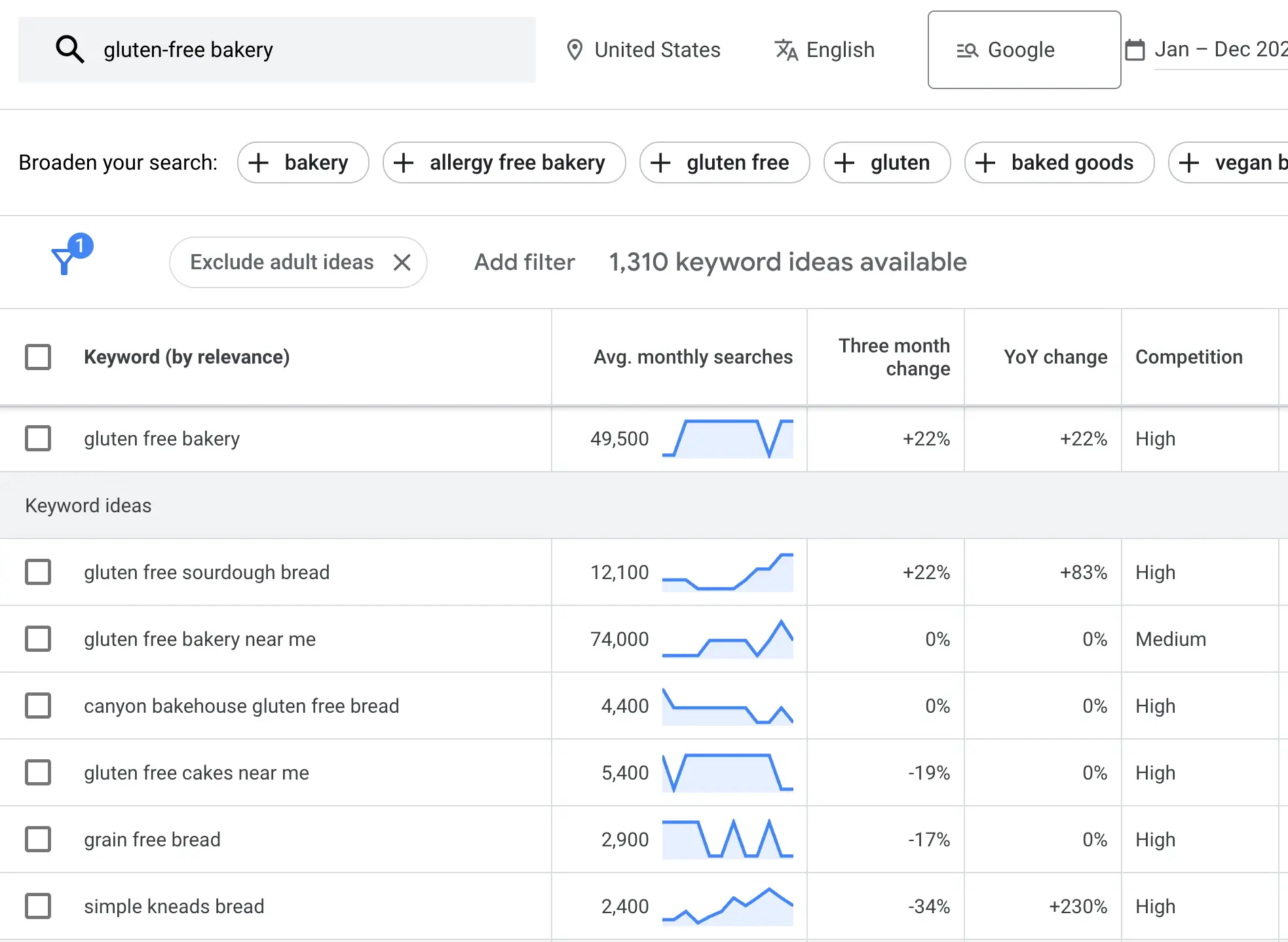
Analyzing search intent, they might find that people searching for these terms are not just looking for products but also for recipes, ingredients, and baking tips.
This insight can guide the bakery to optimize its website for product listings and include a blog section with recipes, baking tips, and information about the benefits of gluten-free products.
5. Analyze Your SEO Competitors
The next step is to analyze the SERPS and find your SEO competitors. These companies target the same keywords as you and appear in the top positions of the search results or the local pack.
It's necessary to do this exercise for two reasons:
- Understand who you must compete with and what effort is required to achieve high rankings.
- Find your competitor's keywords and what content strategies they use.
Here is how to do this. Go to Google and search for your target keywords. Analyze your SERP competitors by looking at the following:
- The type of content ranking in the top positions. Is it blogs, long-form articles, videos, or listicles?
- Visit their websites and examine their website structure. How many categories do they have? How do they group their products?
- Examine the user experience. Is their website easy to navigate? Is the content easy to read?
- Look at their title tags to see how they use their target keywords.
Don't forget to check both on desktop and mobile when doing your analysis. Google is using the mobile version of a website for rankings, so give more attention to that.
Next, take a competitor's URL and use your favorite SEO tool to see how many published pages they have, for which keywords they rank, and the number and type of incoming links pointing to their domain.
For example, let's say you have a small business dealing with cleaning services in your local area. By running a domain analysis, you can immediately spot ideas for product pages and blog posts that keyword research did not reveal.
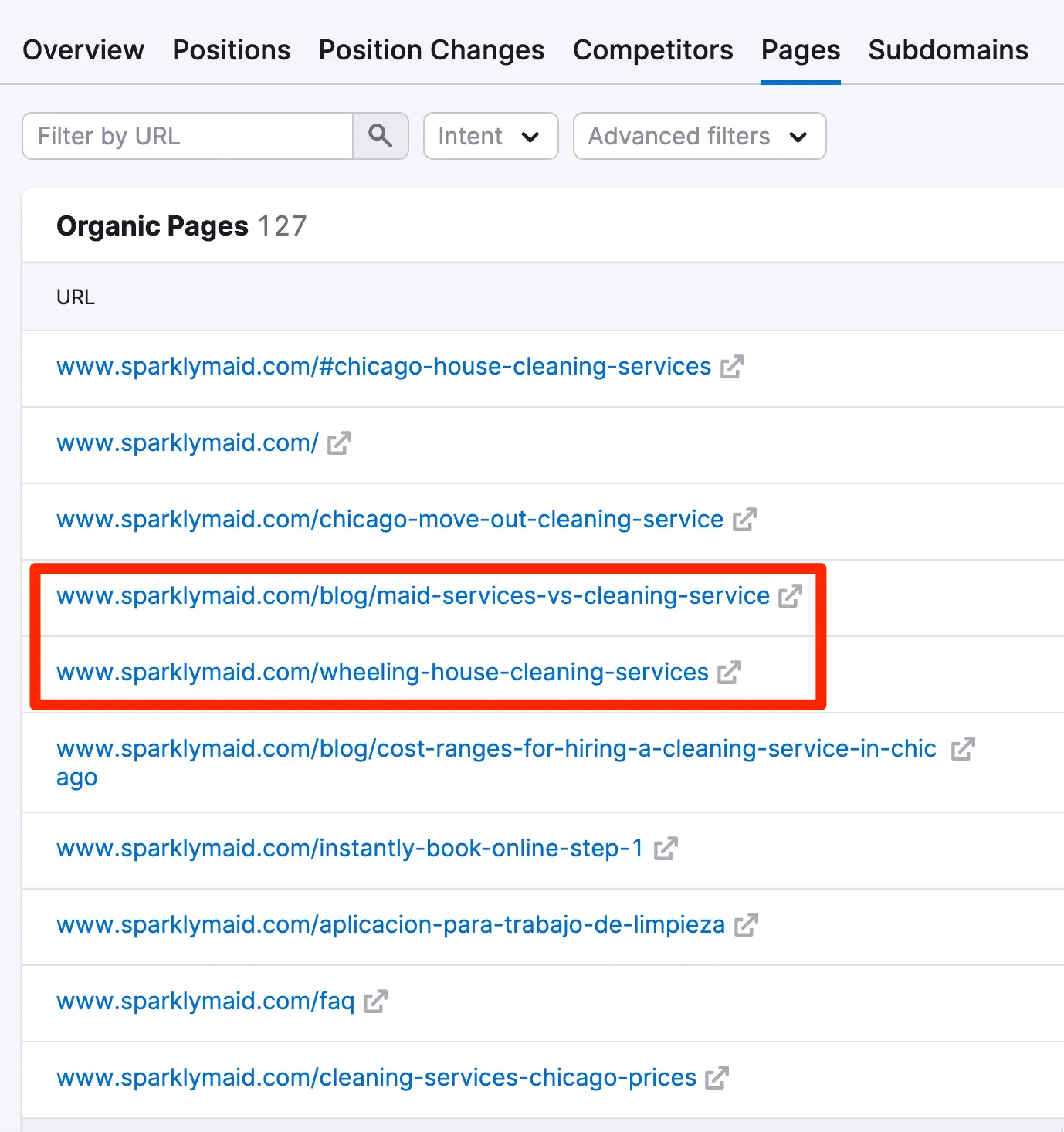
You can also get a very good idea of how many backlinks they have and their link building strategies.
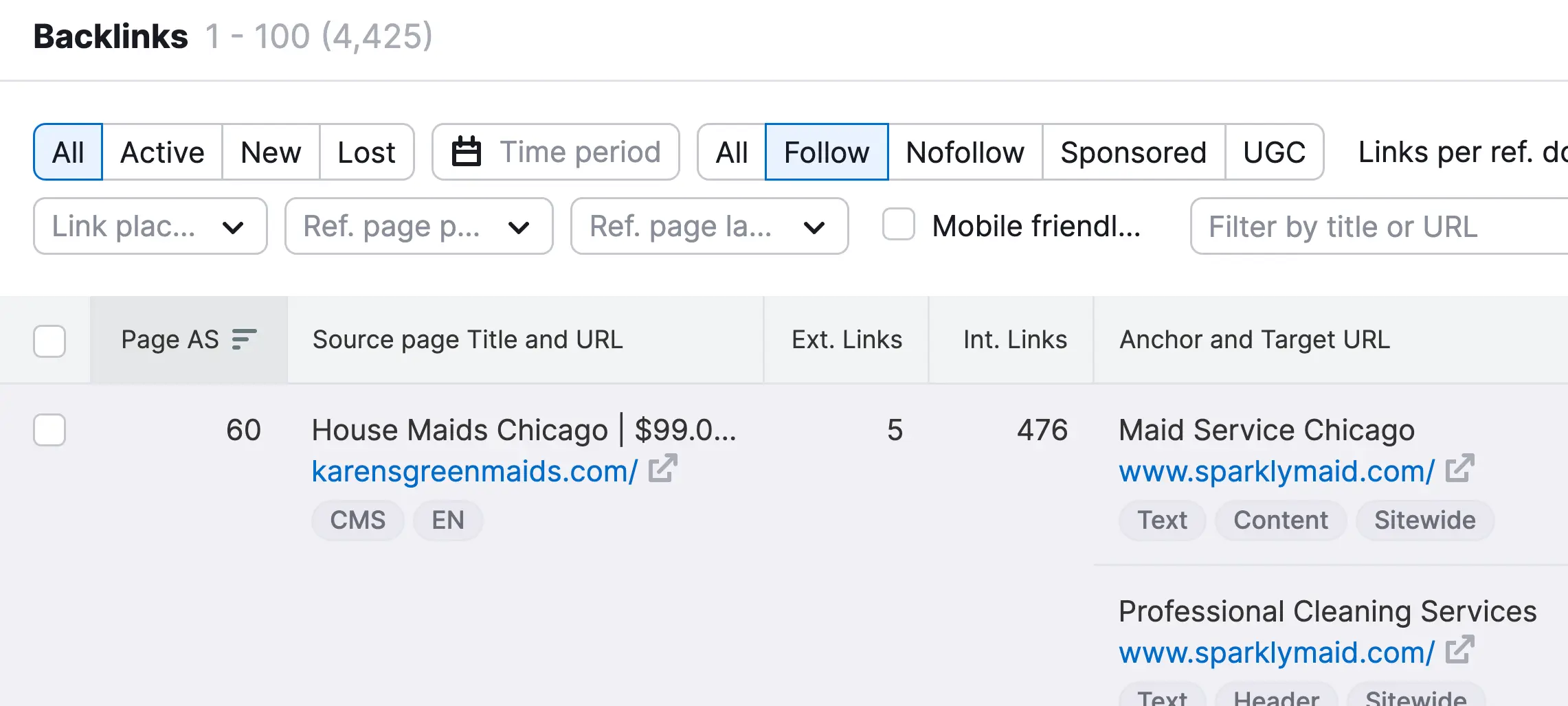
Your goal is to identify gaps or weaknesses in their SEO strategy that you can capitalize on or good practices you can replicate (but not copy) to get the desired results.
6. Review Your Site Structure
The next item on your SEO task list is to review your site structure. A good structure should make it easy for search engines to index your content and for users to find out what they want in less than 3 clicks.
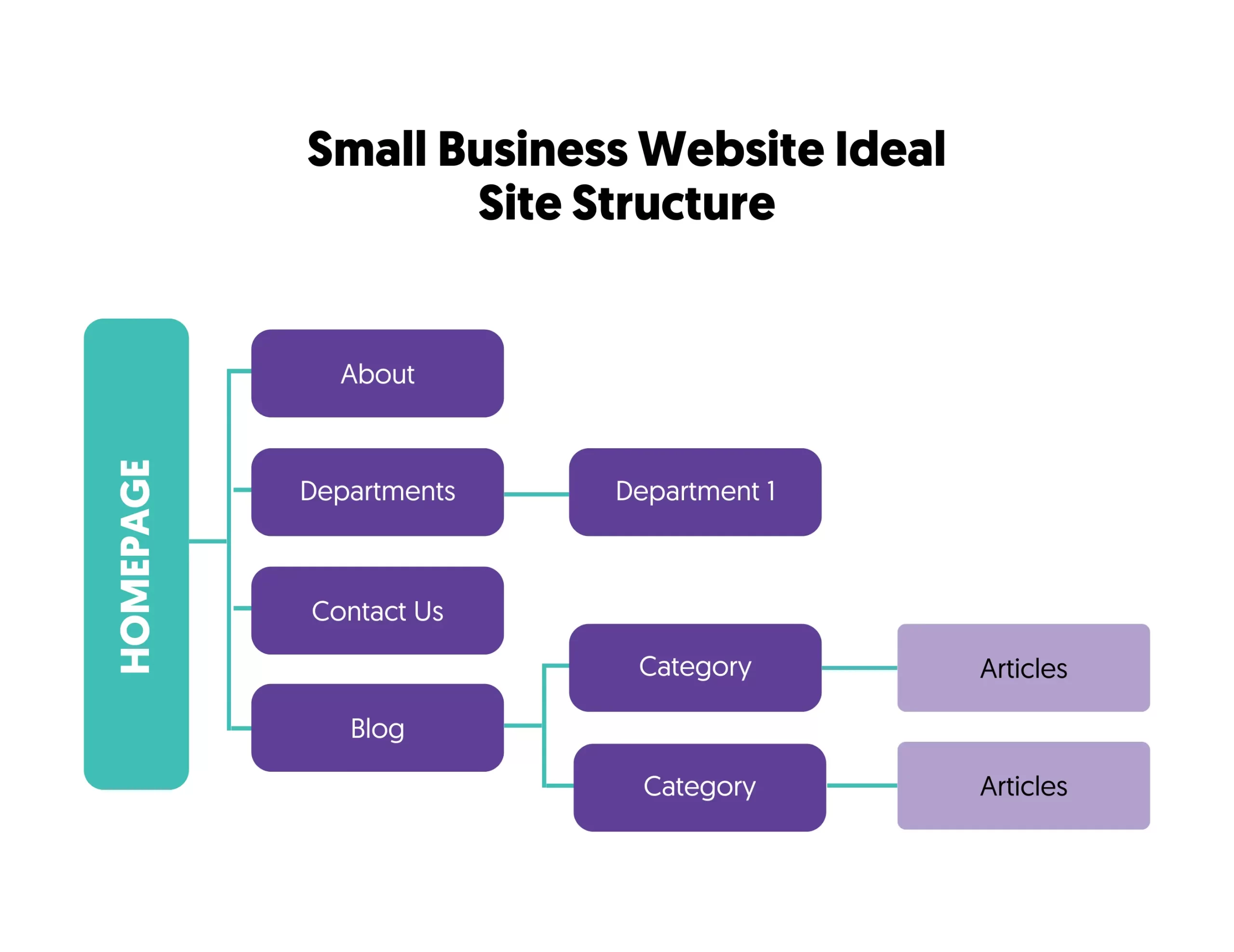
Ensure your website has a hierarchical structure from the home page down to categories (if applicable) and individual pages or posts.
And that your URL structure reflects the hierarchy of your site. Create SEO-Friendly URLs that are readable and include target keywords where relevant.
For example, a small photography business might structure its website with:
- Service pages for "Wedding Photography," "Portrait Photography," and "Event Photography."
- A Blog page (with categories)
- An About page
- Contact Us
- Portfolio
- Customer Testimonials
The URL structure might look like "www.example.com/wedding-photography/plan-your-wedding," clearly reflecting the site's hierarchy.
Use the outcome of your keyword research and competitor analysis to get ideas on what makes sense for your users and adjust your site structure accordingly.
Pro Tip: Read Best Site Structure for SEO to learn how to optimize your website’s pages and categories for search engines and users.
7. Optimize Internal Links
Another SEO factor related to site structure is internal link structure. This refers to how your pages are interlinked together.

Best internal linking practices indicate the following:
- Add internal links on related pages to drive users to your most important pages (for a small business, that's the product or services pages).
- Use relevant anchor text in links to help search engines understand which keywords you want a page to rank for.
- Don't use the same anchor text in links to different pages (see diagram above).
- Ensure that each page on your site has at least one internal link.
For example, if you have a law firm and one of your pages describes your services, then from your home page, you can link to that page by saying: ‘You can find out more about our legal services and….’ Legal services, in this case, is the anchor text of the link that goes to the services page.
This gives search engines a solid clue that the referenced page is about legal services.
8. Utilize Schema Markup
A way to make your website stand out in the search results is to use schema markup (aka structured data). Schema markup is code you can add to your website to help search engines understand the context and meaning of your content.
By implementing schema markup, your site can qualify for rich results, which are enhanced search listings that include elements like star ratings, images, and additional information directly within your search snippet. Here is an example:
Different types of structured data are suitable for small businesses, and for best results, you should implement all relevant to your business. Here are some examples:
LocalBusiness - Very important for local SEO rankings (in Google Results and Google Maps). You can use it to provide details about your business, like address, phone number, and opening hours.
Product schema - suitable for ecommerce websites. You can use it to provide product information to Google.
Review schema - you can use it to show star ratings and the total number of reviews (like the example above).
Event schema - suitable for businesses hosting events. Provides more visibility to your website by making it easier for users to find event dates, locations, and details from the search results.
Read our guide on Schema Markup to learn how to implement structured data on your website.
9. Create Content To Match Your Customer's Search Intent
One of the critical success factors of small business SEO is to publish content that matches your customers' search intent. In simple words, this means understanding what they're seeking when they type a query into a search engine.
Are they looking to buy, learn, or find details about a particular product or service?
Review your SERP analysis again (Step 5) and see which pages rank for your target keywords. Look at their content and, in particular, what they talk about. When writing your content, ensure that you cover this by giving your angle and showcasing your expertise about the topic.
Look at the 'People Also Ask' section in Google to get ideas of your customers' questions related to your products or services. For example, if you have a small business selling cat food, you can find great questions to target in your blog posts.

Keep in mind that creating high-quality content is non-negotiable. It's not just about stuffing keywords; it's about delivering value that addresses your customer's pain points. Your content should guide them through their buyer's journey, eventually nurturing them to become customers.
For more information, read our Content Strategy guide.
10. Optimize On-Page SEO
Another important SEO strategy is to work on your on-page SEO. On-page SEO is the process of optimizing the content of a page to achieve higher rankings for your target keywords.
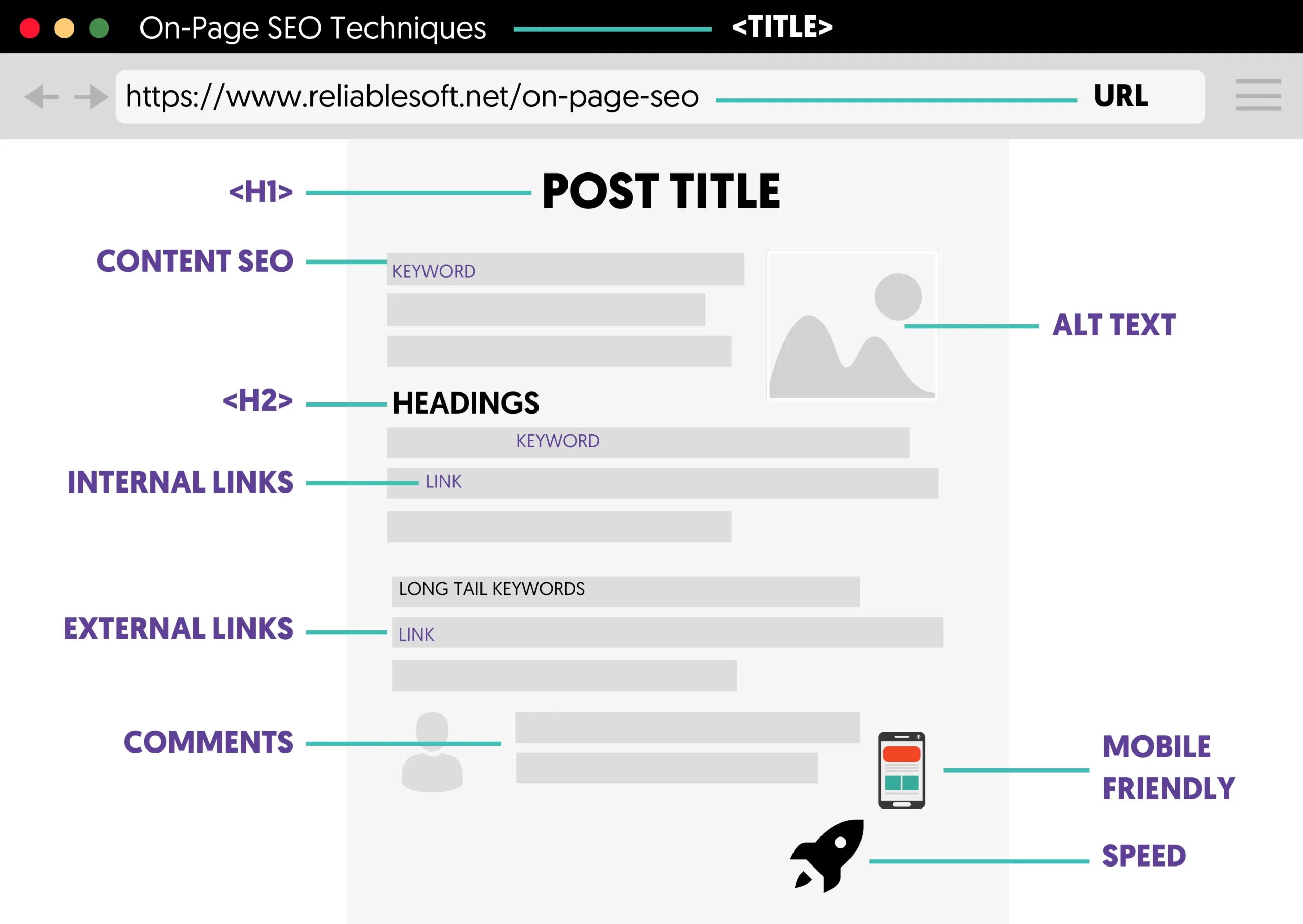
You can do this by giving special attention to on-page SEO elements like:
Page Titles
The page title tag is what users see in the search results and one of the first elements that search engine crawlers read. It is thus essential to provide unique titles for all your website pages.
A well-optimized page title should include your primary keyword and accurately describe the page content. For example, a local bakery might use "[Bakery Name ] Gluten-Free Bakery in [City Name]" for its homepage title. Here is an example:
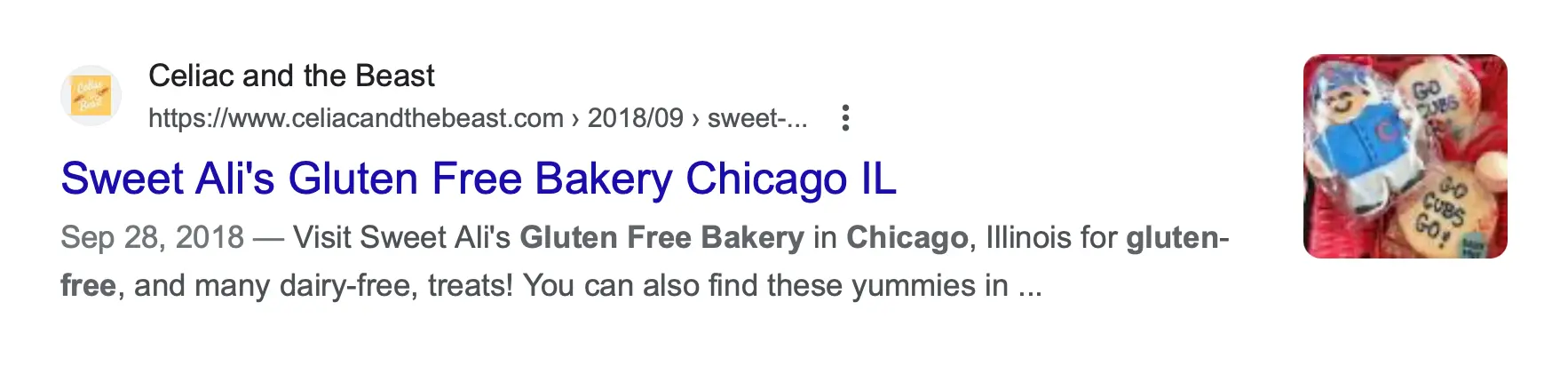
Meta Descriptions
Although not a ranking factor, meta descriptions significantly influence click-through rates. A good meta description should summarize the page content and include a call-to-action, like the example shown above.
H1 Tag and Page Headings
The H1 tag is shown on the page and can be the same or different than the page title. It should include your primary keyword and clearly indicate the page content.
Any other headings (H2, H3, etc.) should structure the content for easy readability and include secondary keywords.

For example, a small business blog post might use H1 for the title "Top 10 SEO Strategies for Small Businesses" and H2s for each strategy discussed (a good example is the article you're reading now).
Images
Images make your content easier to read, and it's a great way to showcase your products to potential customers. You should optimize your images by:
- Compressing them for faster loading times.
- Using descriptive file names.
- Including alt text with relevant keywords improves accessibility and helps search engines understand the image context.
Here is an example: A local cafe might name an image "fresh-organic-coffee-beans.jpg" and use alt text like "Fresh organic coffee beans at [Cafe Name]."
Read our guide on How to Write SEO Content for more SEO tips.
11. Perform a Technical SEO Audit
Besides taking care of your content, you should also pay attention to the technical SEO aspect of your website. Technical SEO will ensure that search engines can crawl and index your content without any problem.
Here are key areas to focus on:
Crawl Errors
Use Google Search Console to find any crawl errors that prevent search engines from accessing and indexing your pages. These errors could be due to server issues, incorrect robots.txt configurations, or non-existent pages (404s).
Broken Links
Broken links lead to a poor user experience and can negatively impact your site's SEO. Regularly check for and fix broken internal and external links to ensure a smooth navigation experience for both users and search engine crawlers.
Core Web Vitals
Google's Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics related to speed and the overall user experience. Use tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights to analyze your website and make necessary adjustments. Improving these aspects can boost your site's user experience and performance in search results.
Web Security
Implementing HTTPS by acquiring an SSL certificate is critical for website security. Google considers HTTPS as a ranking signal and reassures your site visitors that their data is protected, which is especially important for ecommerce sites handling sensitive information.
For more checks, go through our comprehensive SEO checklist.
12. Get Links From Partners
Getting links from other websites will increase your visibility in the SERPs and help you outrank your competitors. When search engines find links pointing to a website, they consider this a vote of confidence from one site to another.
A website with good content and links is likelier to appear on top of the organic results and in local packs (for local businesses).
Link building is a challenging process (for you and your competitors), so you need to think outside the box and find ways to get links from other related websites.
One easy way is to reach out to companies you work with. These are your suppliers, manufacturers, software partners, business associations, or even B2B customers. Examine their websites, and if they have a blog, directory listing, or other sections that list their partners, ask them to be included with a link to your website.
Read our eCommerce Link Building Strategies post for more ways to build links to your small business.
13. Register Your Business With Online Directories
Registering your website with online directories is another way to get links, traffic, and more exposure for your small business. Besides Google Business, you can create profiles for your business in:
- Bing Places For Business (you can automatically import your Google Business Profile data).
- Yelp For Business
- Foursquare
- Apple Business Connect
In addition, search for any organizations related to your business (like your local chamber of commerce) and others used by your competitors and secure your place.
14. Get Positive Online Reviews
One confirmed ranking factor for appearing higher in the results, especially for local rankings, is the number of positive ratings in your Google Business Profile. As stated by Google, more reviews and positive ratings can improve your business's local ranking.
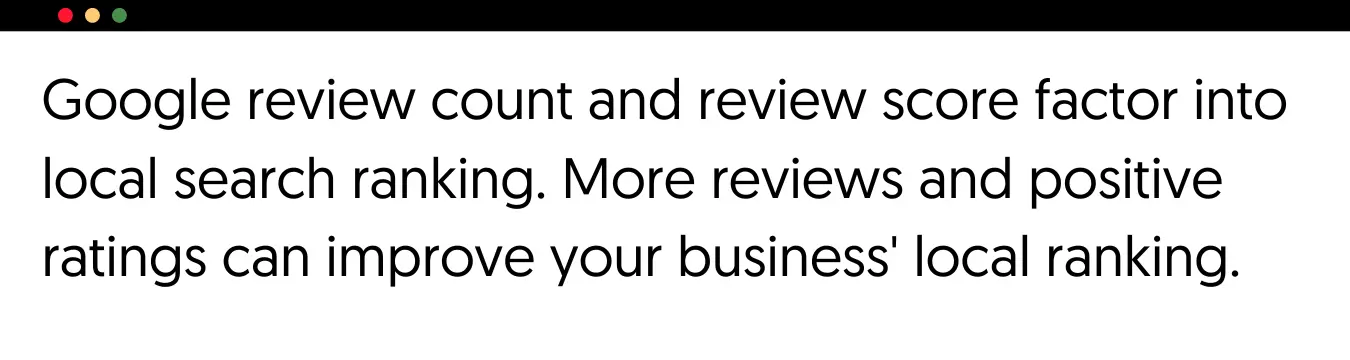
In practice, this means you should make every effort to get your customers to review your business, products, and services on your Google profile.
First, get your review link from your Google Business Profile page.
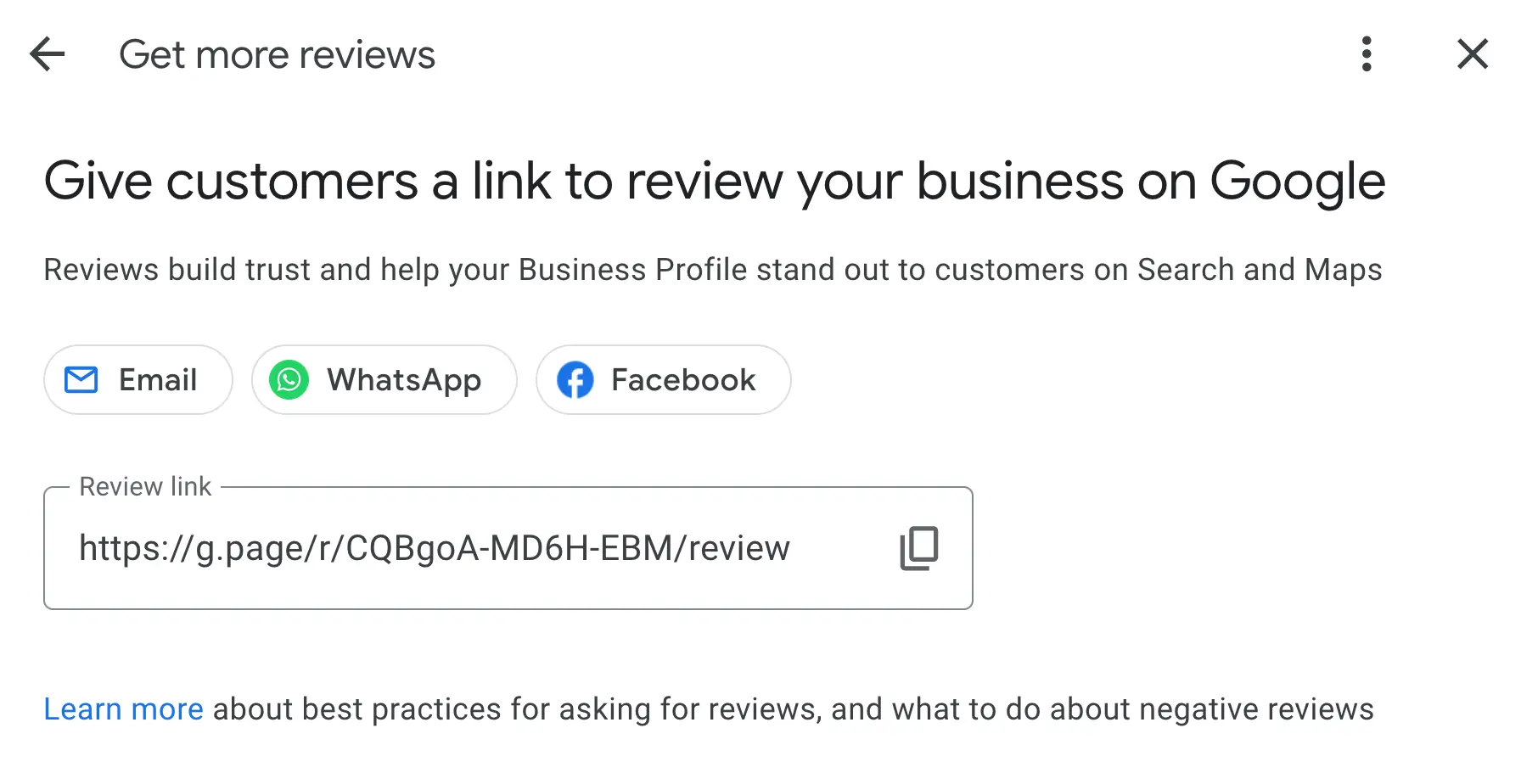
Then, follow these proven techniques:
- Follow up with customers after purchasing or interacting with your business through email or SMS, politely asking for feedback, and pasting your review link.
- Offer incentives for leaving a review, such as discounts on future purchases or entries into a contest. Ensure this is done ethically and in compliance with Google's review guidelines.
- Respond to all positive and negative reviews to show that you value customer feedback and are committed to improving their experience.
- Turn your review link into a QR code and add it to your packaging, receipts, or business cards.
- Train your staff to ask for reviews in person, especially after positive customer interactions.
15. Work On Brand Awareness
Branding is vital for the success of a business, and it’s also crucial for small business SEO.
If many people search for your brand name on Google, this is a good SEO signal, and Google considers it during the ranking process. They (Google) repeatedly said that they want to rank brands in their search results, and anything you can do online or offline to promote your business works in that direction.
Utilize Facebook Ads, Instagram paid campaigns, and other social networks relevant to your business. Don't just advertise your products; try to become an authoritative source in your industry by providing valuable information to your customers through your blogs and content.
Engage with community activities, advertise in local press, run events, make sponsorships, and use every opportunity to position your brand in front of your potential customers.
Monitor for brand mentions on the web and ensure that fake comments or unhappy customers do not damage your reputation.
16. Monitor Your Rankings
One final step is to monitor your SEO performance, particularly your rankings in the various search engines.
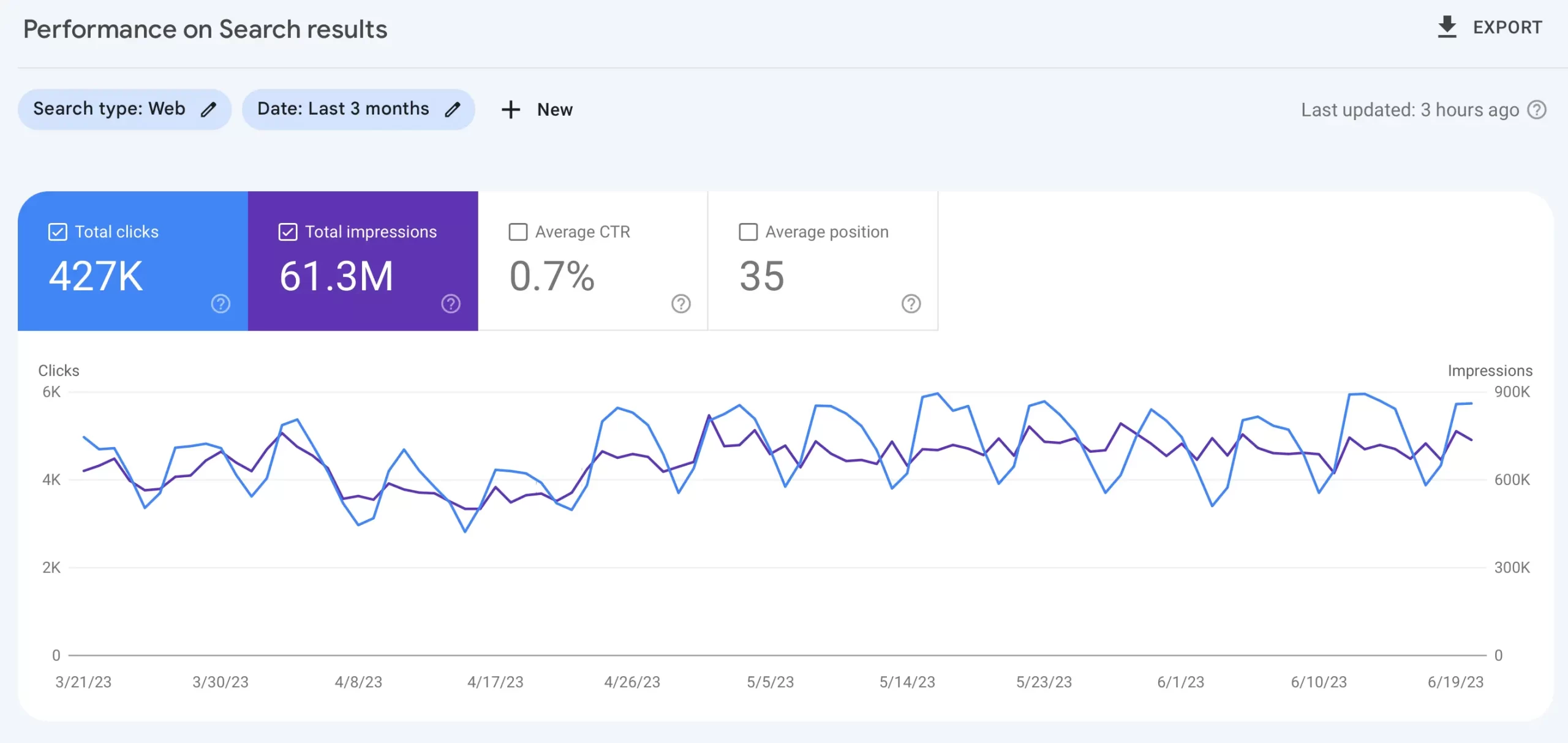
Use the Google Search Console "Performance on Search Results Report" to track how often your site appears in Google search results, which queries show your site, your average position for those queries, and how many clicks and impressions each query receives.
This data is invaluable for understanding which keywords and pages are performing well and which ones may need further optimization.
By analyzing the queries and pages generating the most impressions but not as many clicks, you can identify opportunities to improve your titles and content to make them more relevant to searchers.
Additionally, consider using a dedicated SEO tool, like Semrush or Ahrefs, to monitor your rankings across different search engines, not just Google. These tools can help you track your SEO performance over time, compare it against your competitors, and spot opportunities and issues affecting your search engine visibility.
Small Business SEO Tools
Even if you hire an SEO firm for your small business, it’s always good to know how to use tools to monitor your rankings and traffic, spy on your competitors, and clearly understand how your website performs online.
You can use several digital marketing tools (free and paid) to help you with this task.
- Semrush – You can analyze your rankings, perform keyword research, spy on your competitors, find new link opportunities, monitor brand mentions across the Internet, and many more useful functions. It’s not free; it comes with a monthly subscription, but it’s money well spent.
- Google Search Console – A free tool provided by Google for website owners. You can use the various functions and reports to monitor how your website is performing on Google.
- Google Analytics – Get a deep understanding of how users interact with your website.
- Bing Webmaster tools – Similar to Google search console for Bing.
- Google Trends – You can use it to discover the popular searches in your niche and deliver the right content and products to your customers.
- Google Alerts - a free service to monitor for mentions of your brand.



